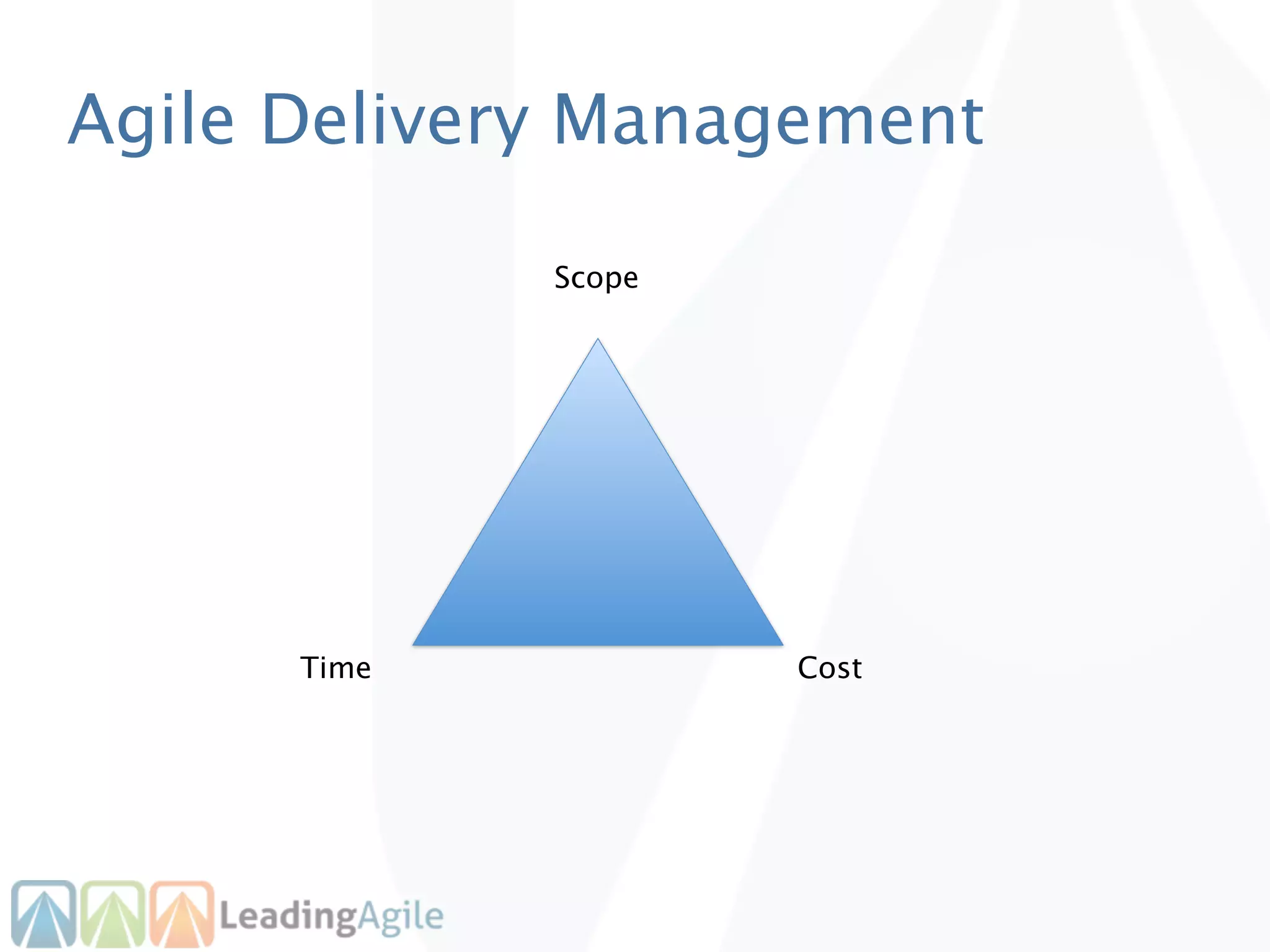
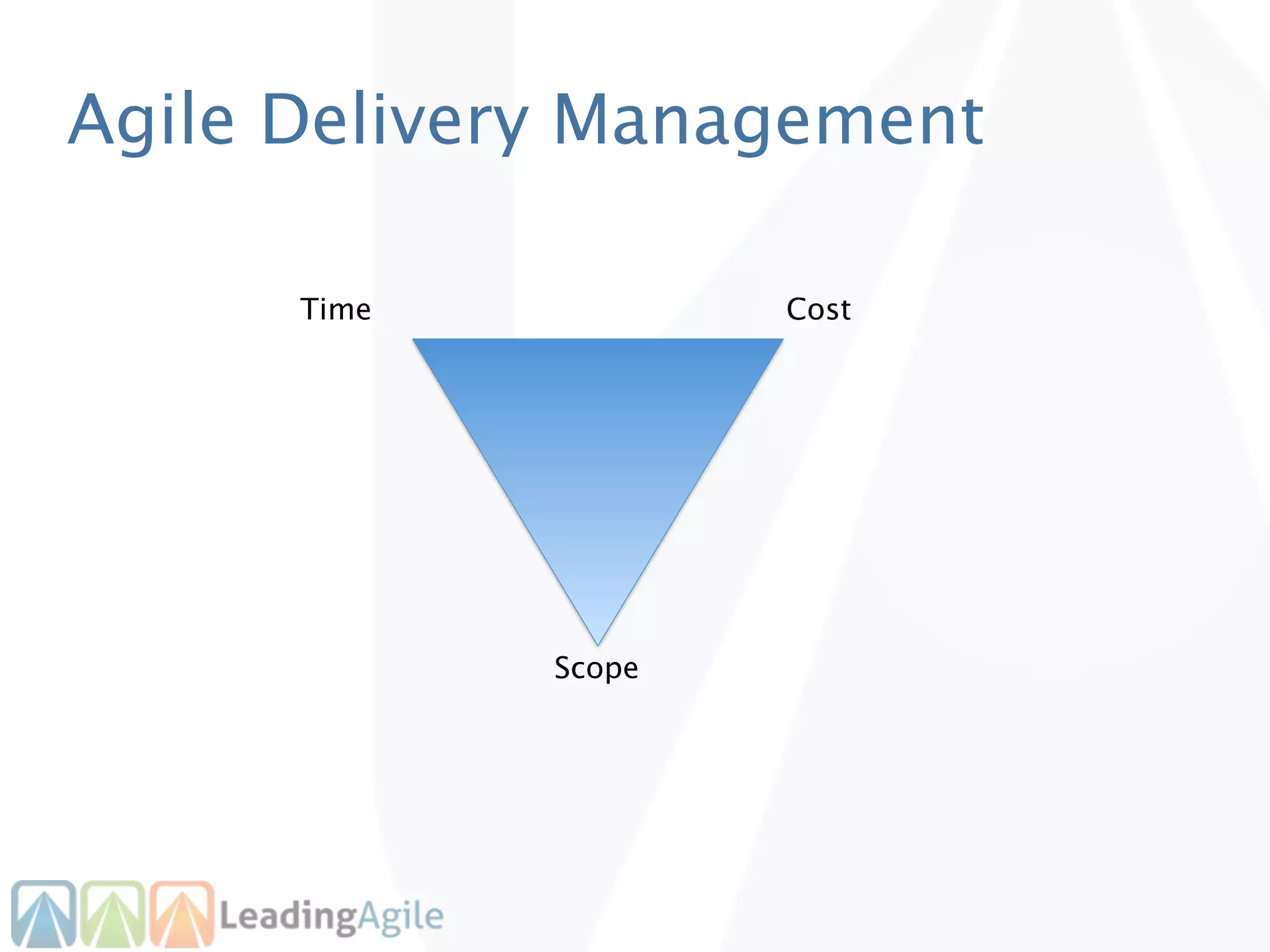
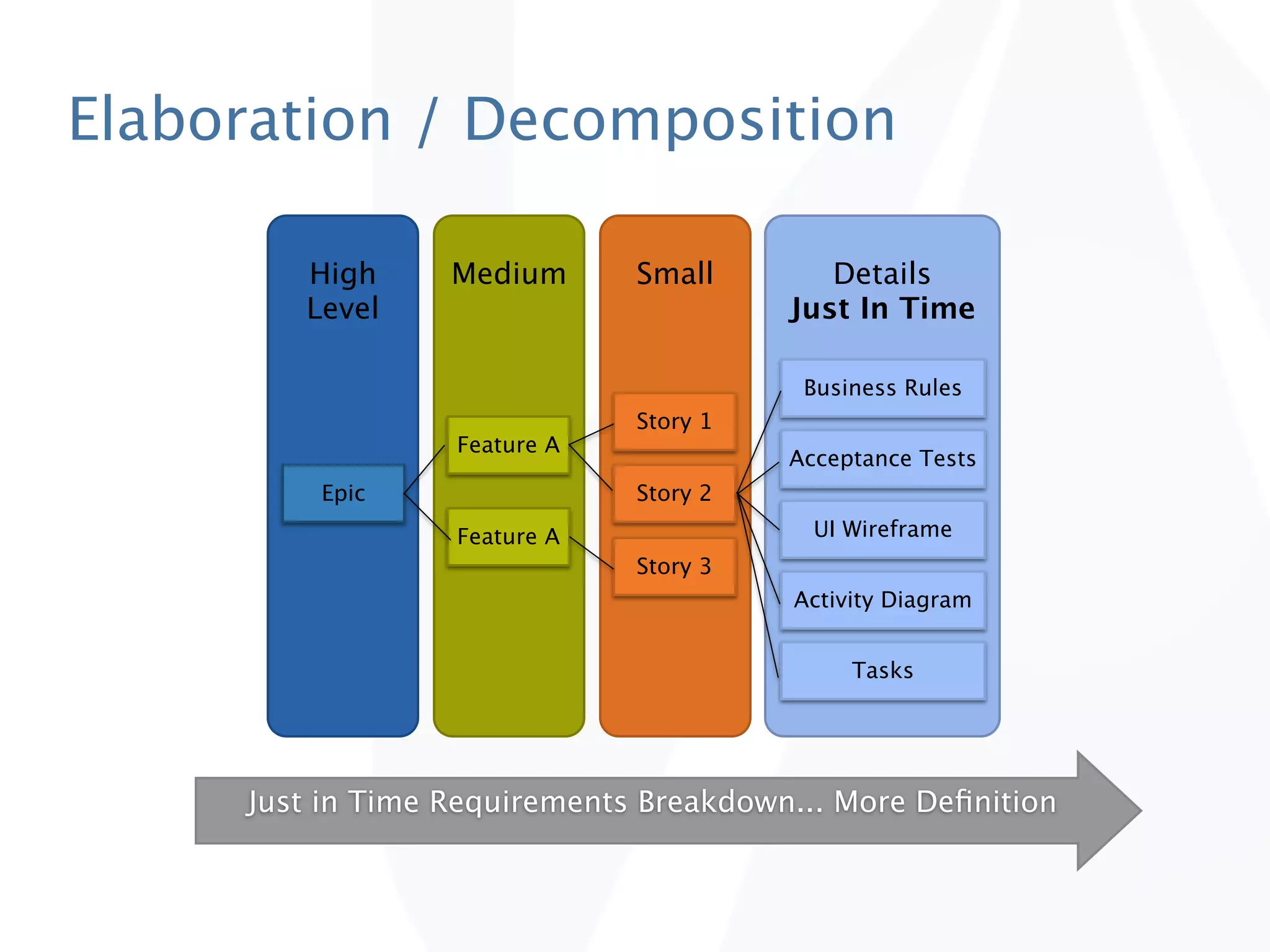
