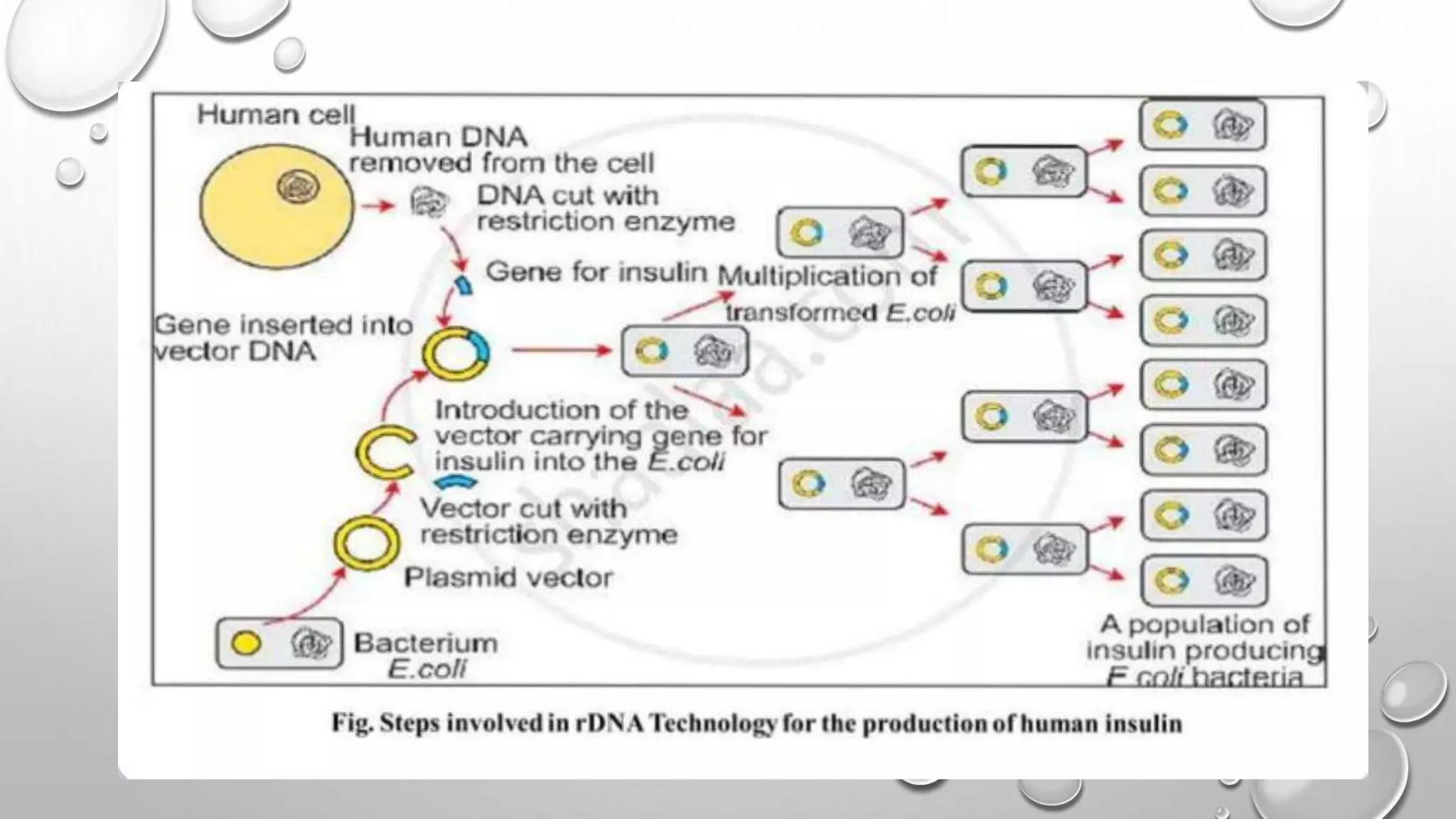
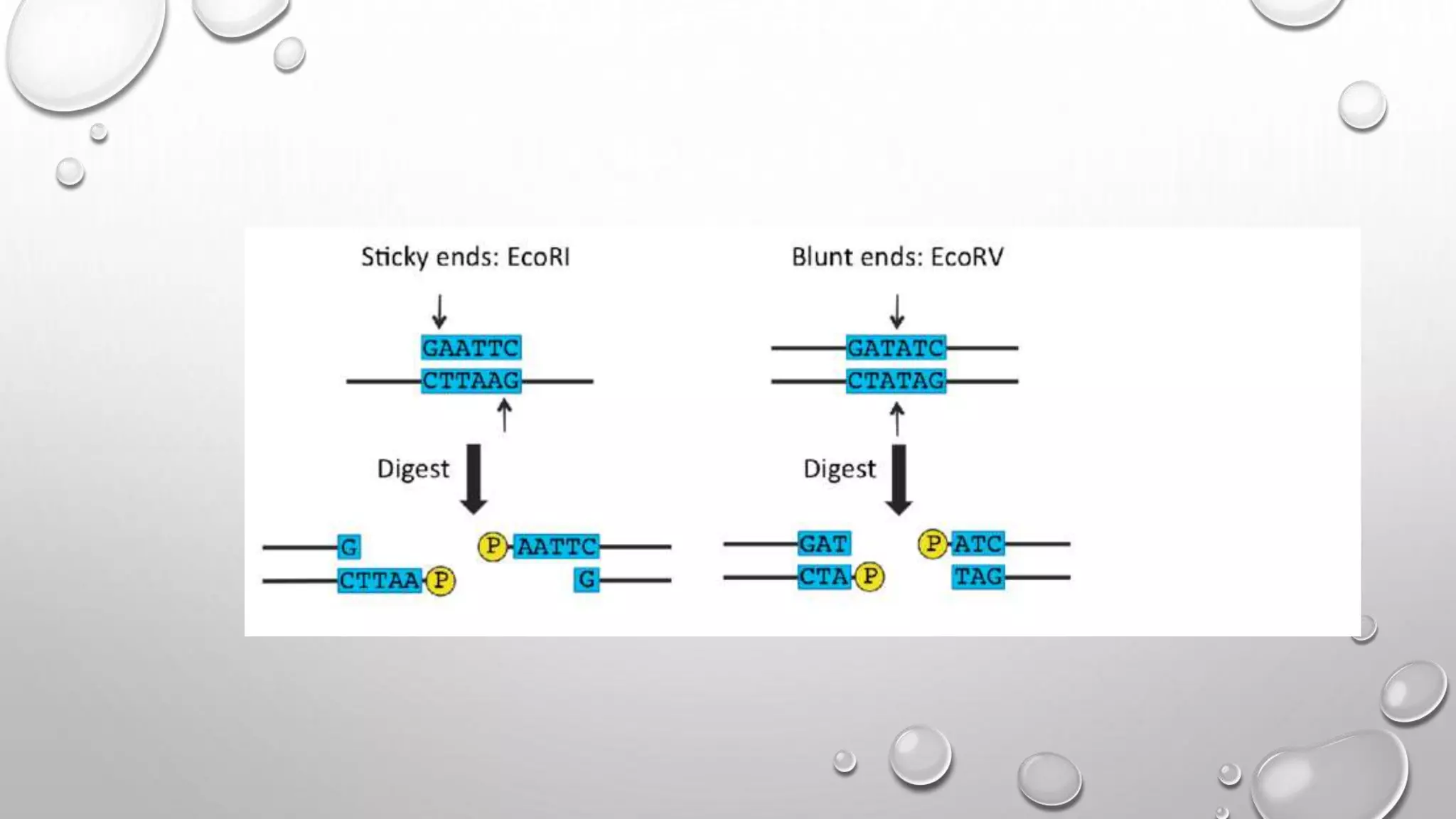
