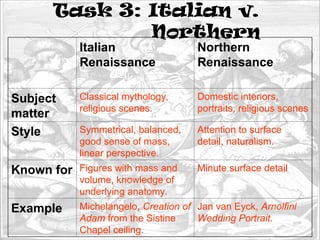
The document outlines the Renaissance era, highlighting significant events like the Black Death and the fall of Constantinople, which set the stage for major societal changes. It discusses the transformation of Europe through intellectual, artistic, and economic developments, and the impact of figures like Gutenberg and Renaissance artists on culture and education. The document contrasts the Italian Renaissance's early progress with that of the Northern Renaissance, emphasizing the differences in subject matter and style.