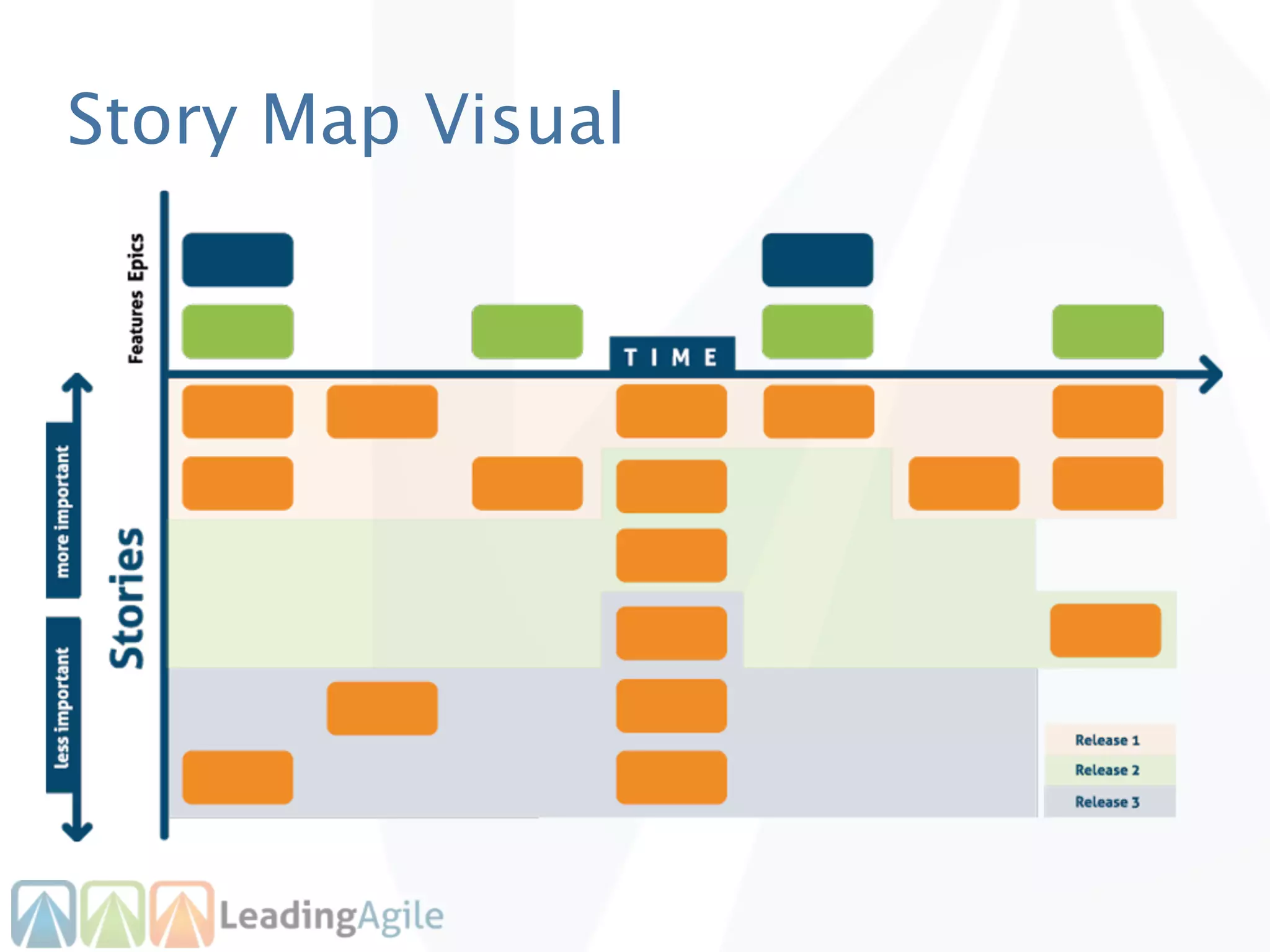
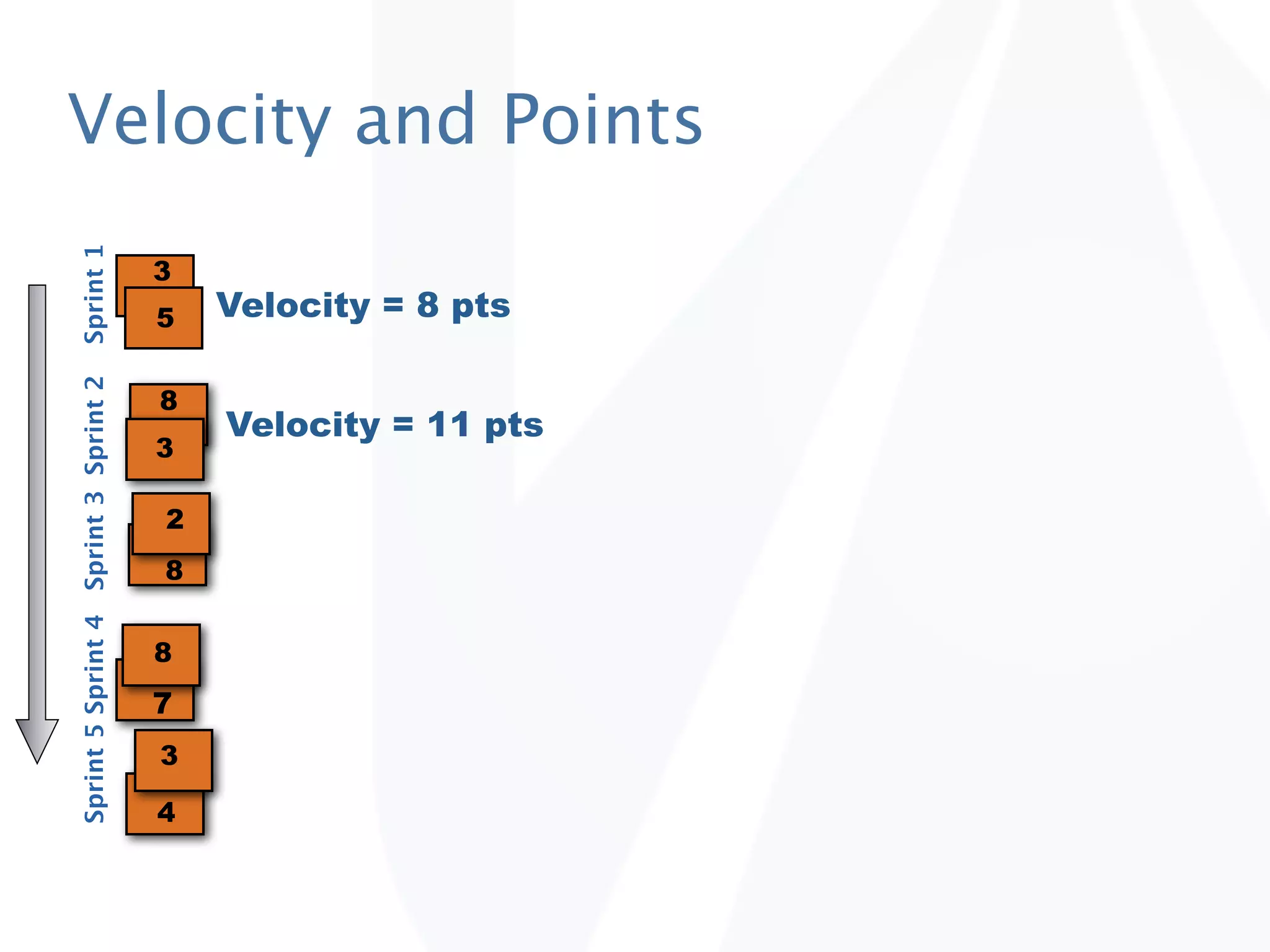
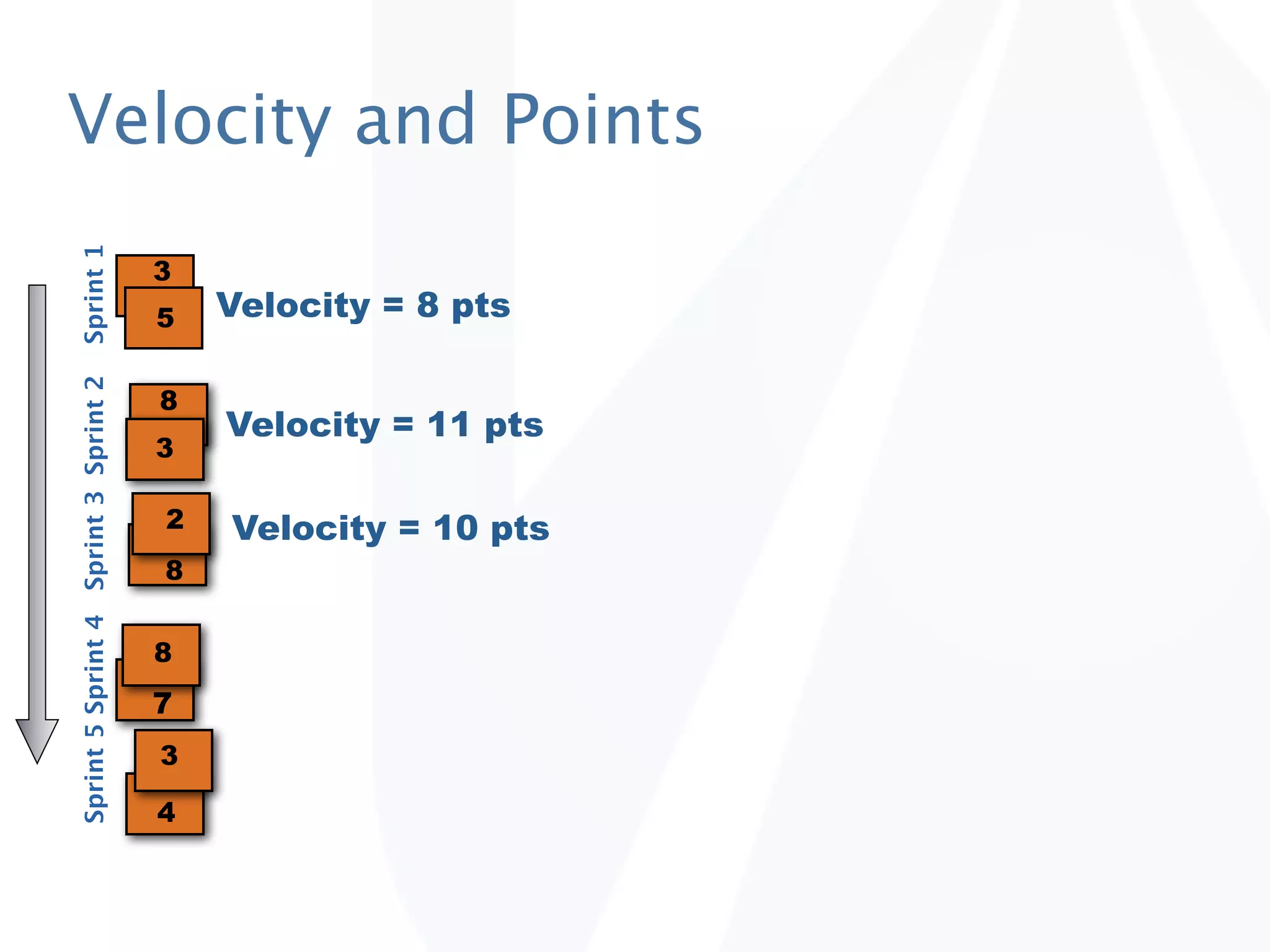
