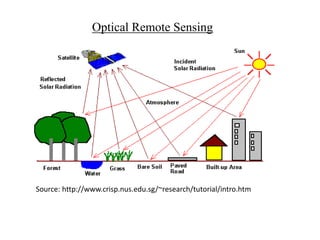
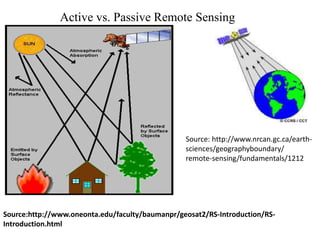
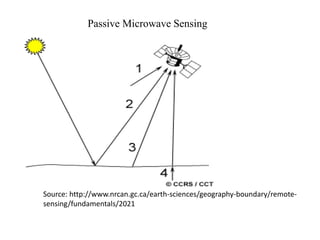
Remote sensing uses sensors to acquire information about objects without physical contact. It involves analyzing electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted from targets. There are two main types: passive sensing which uses natural radiation sources like sunlight, and active sensing which supplies its own radiation source like radar. Remote sensing has advanced from early aerial photography to modern satellite systems that provide synoptic imaging across various wavelengths at increasing spatial, spectral, temporal and radiometric resolutions. This allows analysis of surface features and conditions from local to global scales.