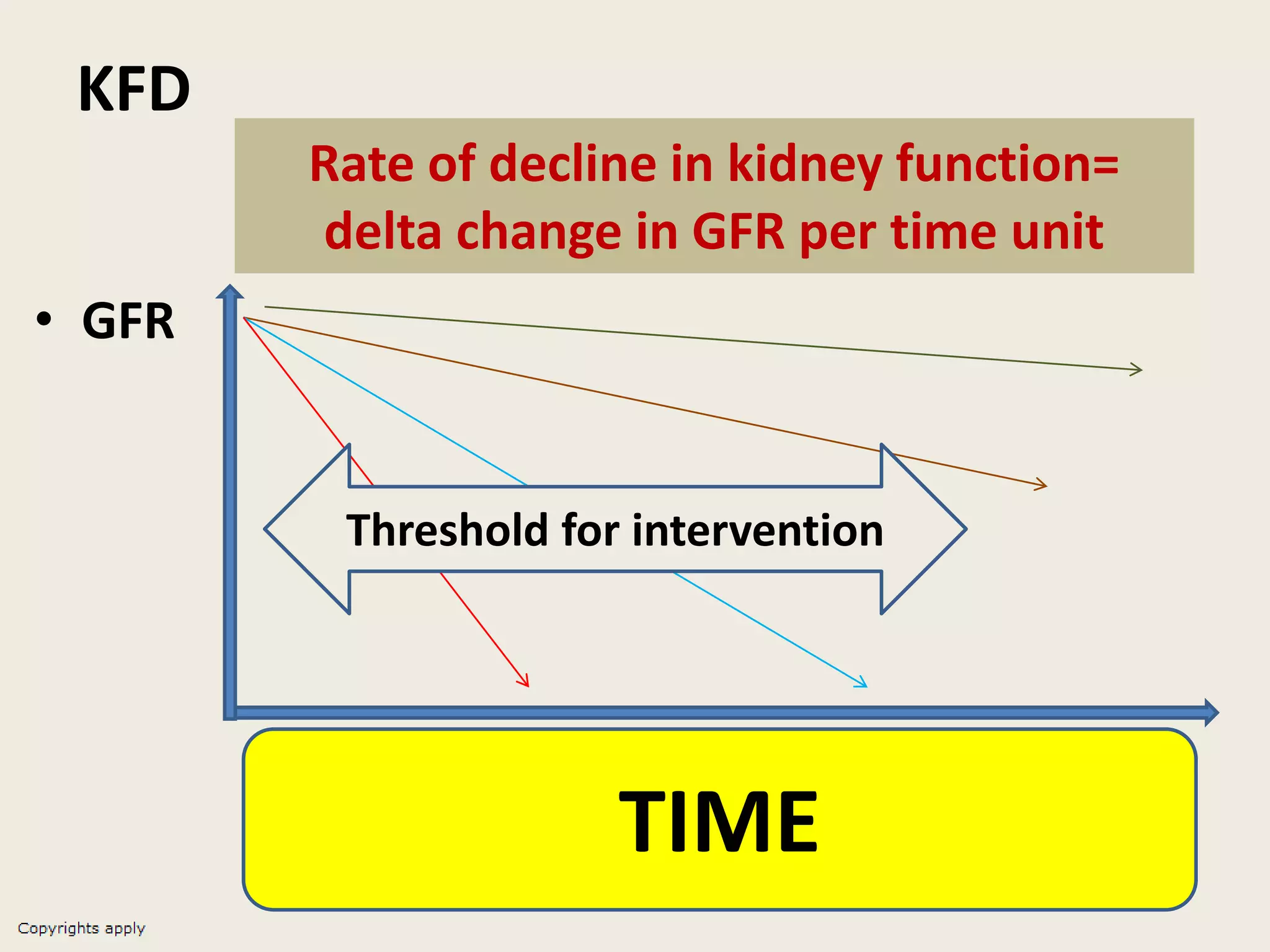
