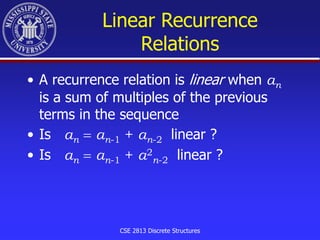
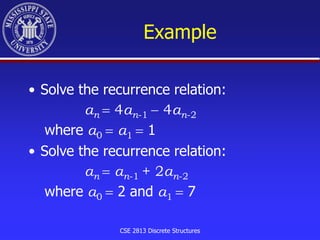
The document discusses recurrence relations in discrete structures, highlighting the concepts of degree, linearity, and homogeneity in recurrence relations. It provides a step-by-step approach to solve first and second order linear homogeneous recurrence relations with constant coefficients, including finding characteristic roots and applying initial conditions. Additionally, it includes examples and exercises to reinforce the concepts presented.