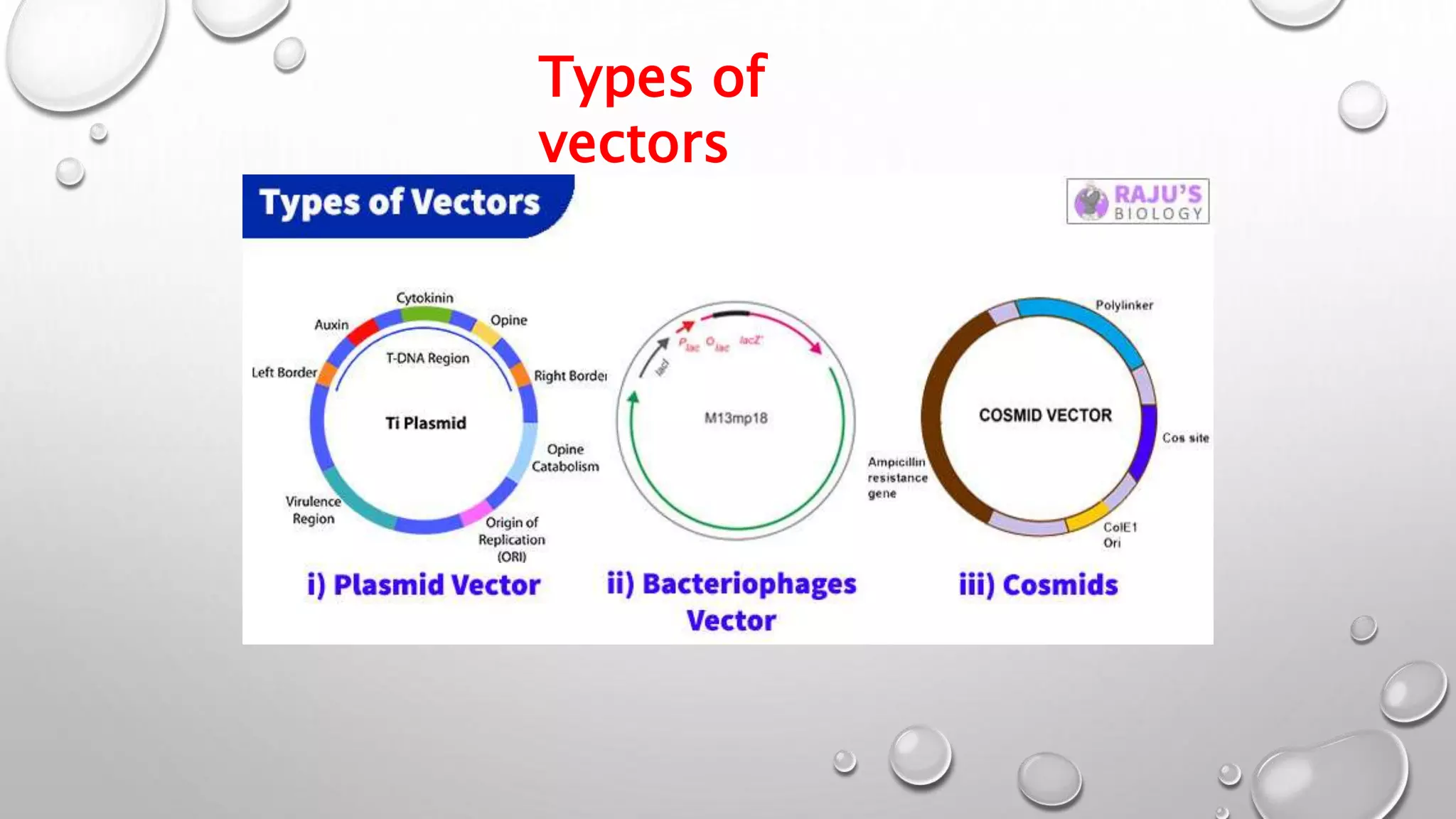
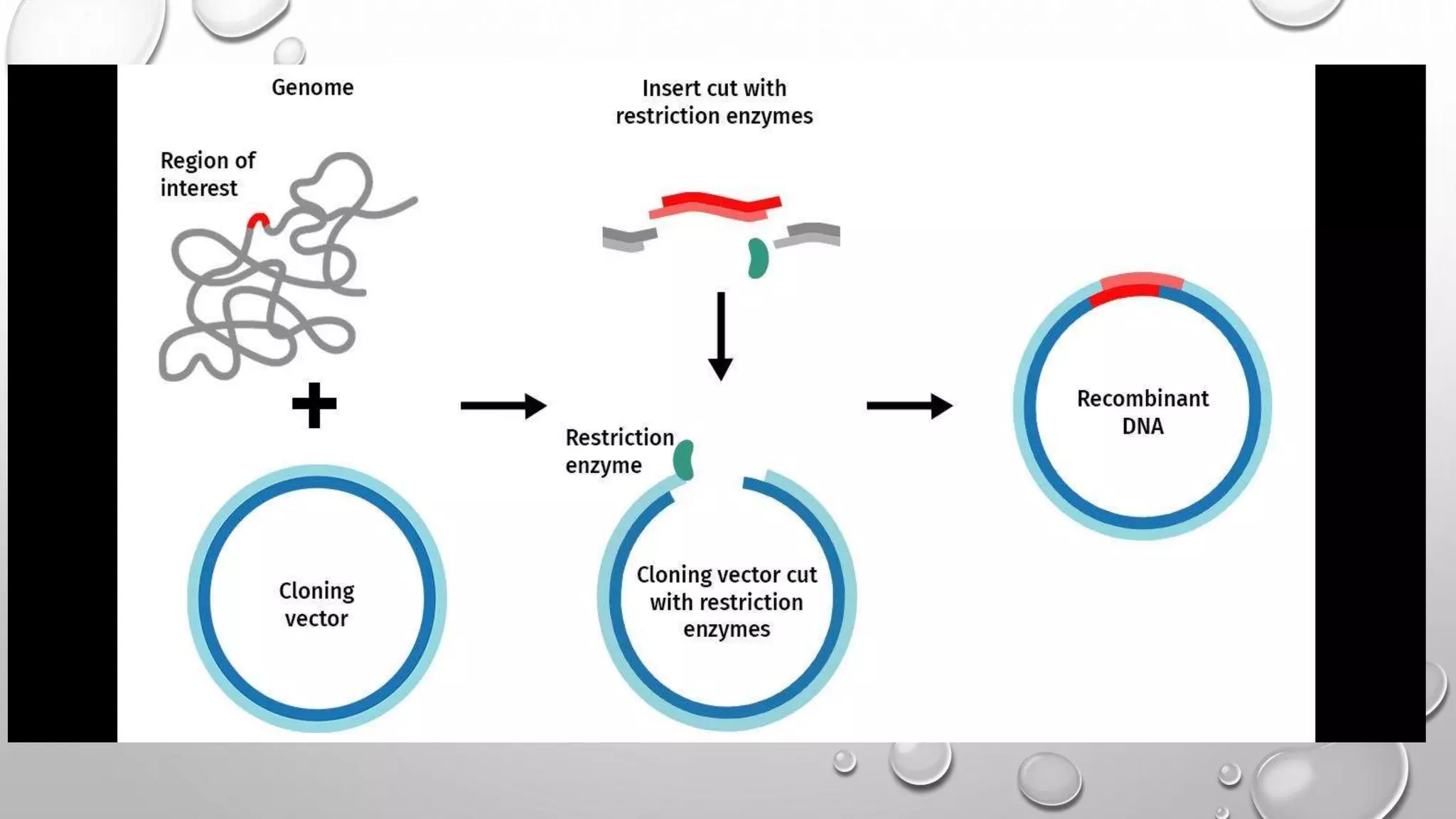
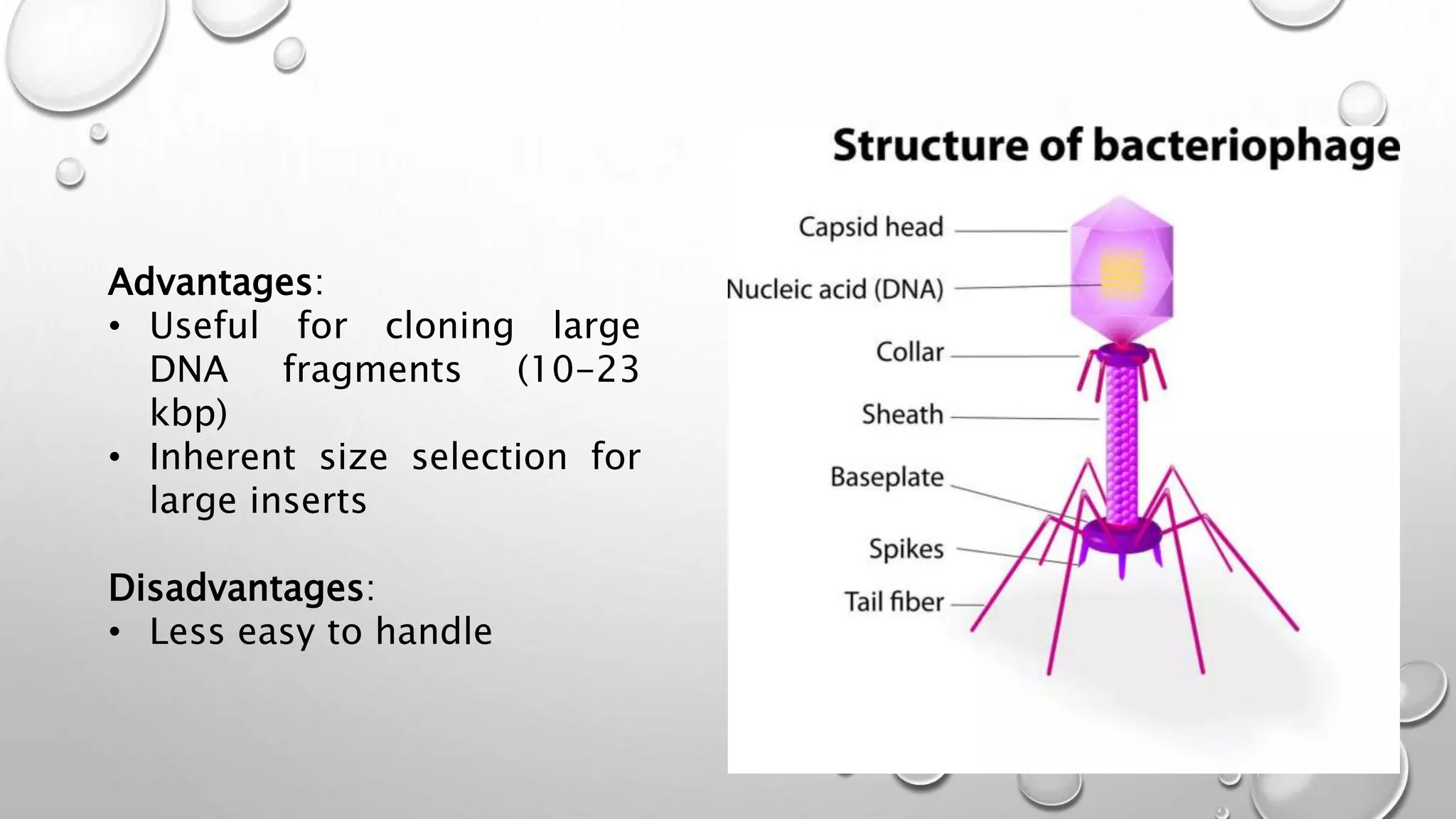