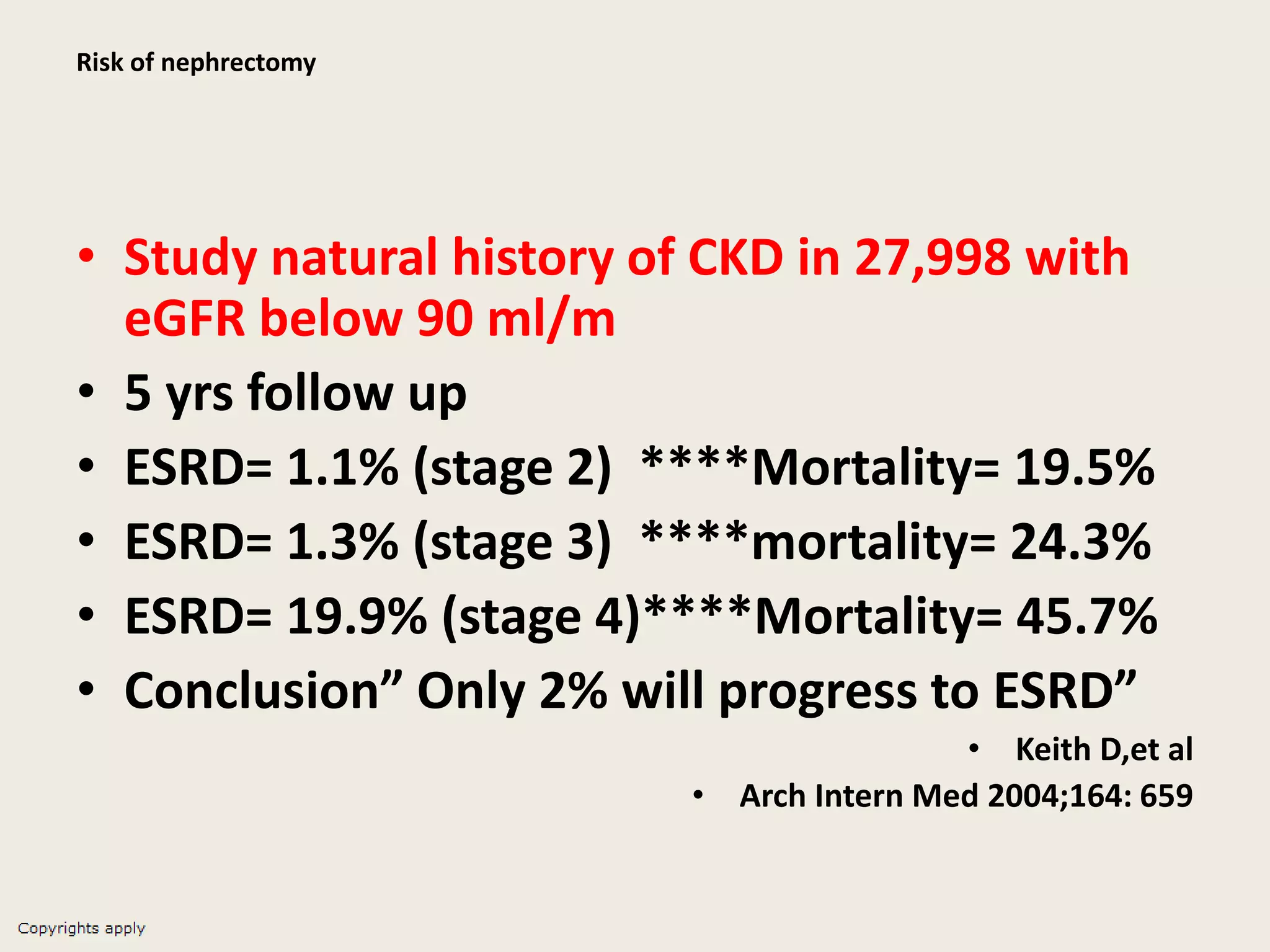
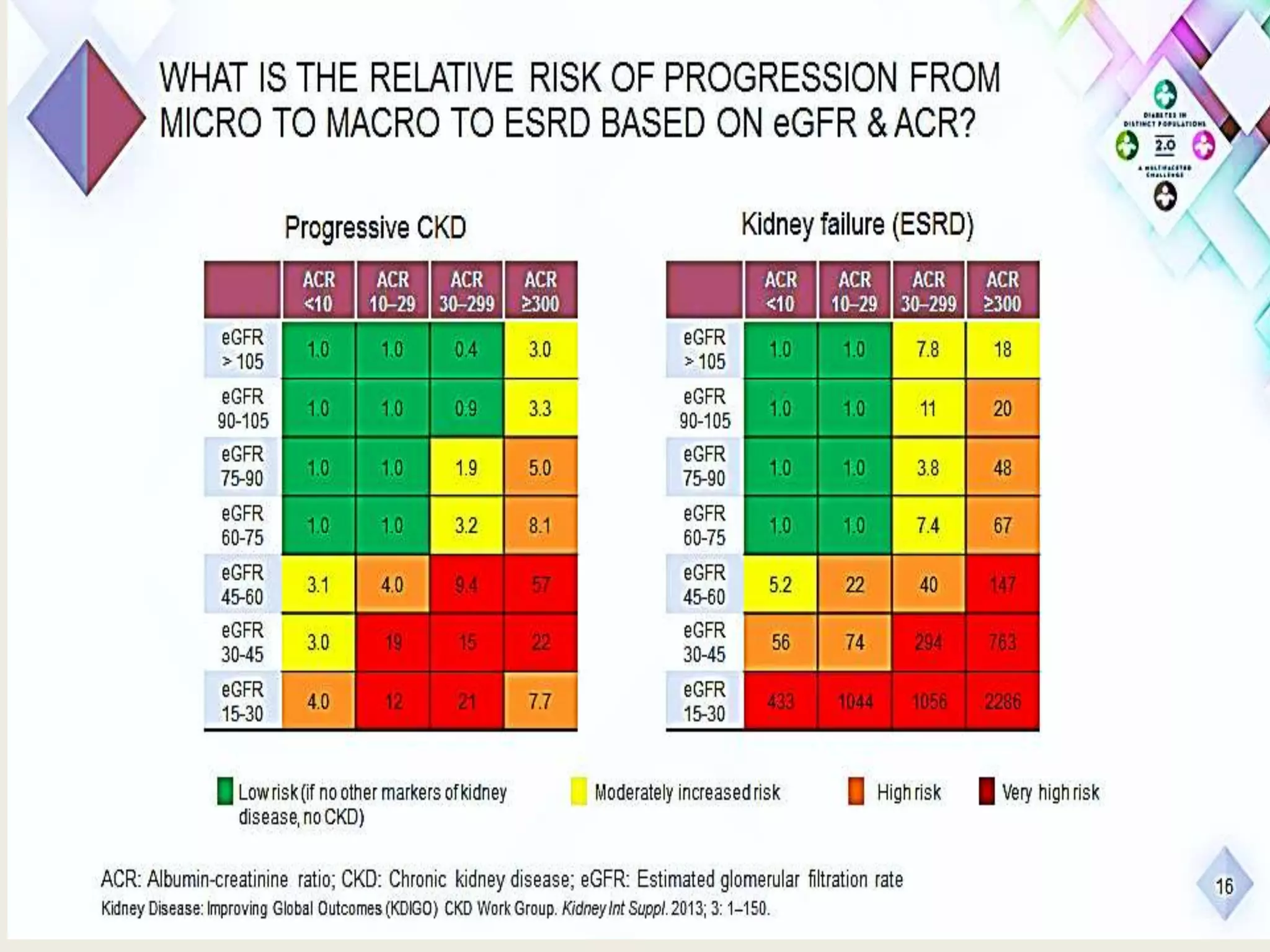
