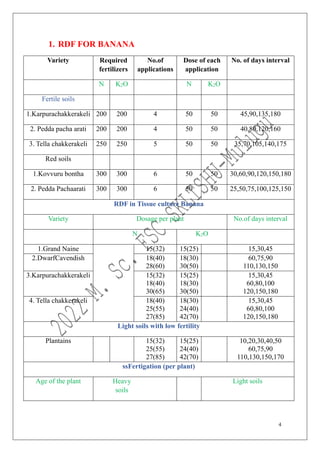
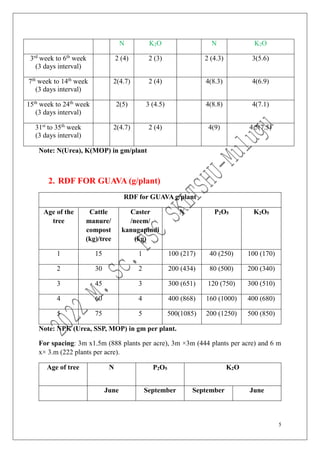
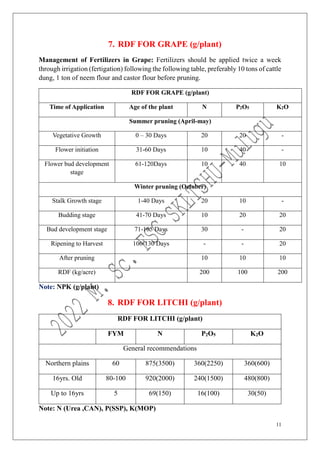
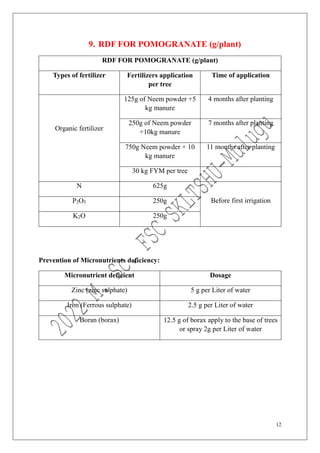
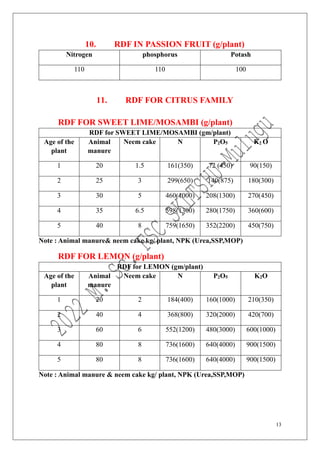
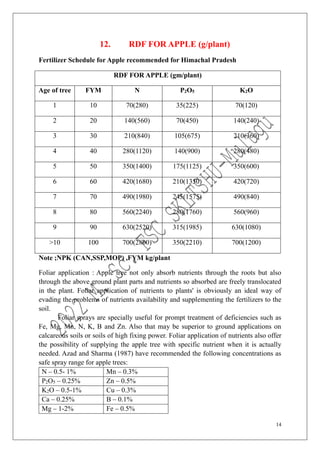
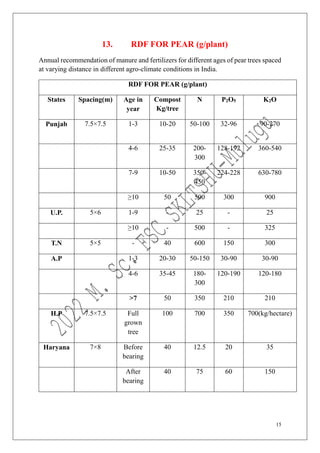
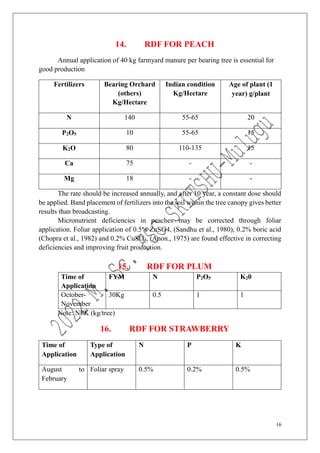
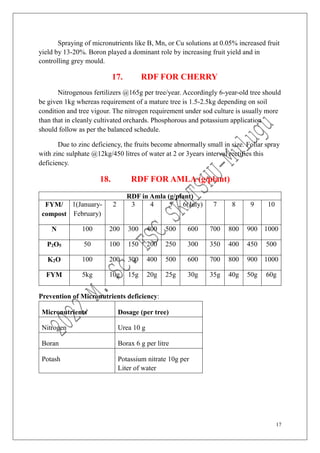
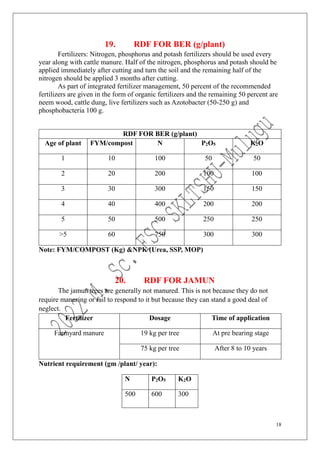
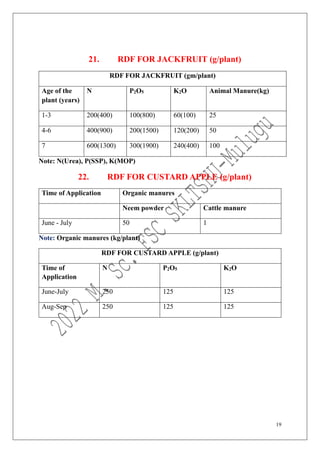
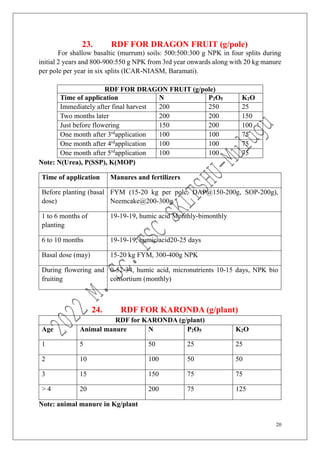
The document outlines the recommended doses of fertilizers for various fruit crops, including banana, guava, papaya, and mango, detailing specific applications based on soil type and crop age. It includes guidelines for micronutrient deficiencies and how to prevent them, along with dosage recommendations for both organic and chemical fertilizers. Additionally, it lists the age-wise nutrient requirements and planting recommendations for different fruit varieties.