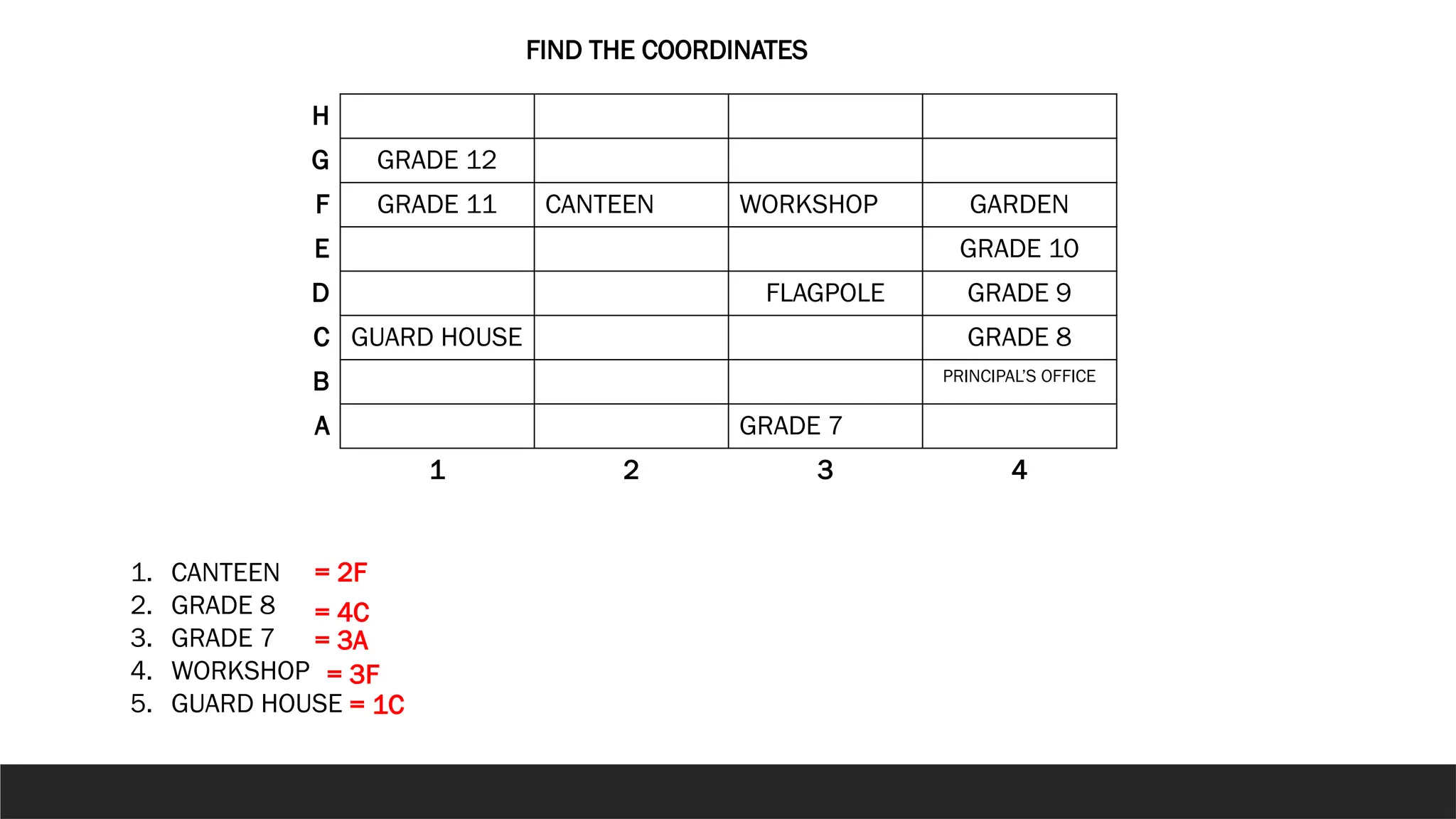
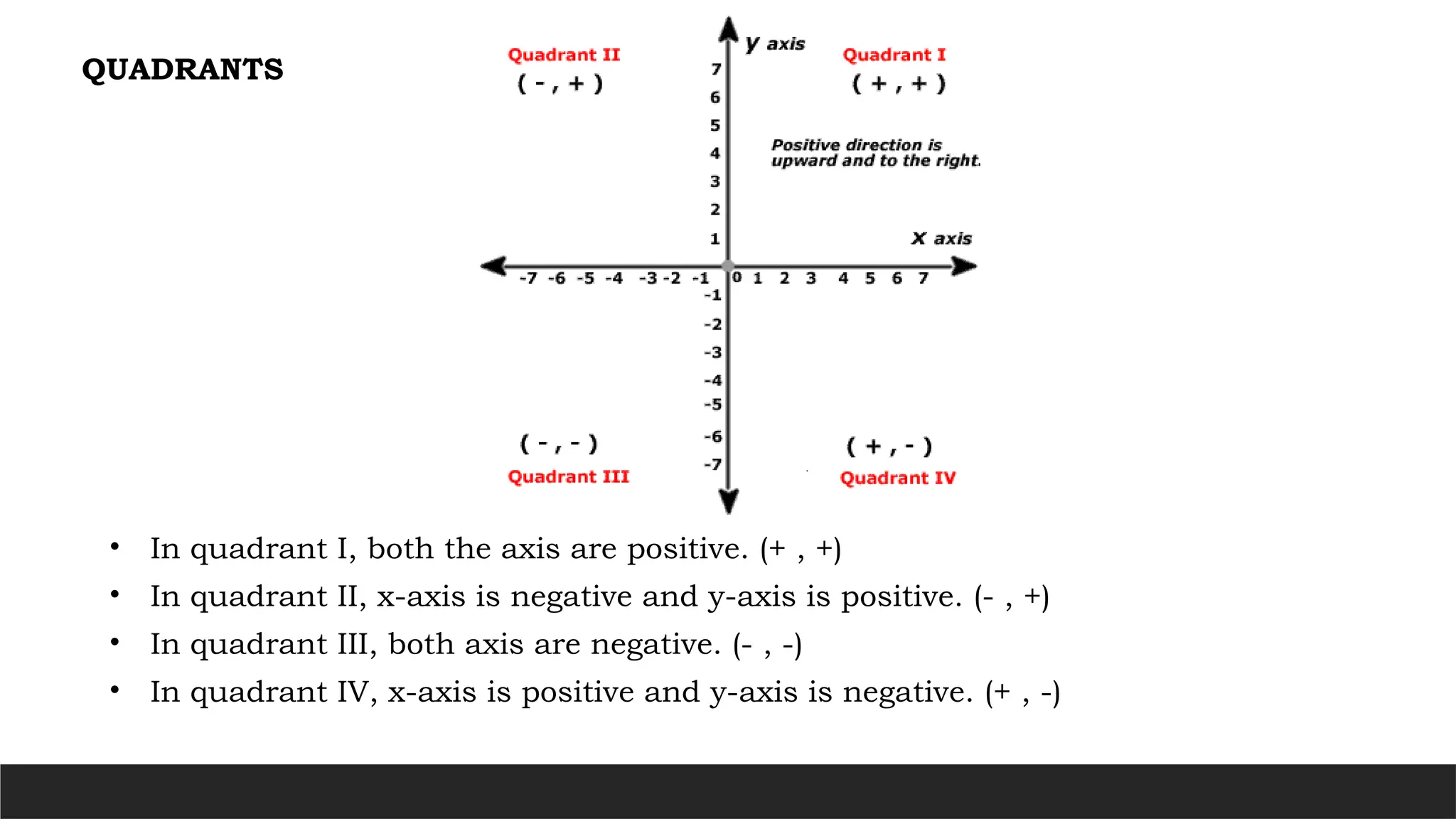
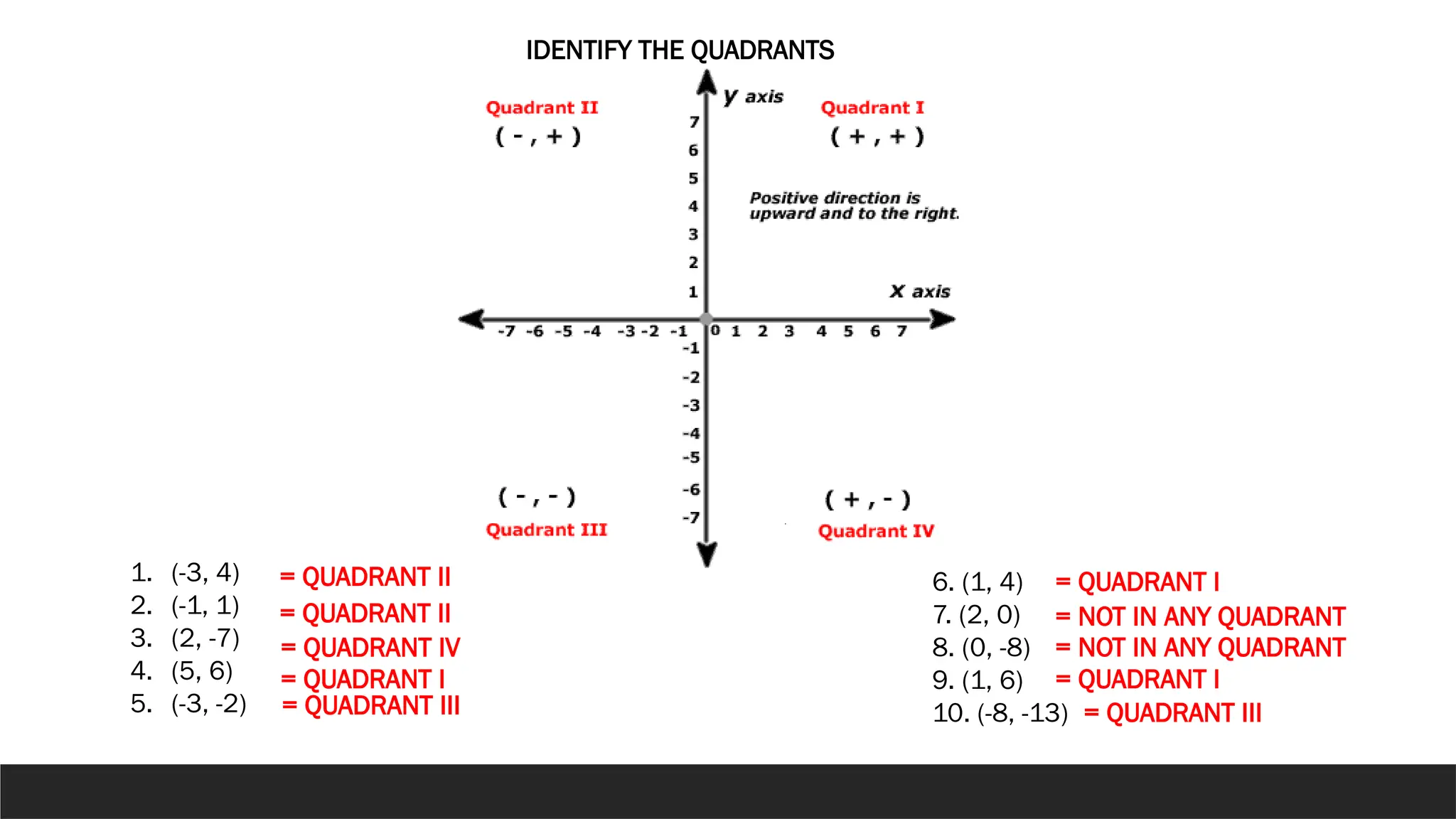