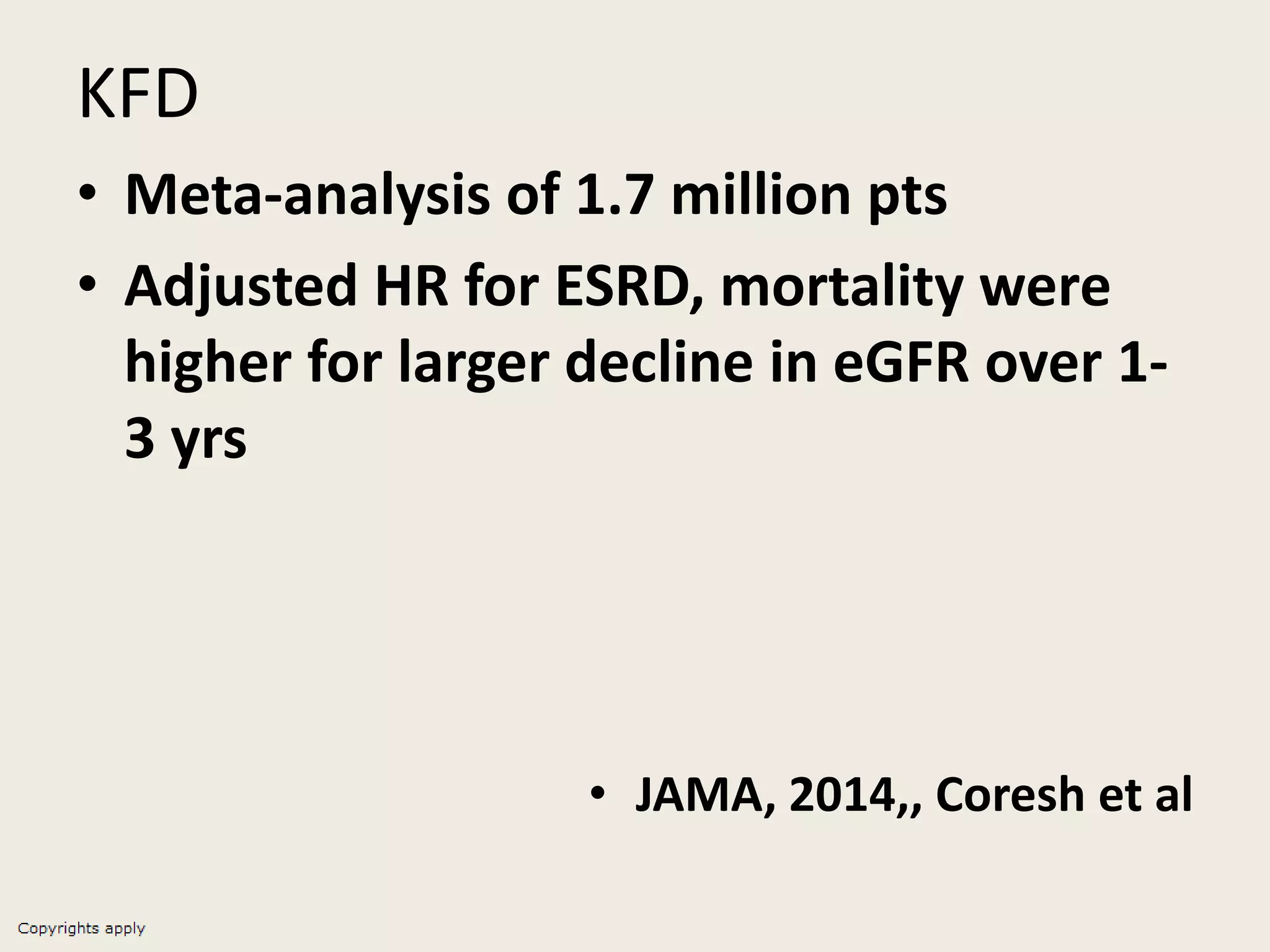
