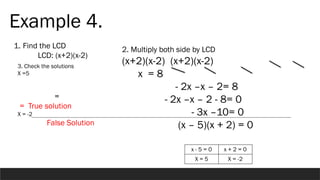
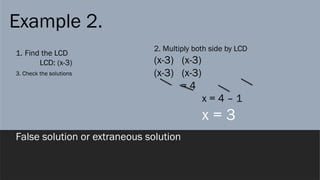
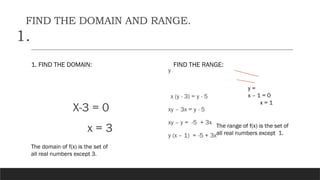
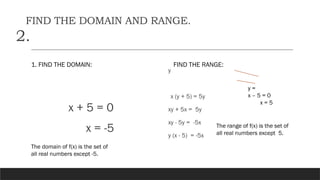
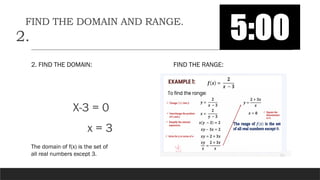
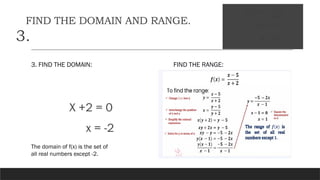
The document provides a comprehensive overview of rational expressions, equations, and inequalities, detailing methods to identify, solve, and check solutions. It includes various examples demonstrating how to find the least common denominator (LCD), determine domain and range, and handle extraneous solutions in solving rational equations. Additional activities and exercises reinforce the concepts discussed, aiming to enhance understanding of rational functions and their applications.