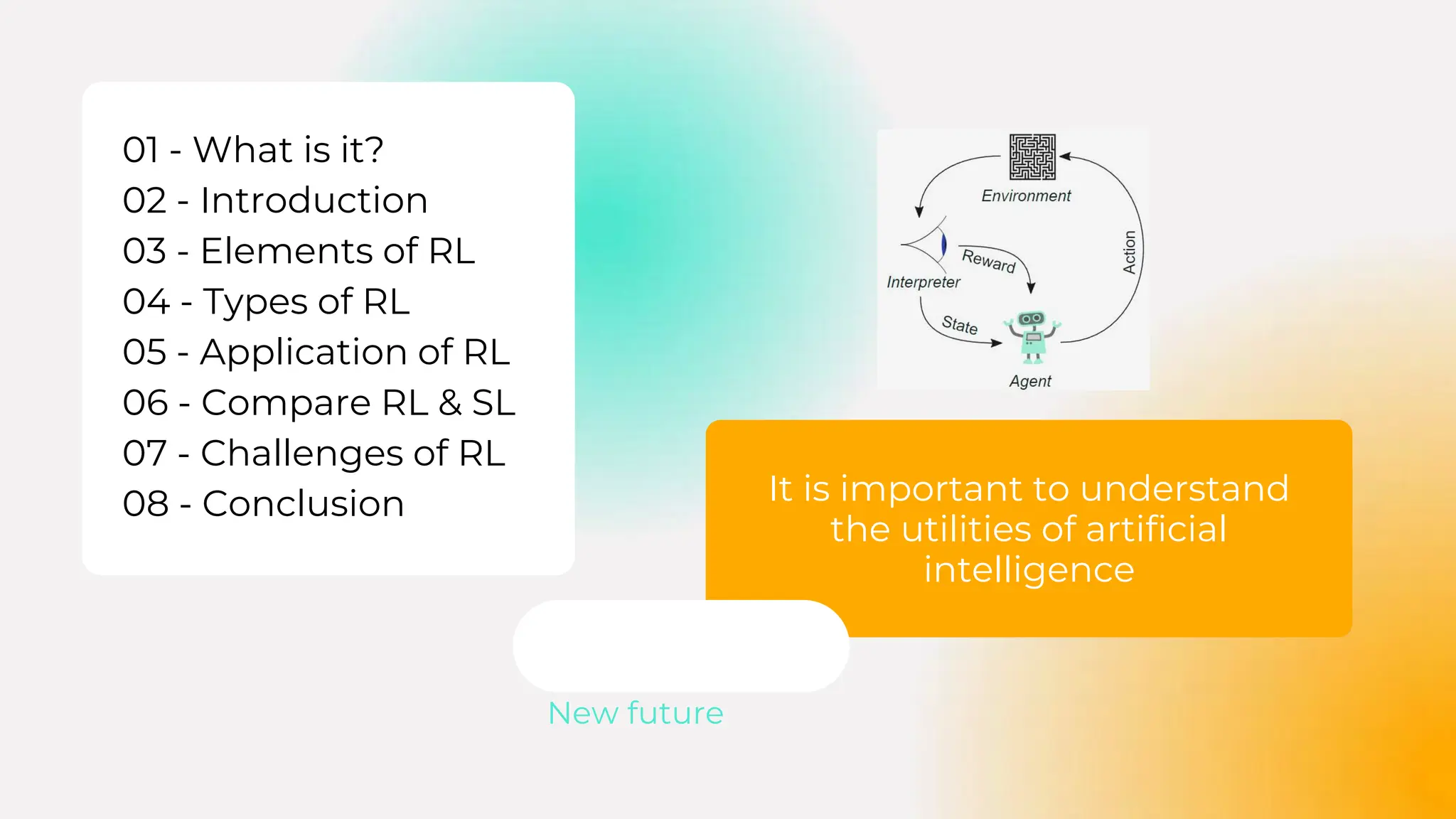
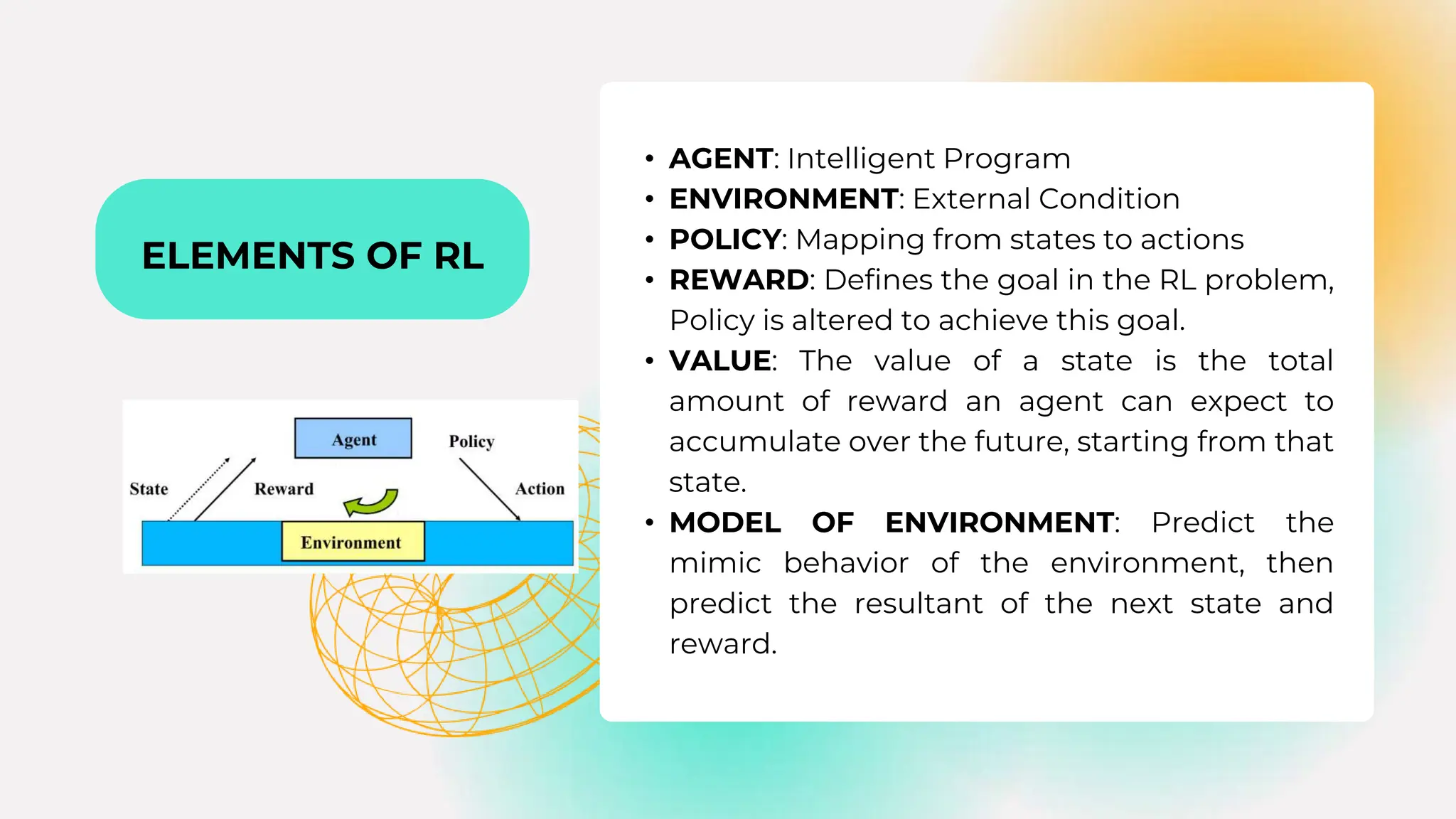
Reinforcement learning (RL) is a key area of artificial intelligence focused on training agents to make decisions through interaction with environments, achieving significant breakthroughs in recent years, including surpassing human performance in various games. The document discusses the elements, types, and applications of RL, alongside the challenges faced, such as the exploration-exploitation dilemma and high computational demands. Looking forward, the future of RL is promising, with potential advancements through interdisciplinary integration that could overcome existing limitations.