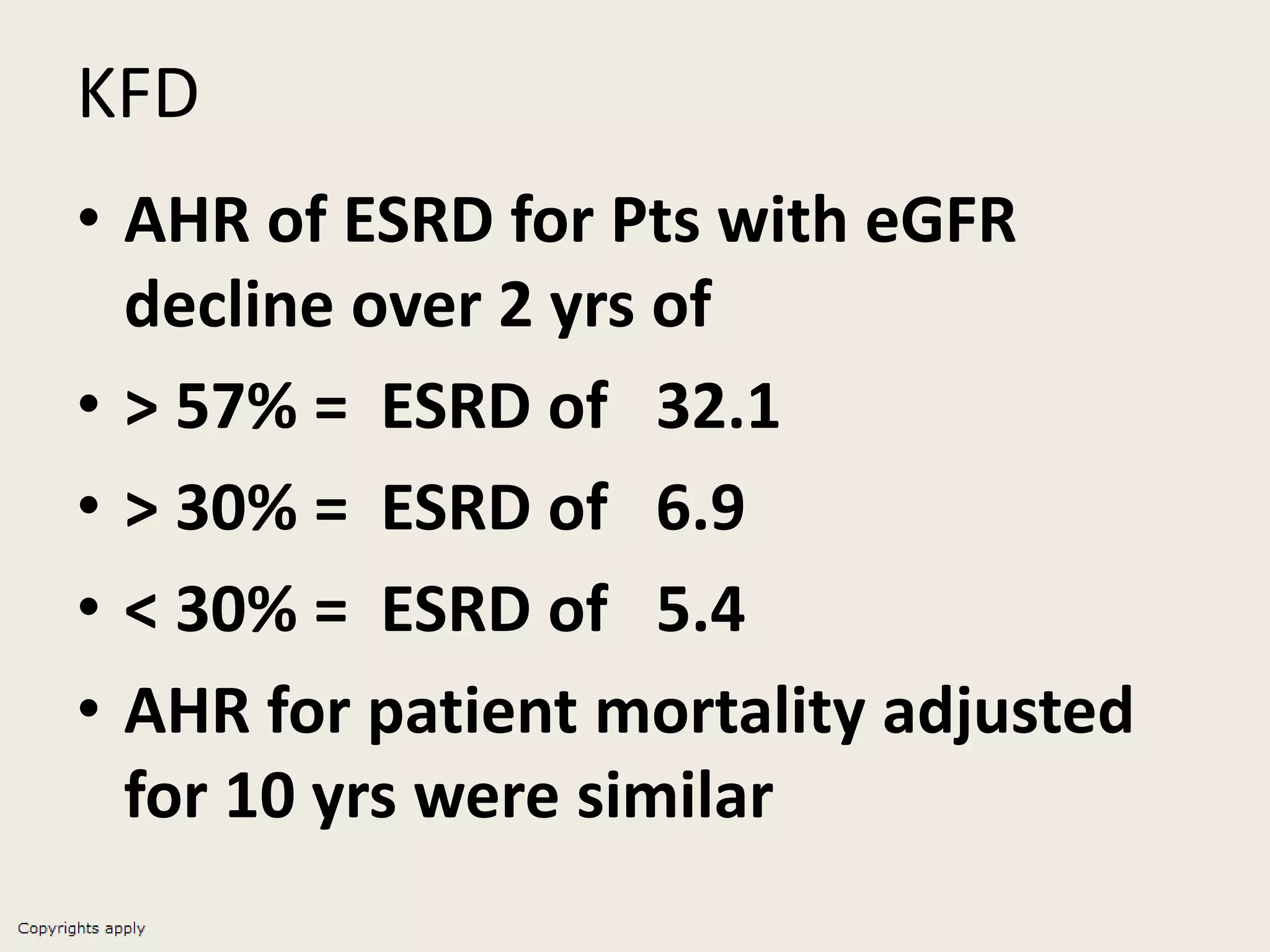
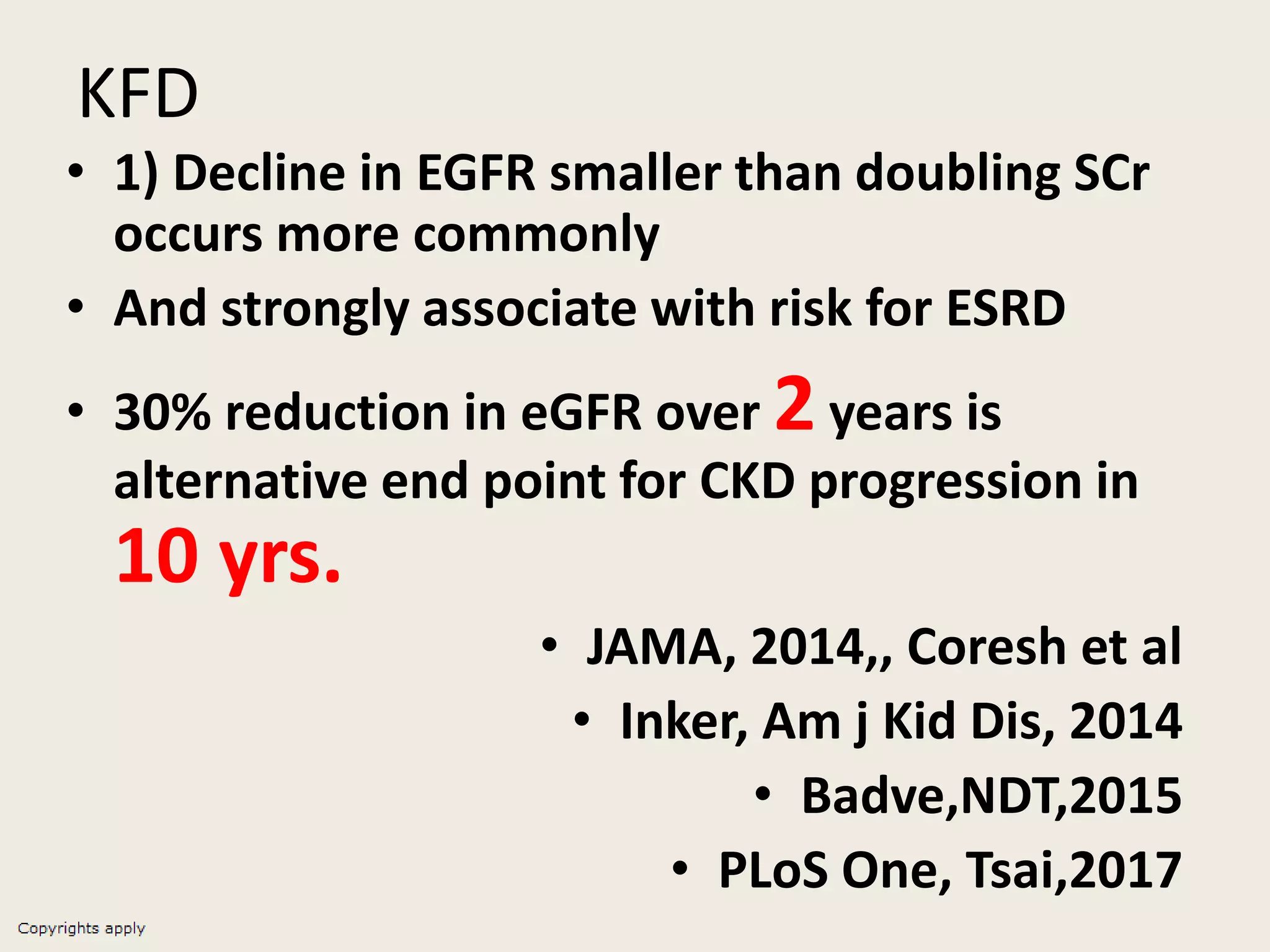