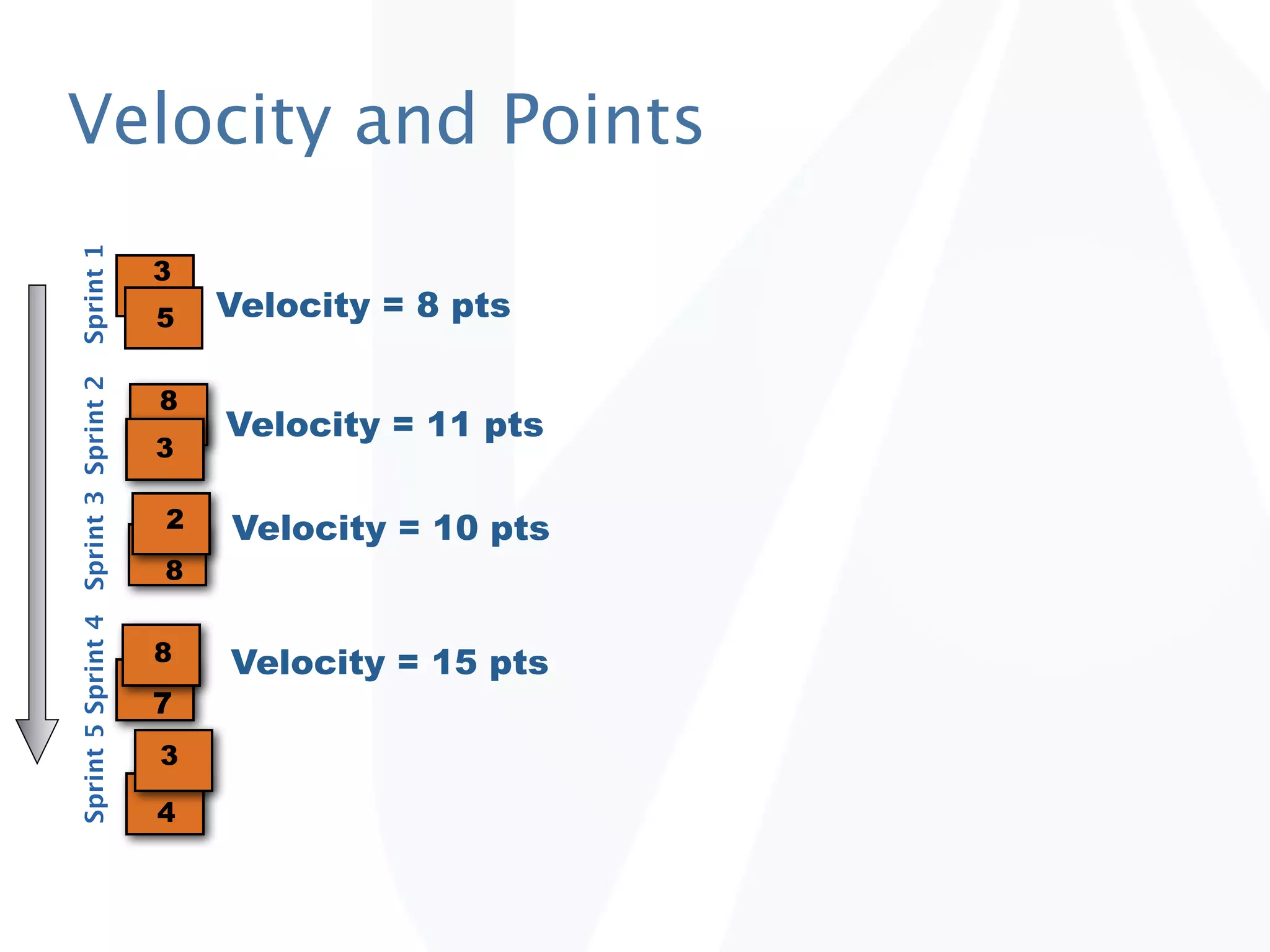
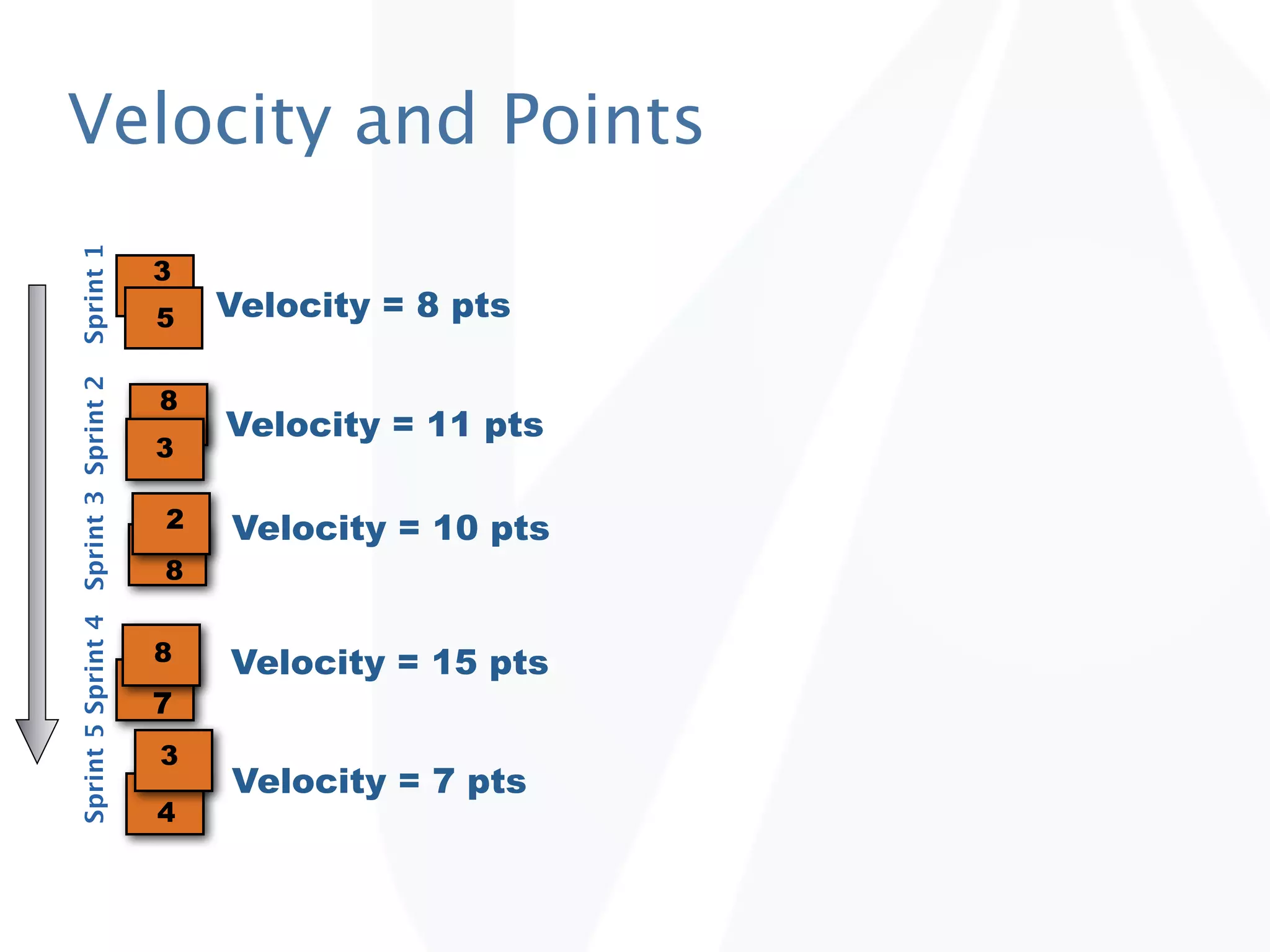
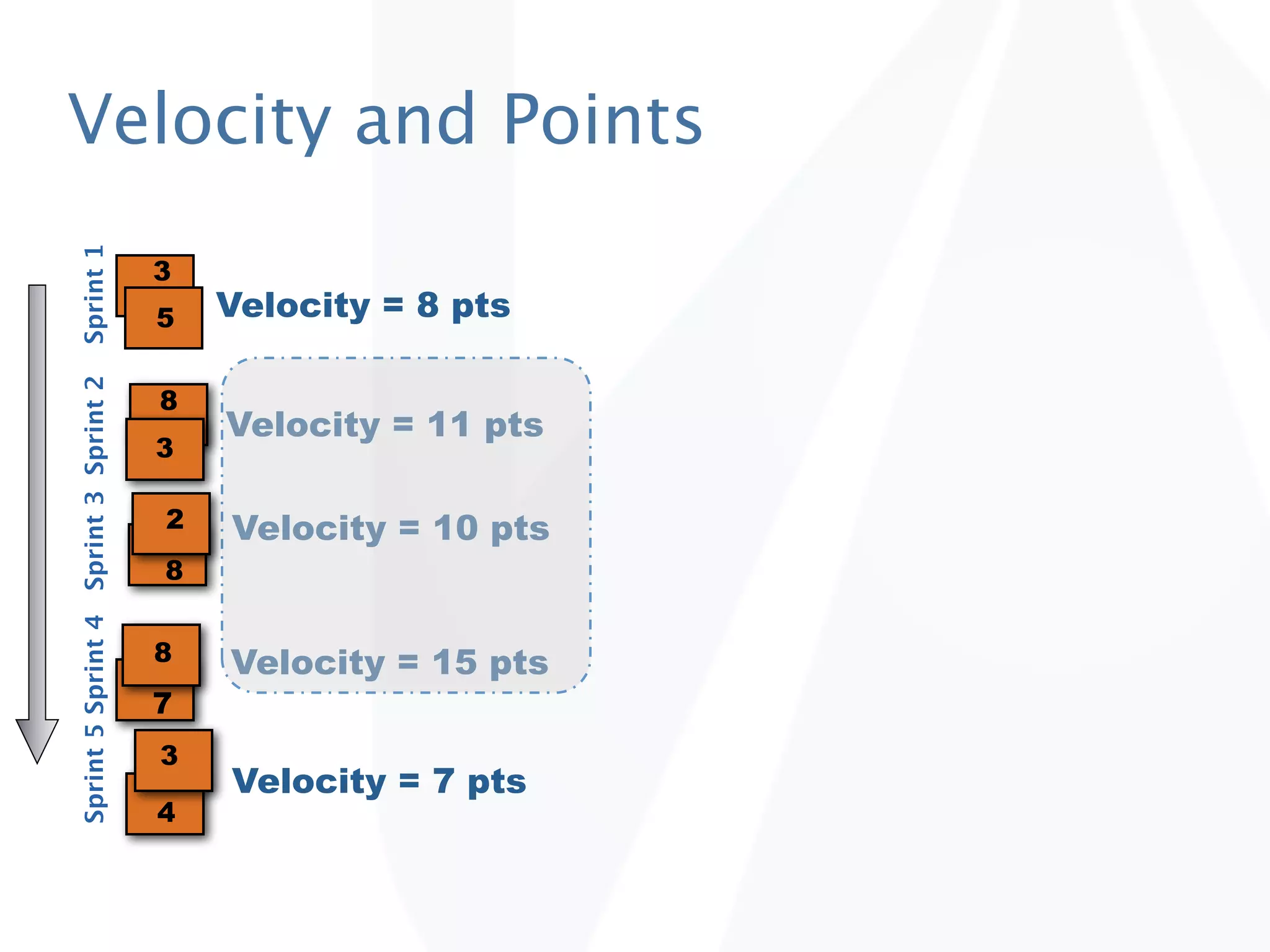