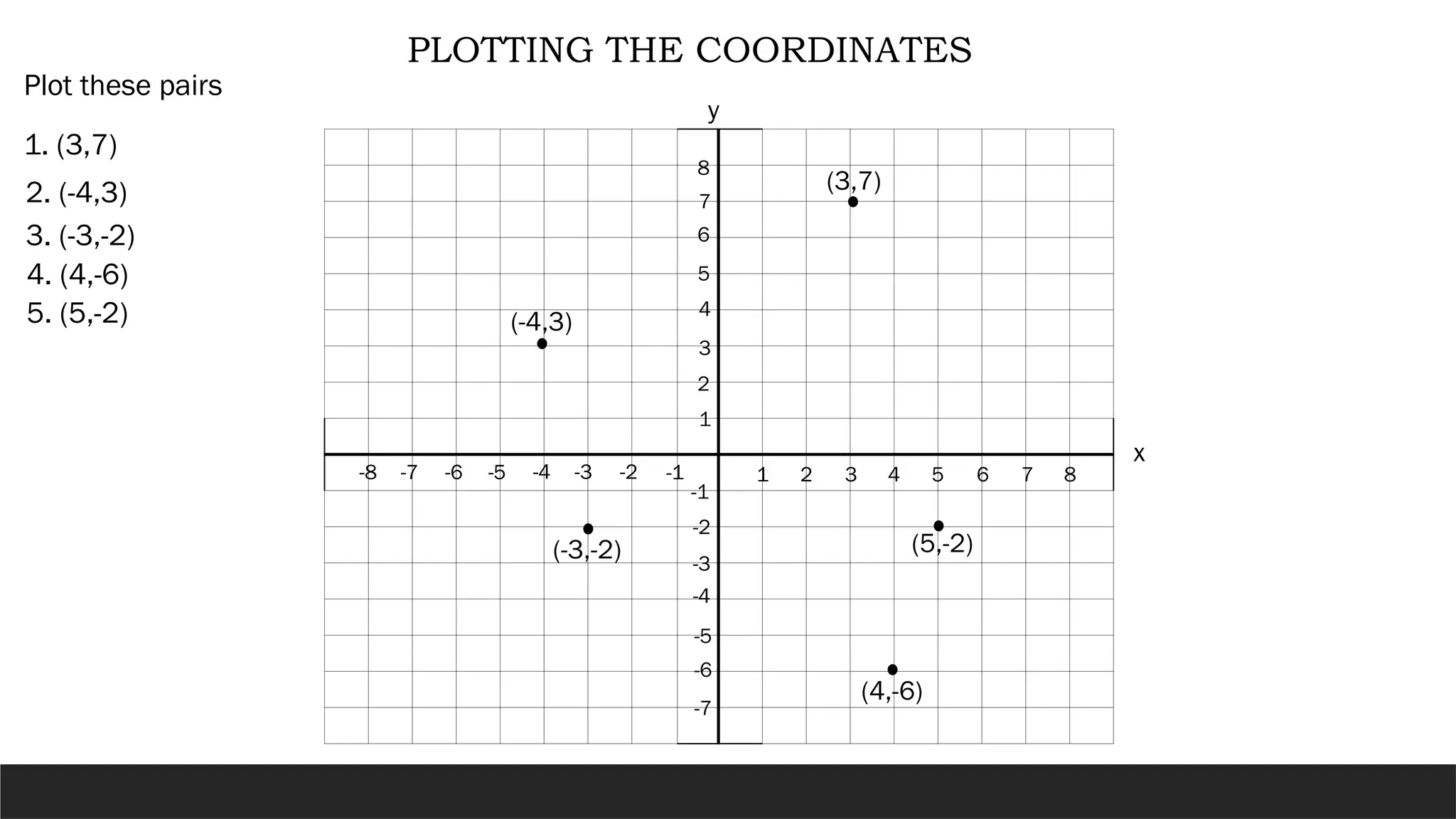
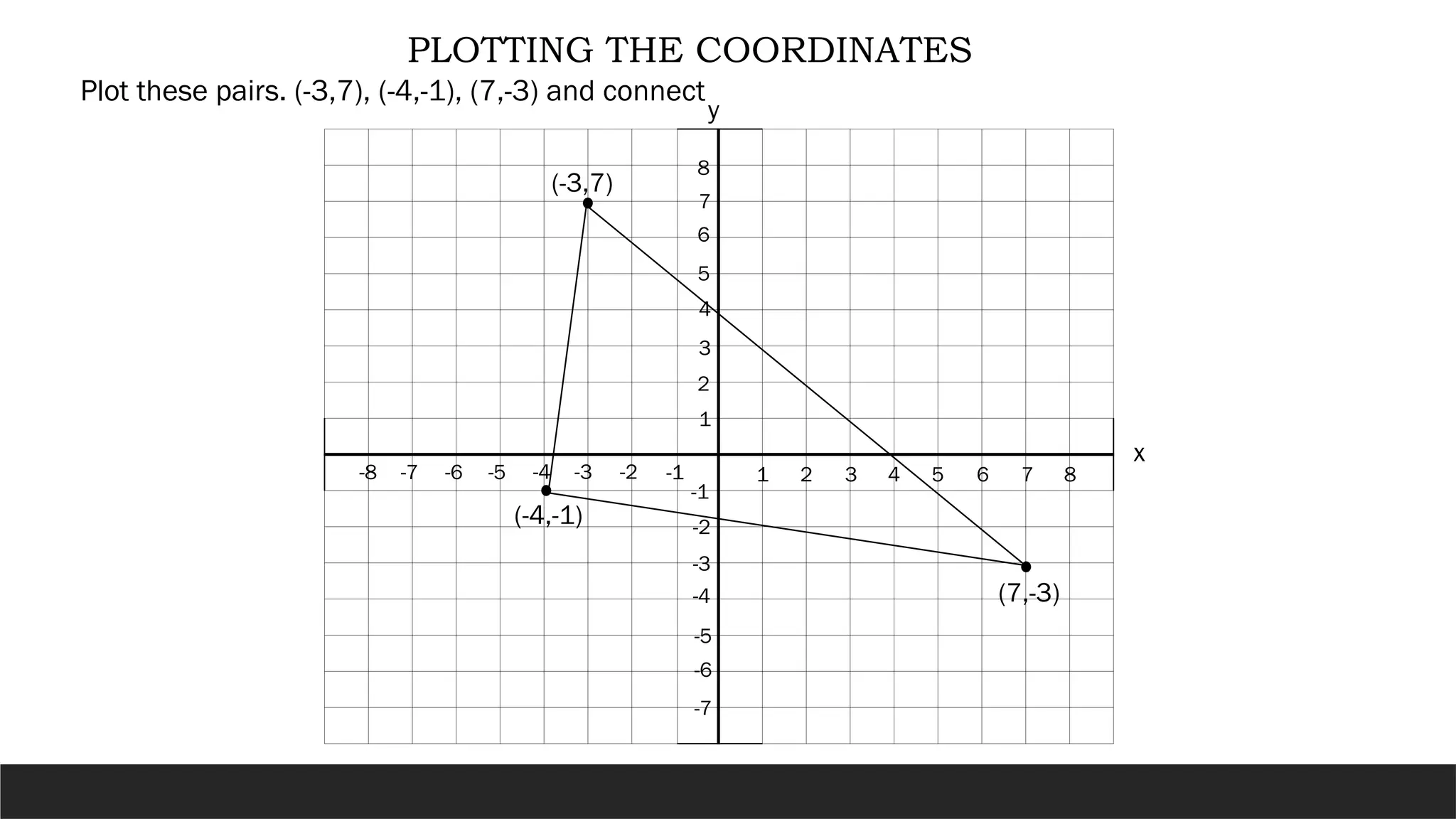
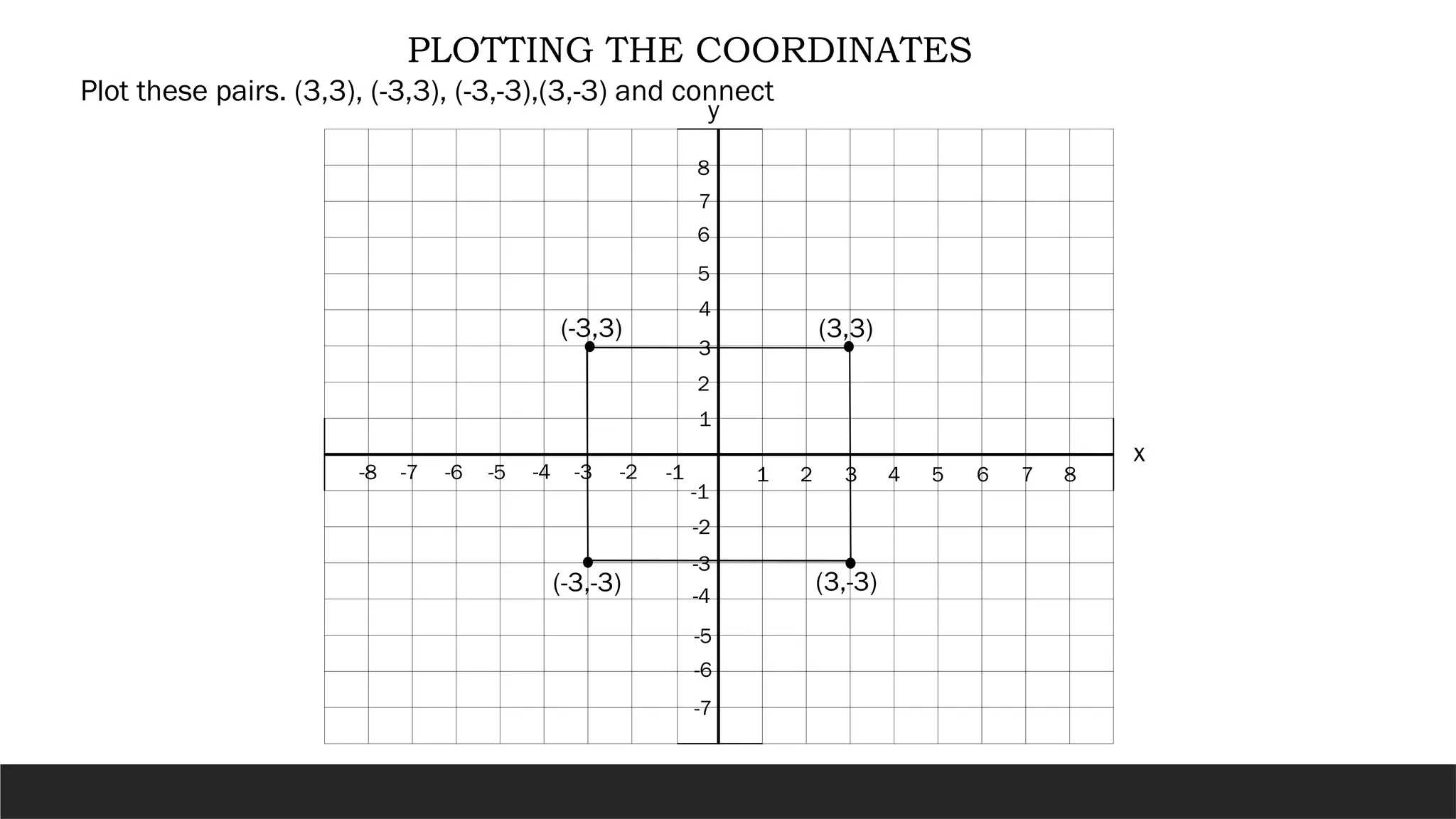