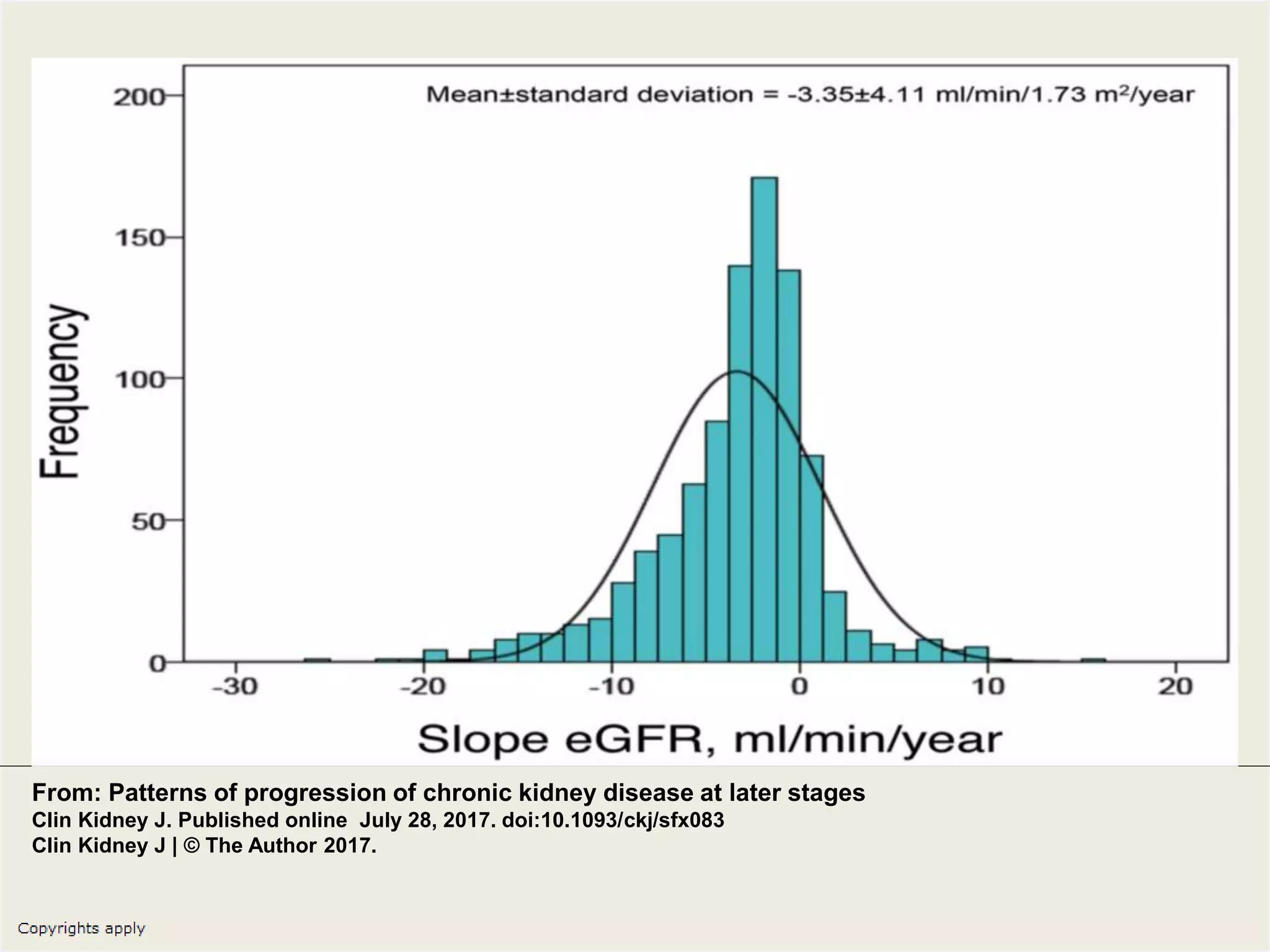
