The document explores various functions and their domains by presenting multiple examples, each demonstrating how to determine when a function is defined based on its algebraic expressions. It discusses various functions such as rational, radical, logarithmic, and absolute functions while emphasizing the necessary conditions for their validity. Additionally, it includes solutions and methodologies for evaluating the domain of real functions, showcasing critical points of interest where the functions are undefined.

![FUNCTIONS
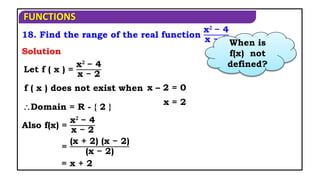
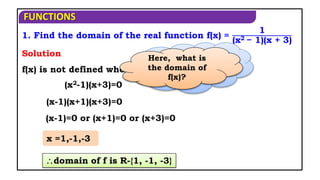
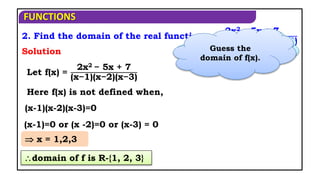
3. Find the domain of the real function f(x)= 16 − x𝟐
Domain of f(x) is [-4, 4]
16−x𝟐 is defined when,
x2 -16 0
x [-4, 4]
Solution
(x + 4) (x - 4) 0
16 - x2 0
When f(x) is
defined?
If
(x-) (x-)≤0x[,]
(x-(-4)(x - 4) 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mat1ajrfunm07problems-240423120027-b5b47dcd/85/FUNCTION-PROBLEMS-FOR-JEE-ANS-STATE-BOARD-PRACTICE-5-320.jpg)
![FUNCTIONS
Domain of f(x) is (-, -5][5, )
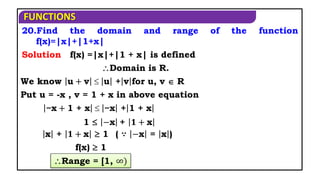
4. Find the domain of the real function f(x) = x𝟐 − 25
x𝟐 − 25 is defined when,
(x-5)(x+5) 0
x(-, -5][5, )
Solution
x𝟐
− 25 0
x-5 x 5
(or)
When f(x) is
defined?
(x-5)(x-(-5)) 0
If
(x-) (x-)≥0x(-, ][, )
x≤ or x≥ ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mat1ajrfunm07problems-240423120027-b5b47dcd/85/FUNCTION-PROBLEMS-FOR-JEE-ANS-STATE-BOARD-PRACTICE-6-320.jpg)
![FUNCTIONS
5. Find the domain of the real function f(x) = 4x − x𝟐
Domain of f(x) is [0,4]
4x − x𝟐 is defined when,
x𝟐
-4x 0
x[0,4]
(x-0)(x-4) 0
Solution
4x − x𝟐
0
x(x-4) 0
0x 4
When f(x) is
defined?
If
(x-) (x-)≤0x[,]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mat1ajrfunm07problems-240423120027-b5b47dcd/85/FUNCTION-PROBLEMS-FOR-JEE-ANS-STATE-BOARD-PRACTICE-7-320.jpg)
![FUNCTIONS
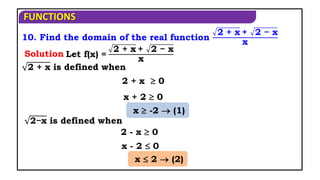
6. Find the domain of the real function f(x) = 2−x + 1+x
x -1(2)
2−x is defined when,
x - 2 0
1+x is defined when,
Solution
2 - x 0
x 2(1)
1 + x 0
Here we find
domain of
2−x , 1+x
seperately
When 2−x is
defined?
When 1+x is
defined?
-2 -1 0 1 2
-
Hence from (1)
-1 x 2 x [-1, 2]
and (2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mat1ajrfunm07problems-240423120027-b5b47dcd/85/FUNCTION-PROBLEMS-FOR-JEE-ANS-STATE-BOARD-PRACTICE-8-320.jpg)
![FUNCTIONS
2
1
0
-1
-2
×
-∞ +∞
From (1), (2) and (3)
1
x
is defined when x 0(3)
x -2 (1)
x 2 (2)
x [-2, 0) (0, 2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mat1ajrfunm07problems-240423120027-b5b47dcd/85/FUNCTION-PROBLEMS-FOR-JEE-ANS-STATE-BOARD-PRACTICE-13-320.jpg)


![FUNCTIONS
12. Find the domain f(x)= x − [x]
Domain of f(x) is R
x − [x] is defined when
Solution
x - [x] 0
which is true x R
x [x]
When f(x)
is defined?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mat1ajrfunm07problems-240423120027-b5b47dcd/85/FUNCTION-PROBLEMS-FOR-JEE-ANS-STATE-BOARD-PRACTICE-16-320.jpg)
![FUNCTIONS
13. Find the domain of f(x)= [x]−x
But [x] > x is not possible.
f(x) exists when
[x] > x (or)
Now [x] = x
Domain of f(x) is Z
Solution
[x] - x 0
[x] x
[x] = x
x Z
So, we must have [x] = x
Is it
possible?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mat1ajrfunm07problems-240423120027-b5b47dcd/85/FUNCTION-PROBLEMS-FOR-JEE-ANS-STATE-BOARD-PRACTICE-17-320.jpg)

![FUNCTIONS
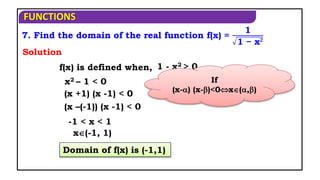
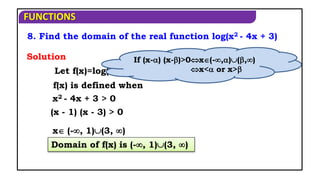
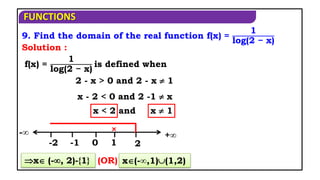
15. Find the domain of f(x) = log(x - [x]) ?
Domain of f(x) is R - Z.
log(x - [x]) is defined when
Solution
x - [x] > 0
x > [x] which is true x R - Z.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mat1ajrfunm07problems-240423120027-b5b47dcd/85/FUNCTION-PROBLEMS-FOR-JEE-ANS-STATE-BOARD-PRACTICE-19-320.jpg)
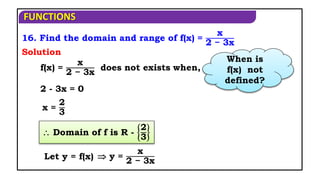

![FUNCTIONS
17. Find the domain and range of the f(x)= 9−x𝟐
Domain of f(x) is [-3, 3]
(i) Domain
f(x)= 9 − x𝟐 is defined when,
x2 – 9 0
x [-3, 3]
Solution
9 - x2 0
(x + 3) (x - 3) 0
-3 x 3
(x – (-3)) (x - 3) 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mat1ajrfunm07problems-240423120027-b5b47dcd/85/FUNCTION-PROBLEMS-FOR-JEE-ANS-STATE-BOARD-PRACTICE-22-320.jpg)
![FUNCTIONS
(ii) Range
We know that x2 0
The range of the f(x) is [0, 3]
-x2 0
9 – x2 9
9 − x2 3
and We know that 9−x2 0
𝟎 9−x2 (2)
From (1) & (2), 𝟎 9 − x2 3
f(x)= 9−x𝟐 0, x [-3,3]
(1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mat1ajrfunm07problems-240423120027-b5b47dcd/85/FUNCTION-PROBLEMS-FOR-JEE-ANS-STATE-BOARD-PRACTICE-23-320.jpg)