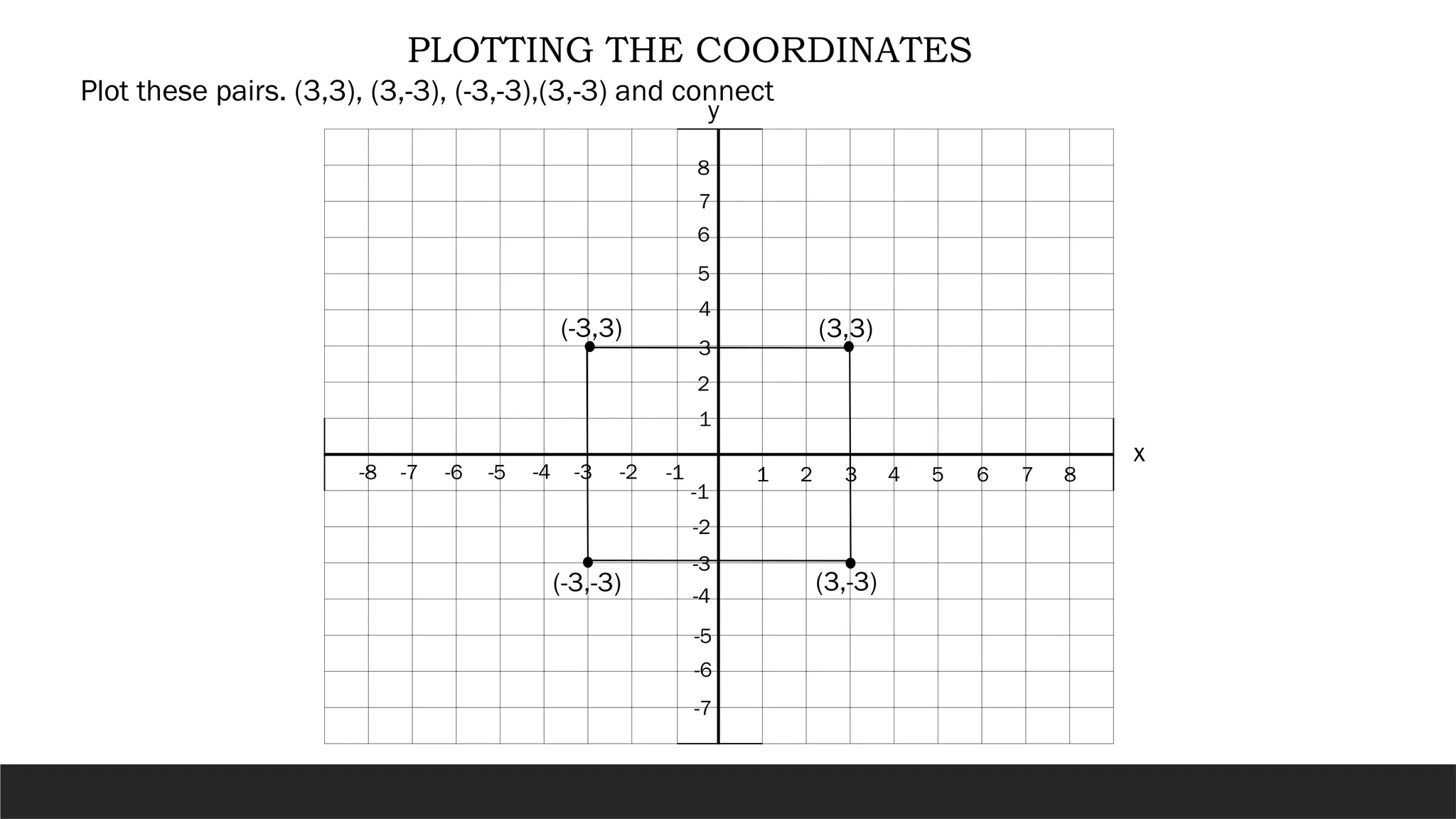
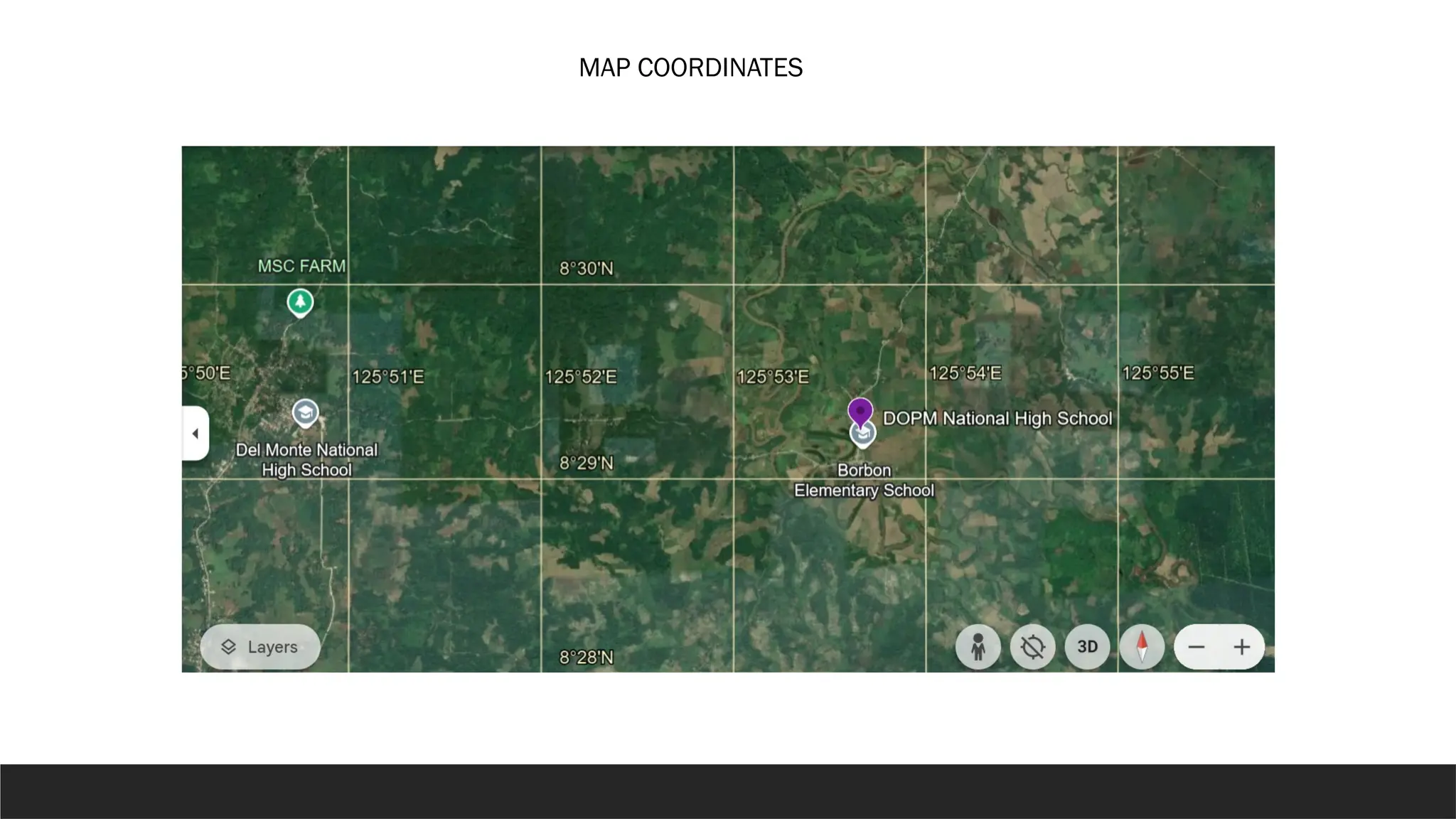