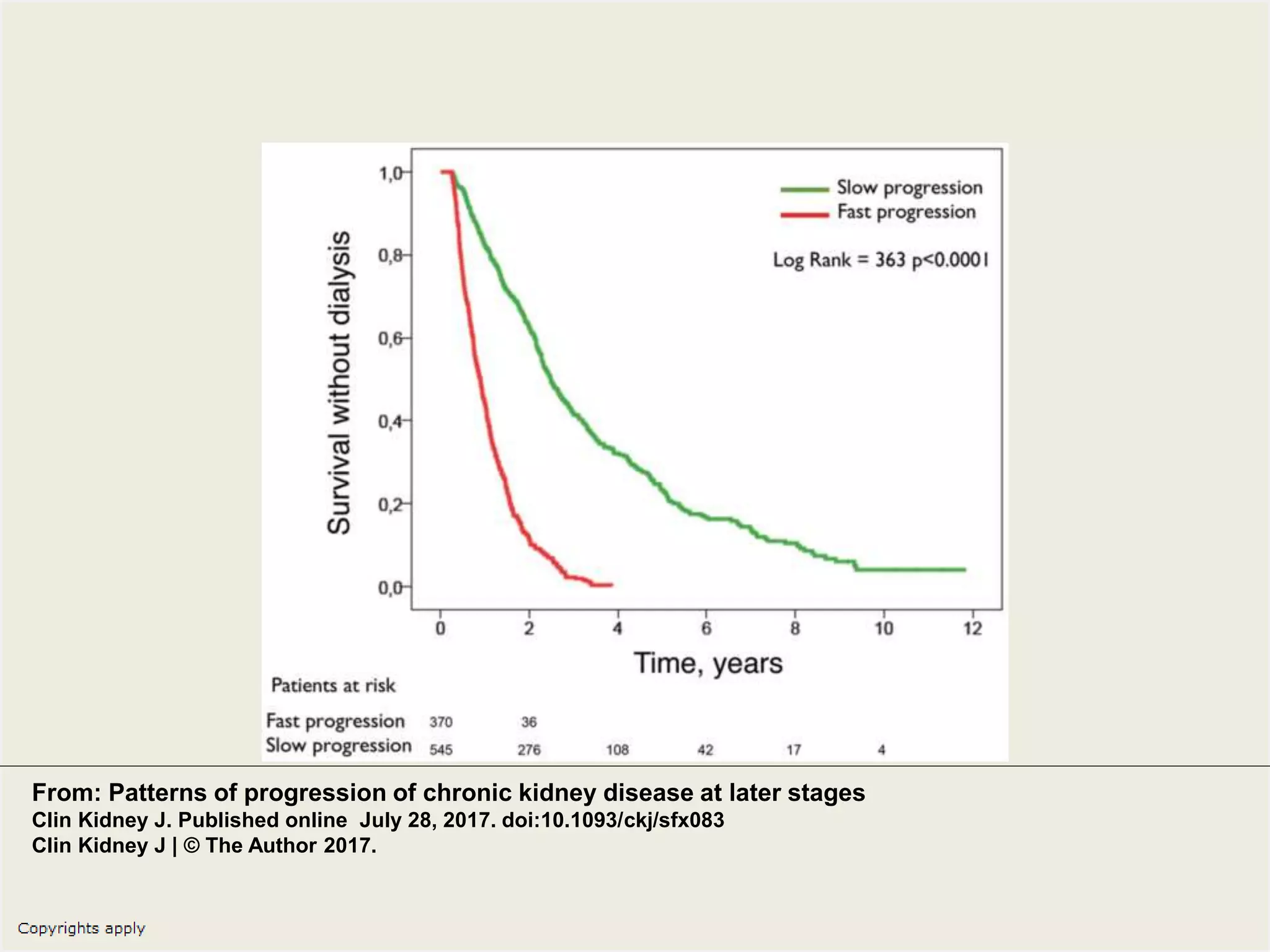