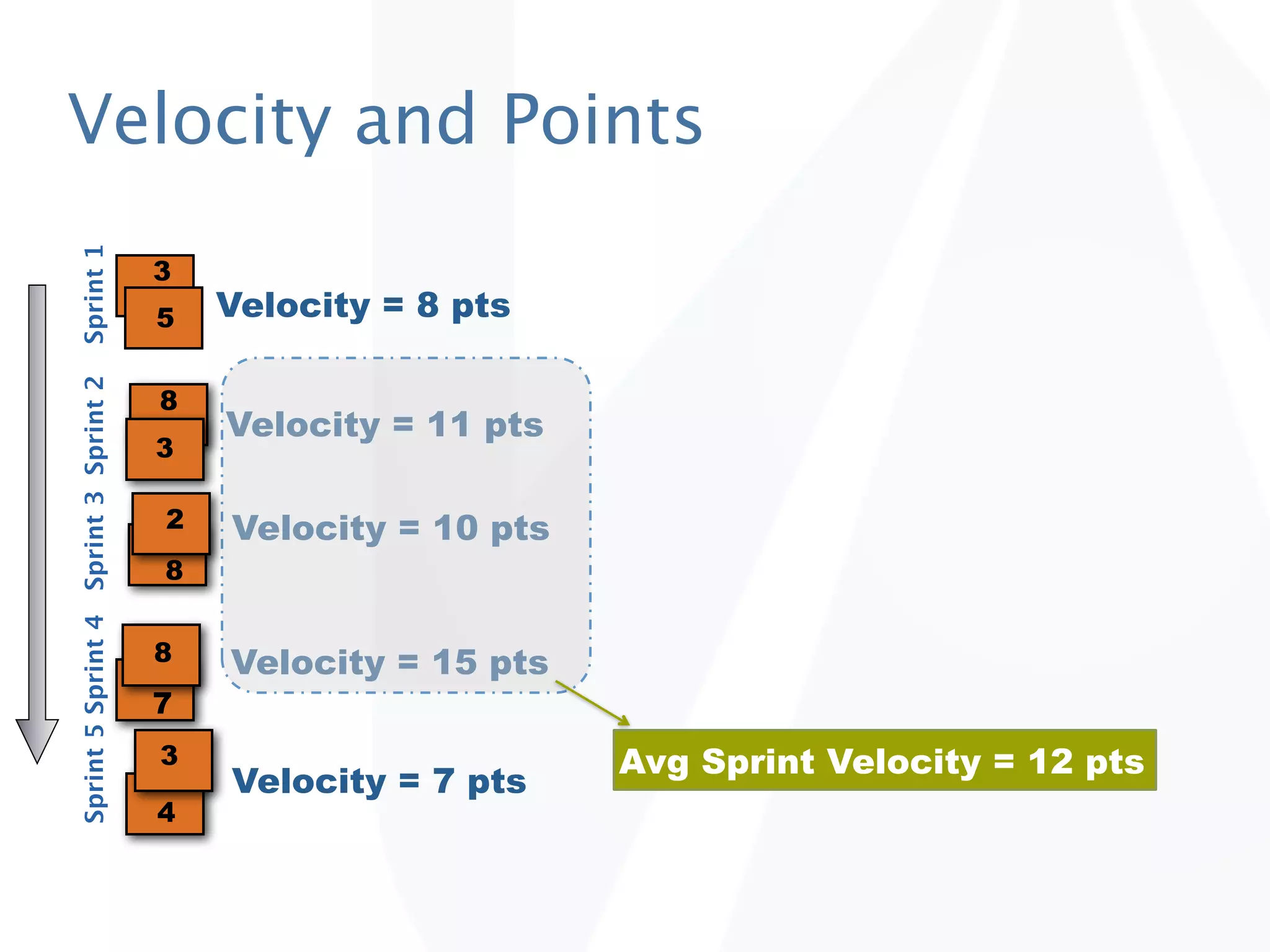
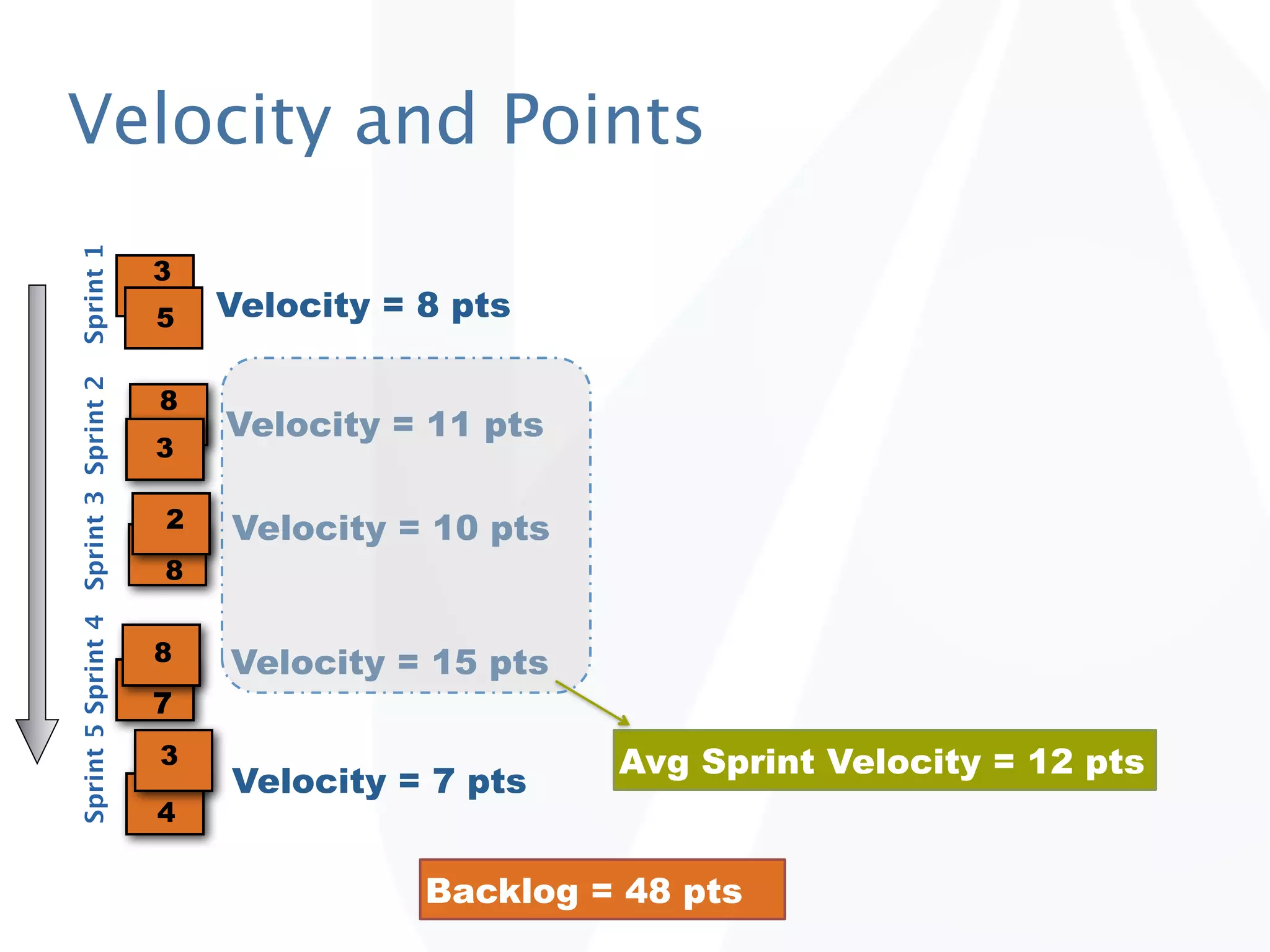
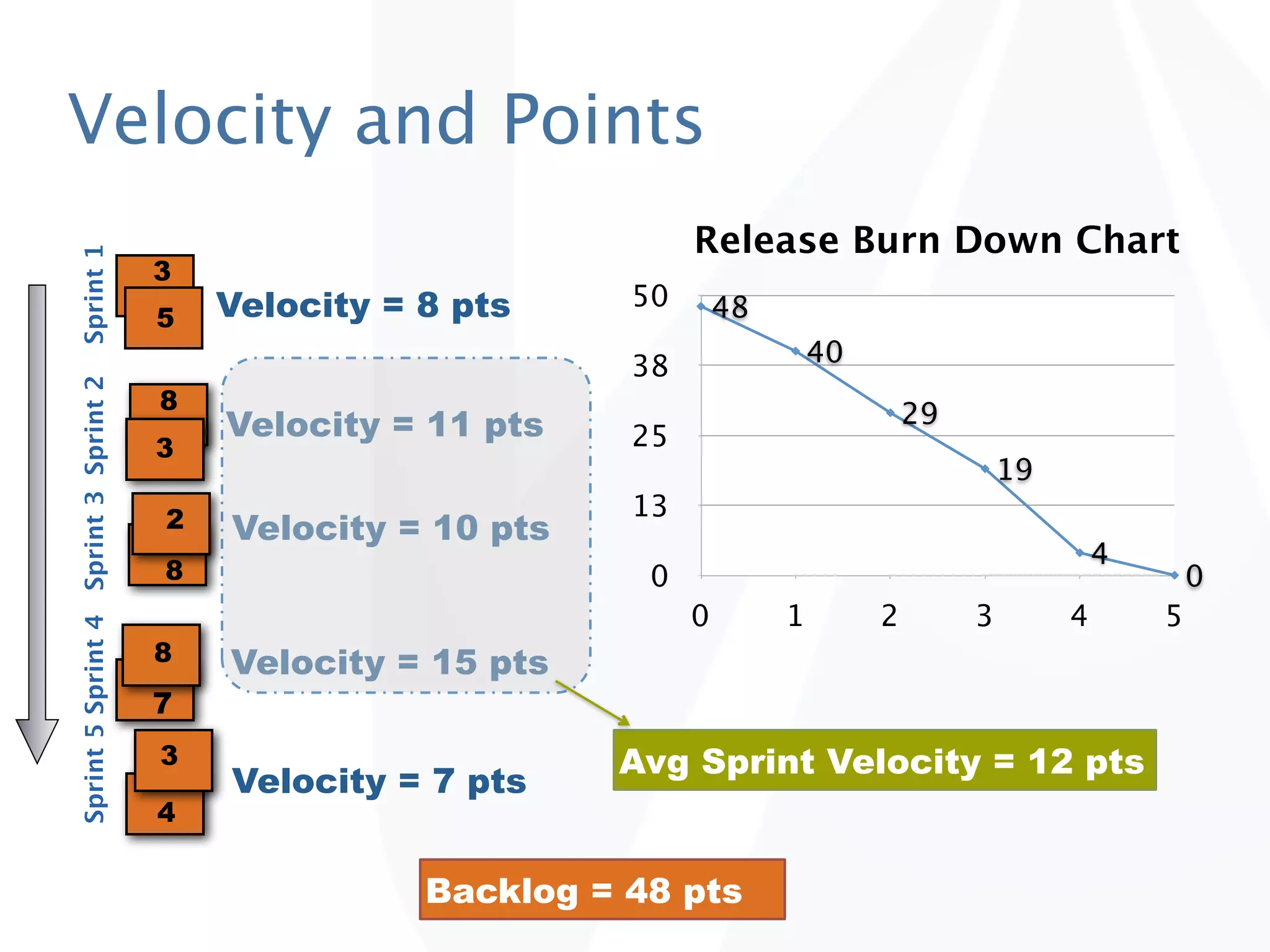
