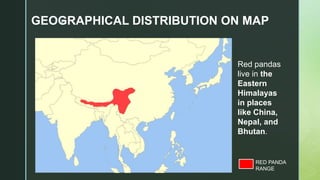
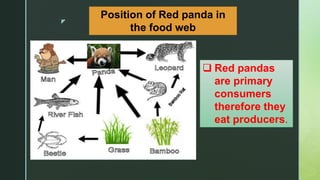
The red panda is a herbivorous mammal native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. It is listed as endangered due to a wild population of fewer than 10,000 individuals that continues to decline because of habitat loss, fragmentation, poaching, and inbreeding depression. Red pandas live in temperate forests with bamboo understories in the Himalayas between 8,000-18,000 feet in elevation, where they eat bamboo leaves and shoots. Conservation efforts aim to increase protected habitat areas and connect isolated populations while patrolling against threats.