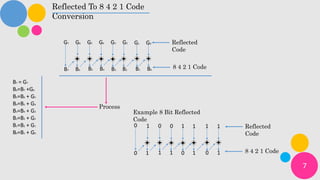
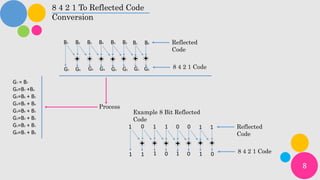
This document discusses reflected code and the conversion between reflected code and 8-4-2-1 binary code. It provides a brief history of binary code and reflected code. Reflected code, also known as Gray code, involves only a single bit changing between adjacent values. The document shows how to convert between 8-bit reflected code and 8-4-2-1 binary code using addition rules. Examples of both conversions are provided.