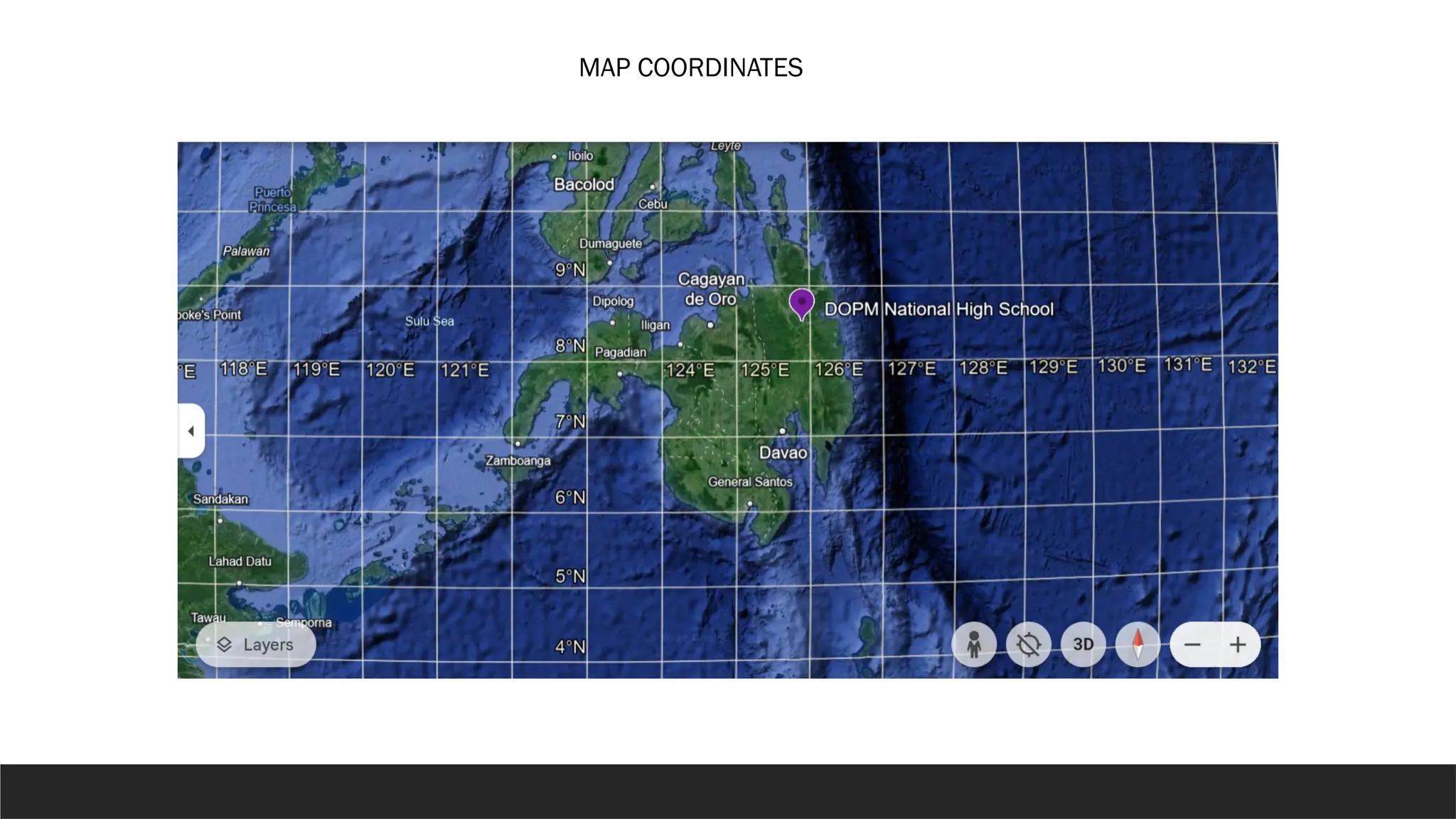
The document describes the rectangular coordinate system, highlighting the role of the x-axis and y-axis in defining a flat surface known as a plane, where each point is represented by an ordered pair (x,y). It outlines the characteristics and position of the quadrants in the Cartesian plane and provides instructions for plotting points and identifying figures based on specified coordinates. Additionally, it includes a historical note on René Descartes, the system's namesake, and a practical application involving plotting various coordinate pairs.