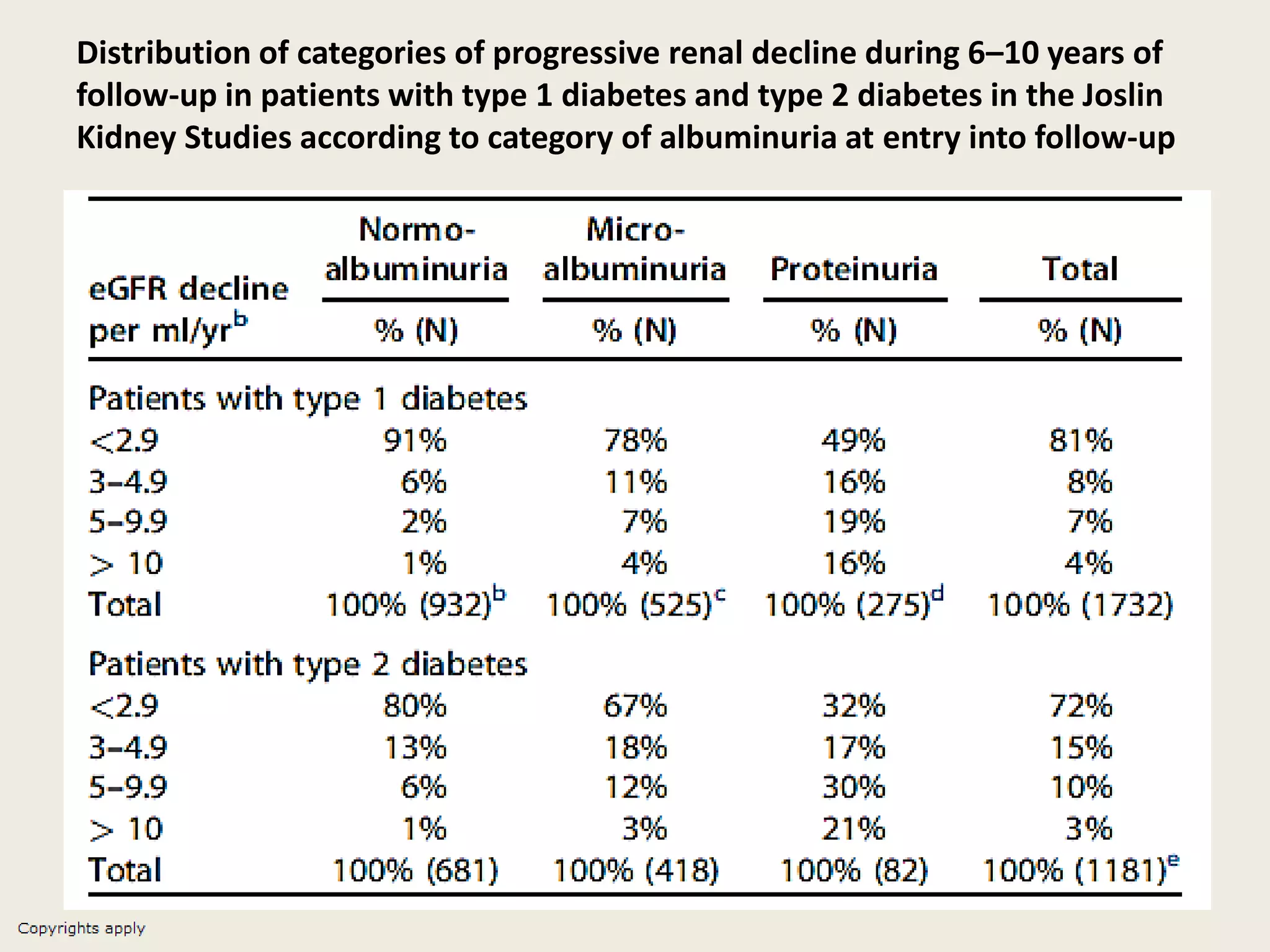
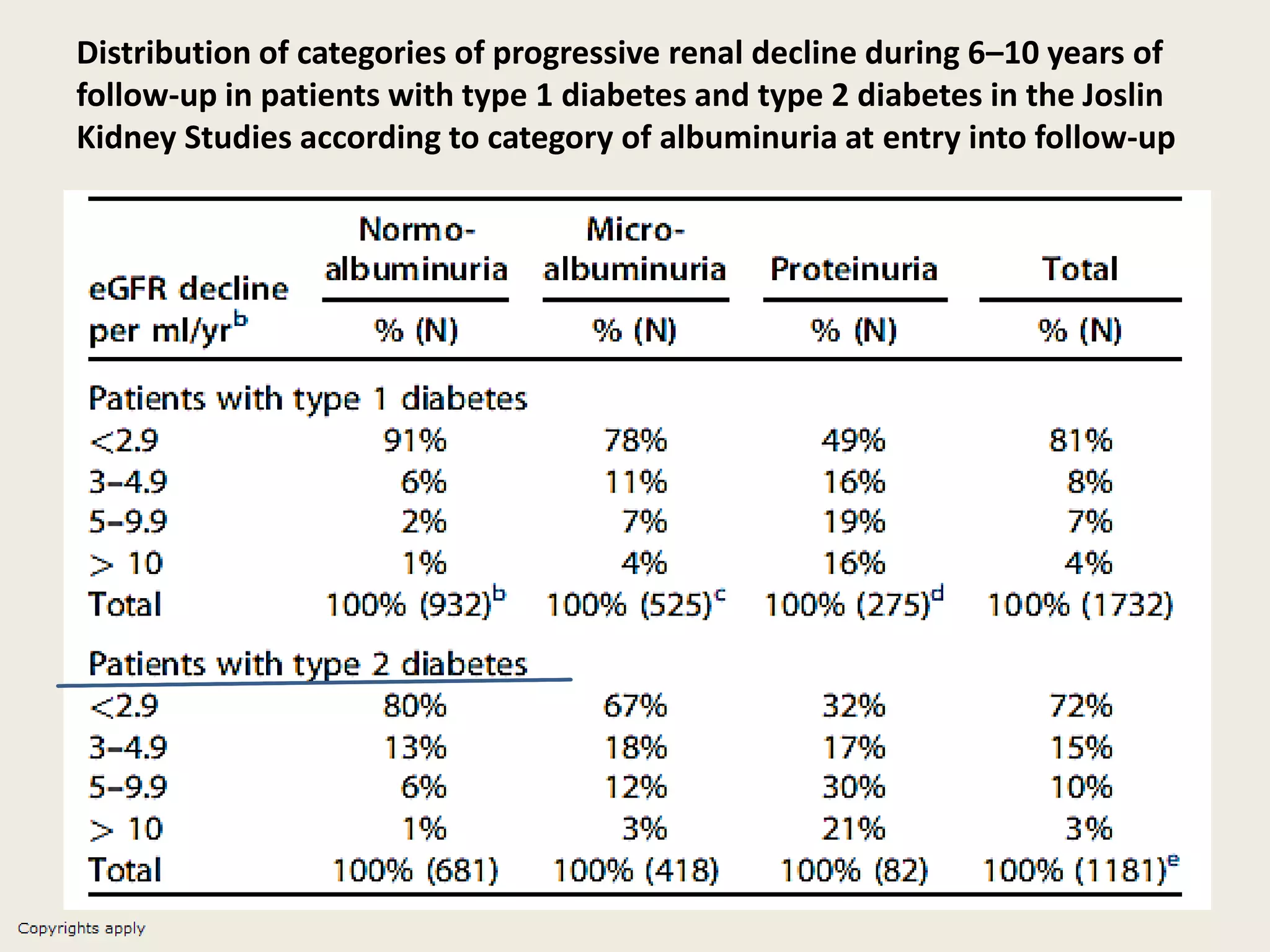
