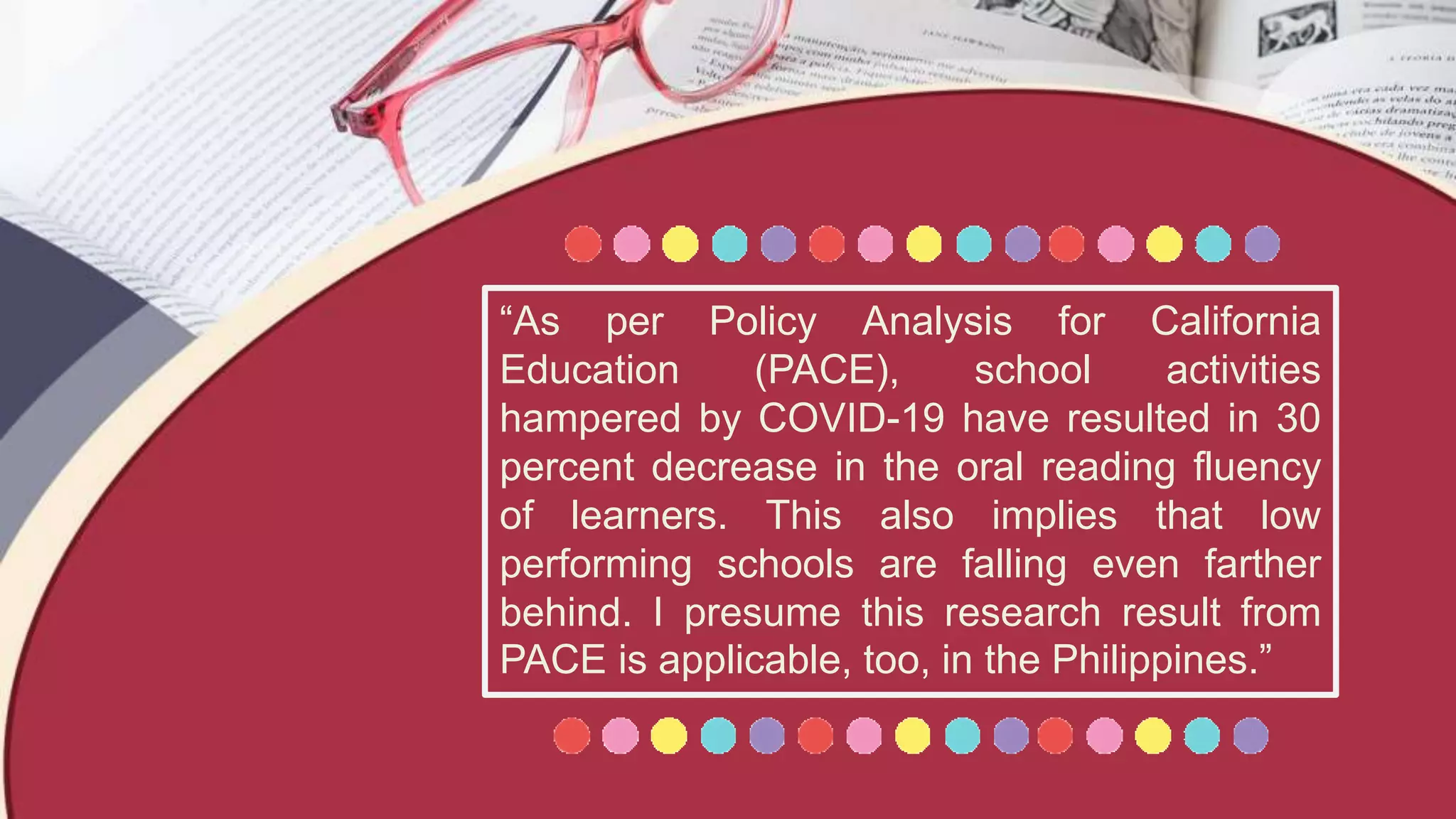
This document discusses challenges with teaching reading comprehension during the COVID-19 pandemic through distance learning modules. It notes that reading skills like decoding are difficult to teach through modules alone without live instruction. Parents and learning facilitators also lacked training to support reading instruction at home. The document advocates training facilitators to teach the five components of reading: phonemic awareness, phonics, fluency, vocabulary, and comprehension. It emphasizes that effective pedagogy requires patience and understanding between facilitators and students.