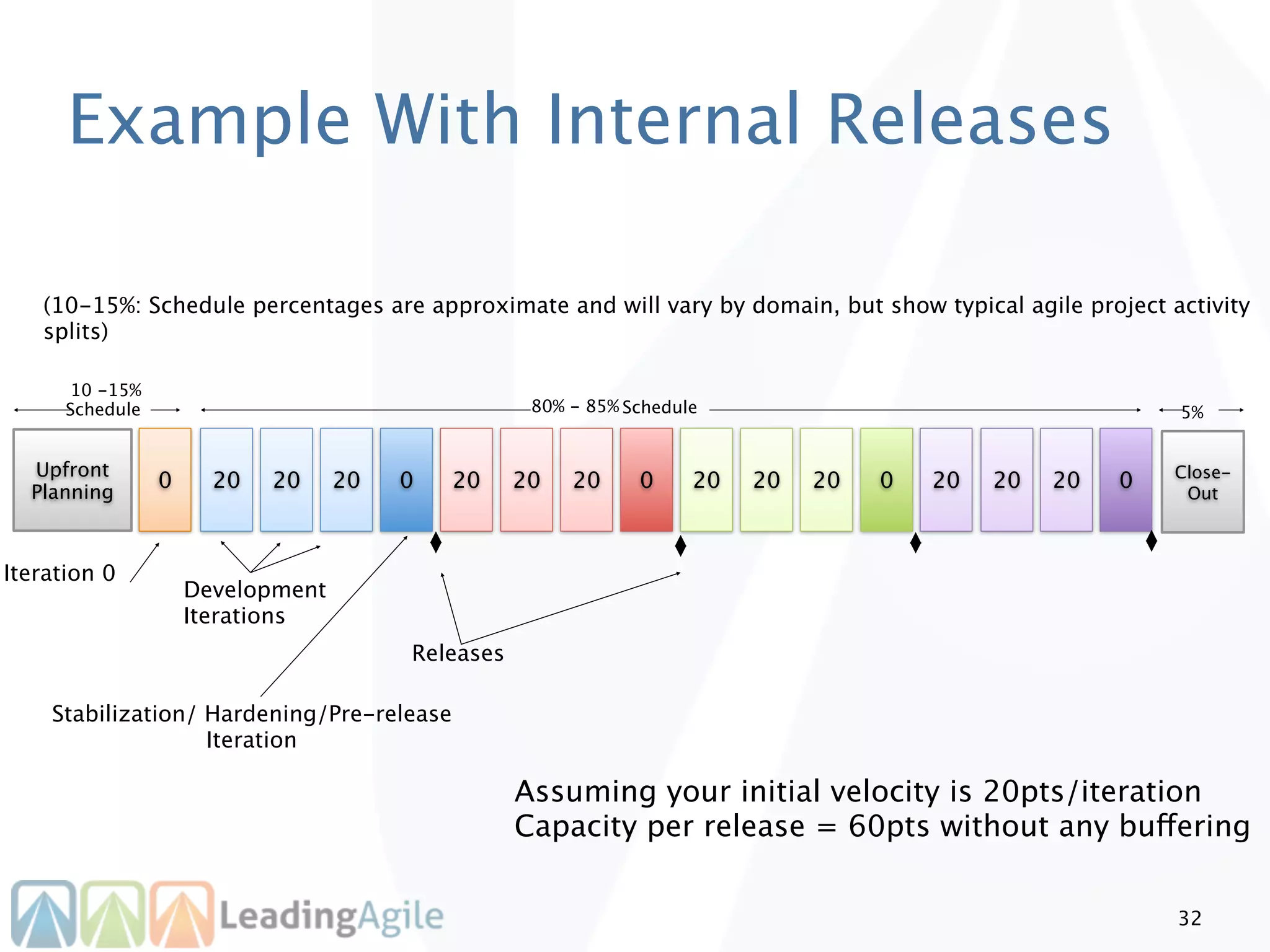
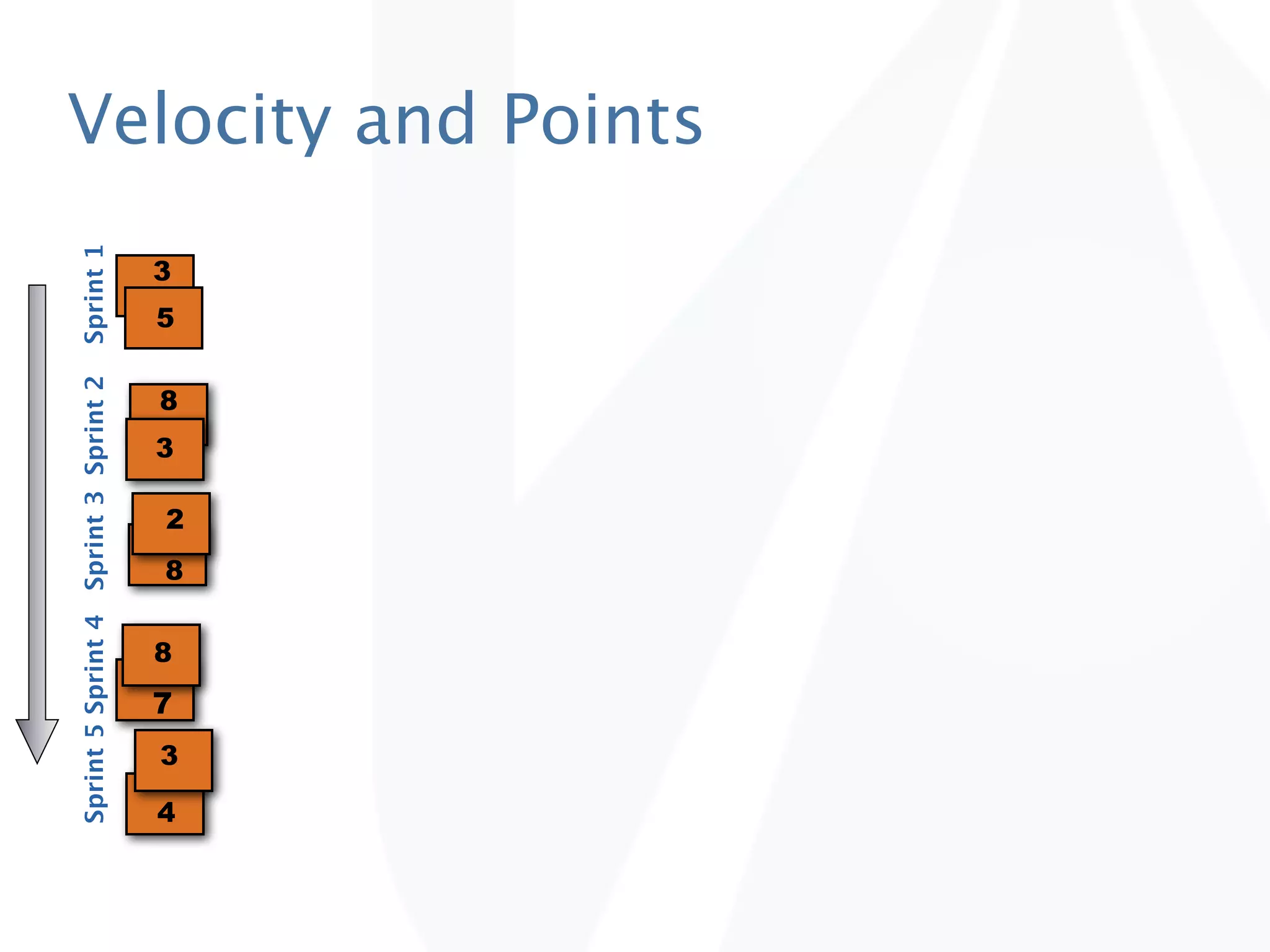The document discusses release planning in an agile environment. It defines what a release plan is and its purpose to communicate the scope and timeline of releases to stakeholders. The process of creating a release plan is described, including identifying epics, features, and user stories to fulfill the release vision, estimating work, and using velocity to determine the timeline and number of iterations needed to complete the planned work.