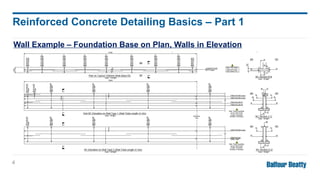
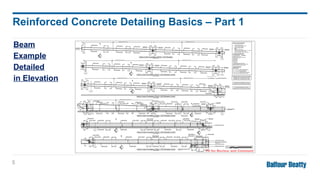
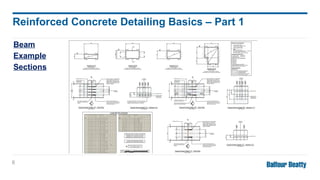
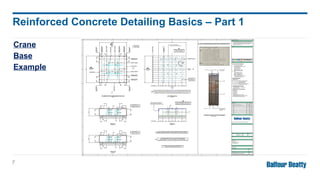
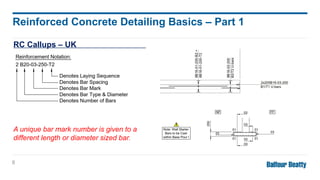
Reinforcing concrete is essential to enhance its tensile strength and flexibility since concrete, while strong, is also brittle. Designers must provide detailed information for reinforced concrete drawings, including bar dimensions, cover, lap lengths, and anchorage details to ensure structural integrity. The detailing responsibilities include ensuring clear drawings, understanding design, and minimizing complexity for efficient on-site construction.