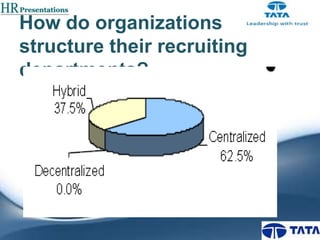
This document provides an overview of recruitment and selection processes at Tata Group, an Indian multinational conglomerate. It discusses manpower planning, factors affecting planning, internal and external recruitment methods, strategic recruiting stages, and selection tools and standards. Tata Group recruits to acquire a high quality workforce to accomplish its long-term mission. The recruitment process involves attracting candidates, screening out unsuitable applicants, and promoting a positive company image.