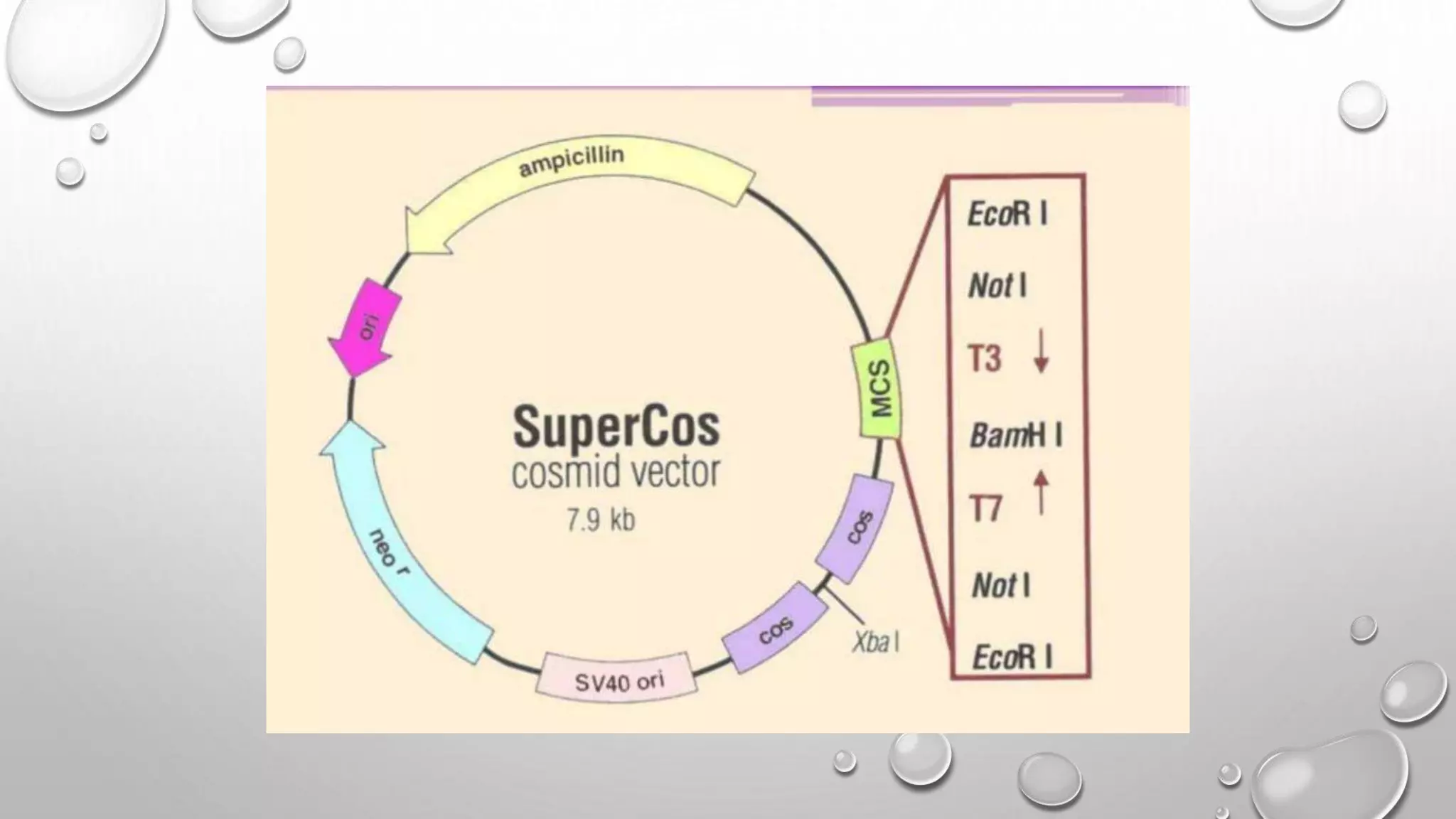
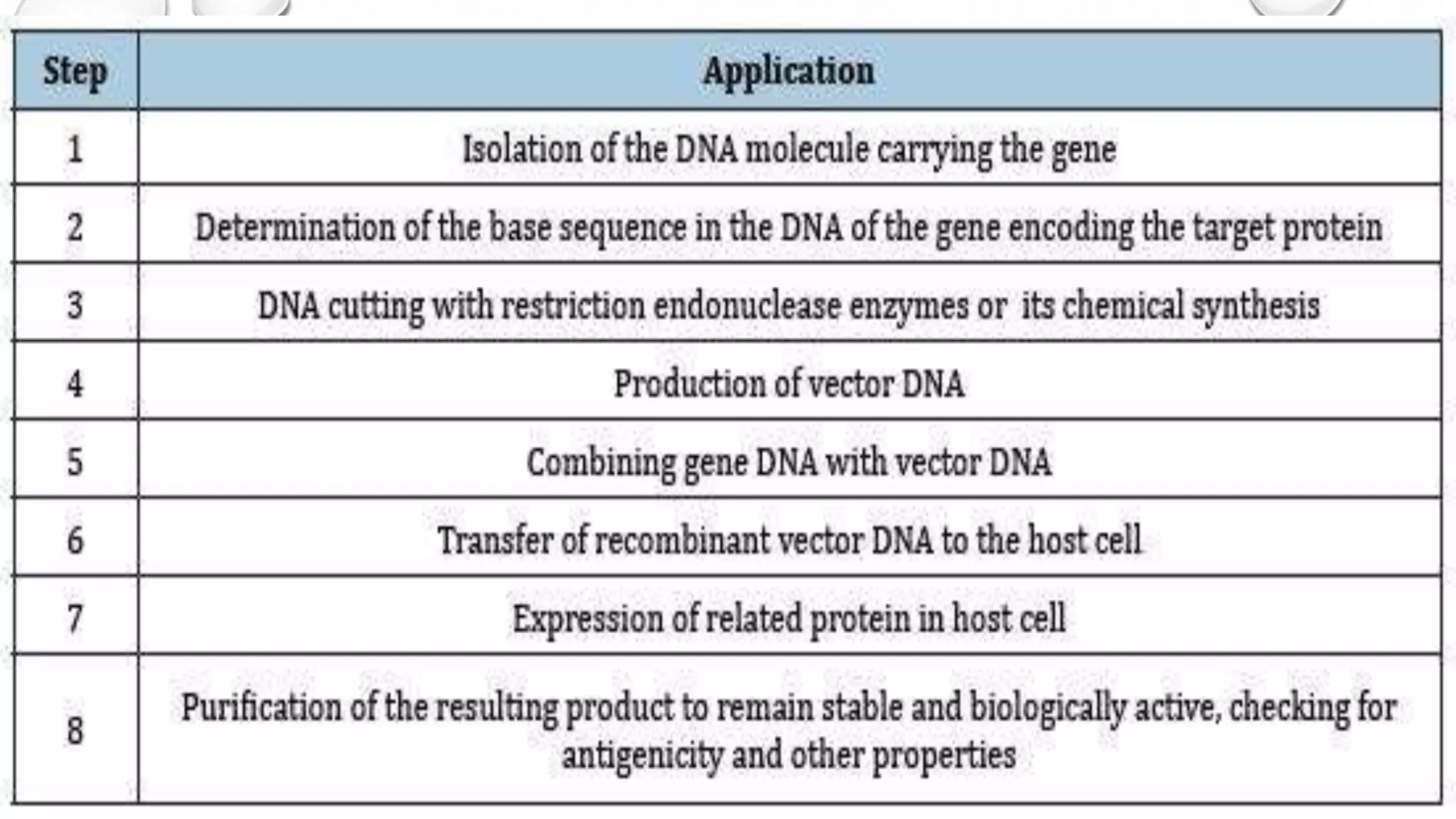
Recombinant DNA technology uses restriction enzymes to cut DNA fragments from a donor organism. The fragments are inserted into a cloning vector like a plasmid or bacteriophage. The recombinant vector is then introduced into a host cell, usually a bacterium, where it can be replicated in large quantities. The multiplied DNA or gene product can then be extracted from the host cells.