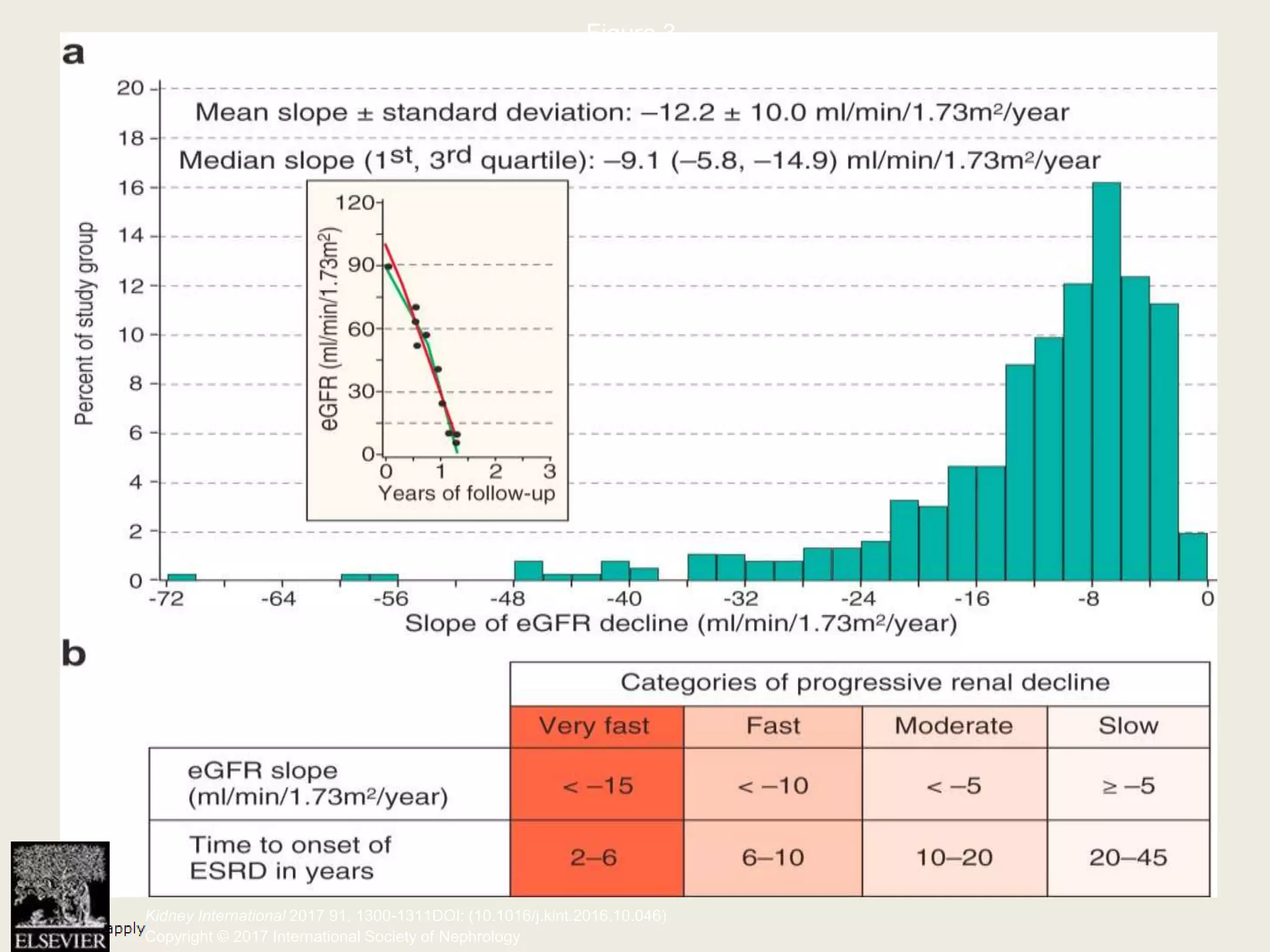
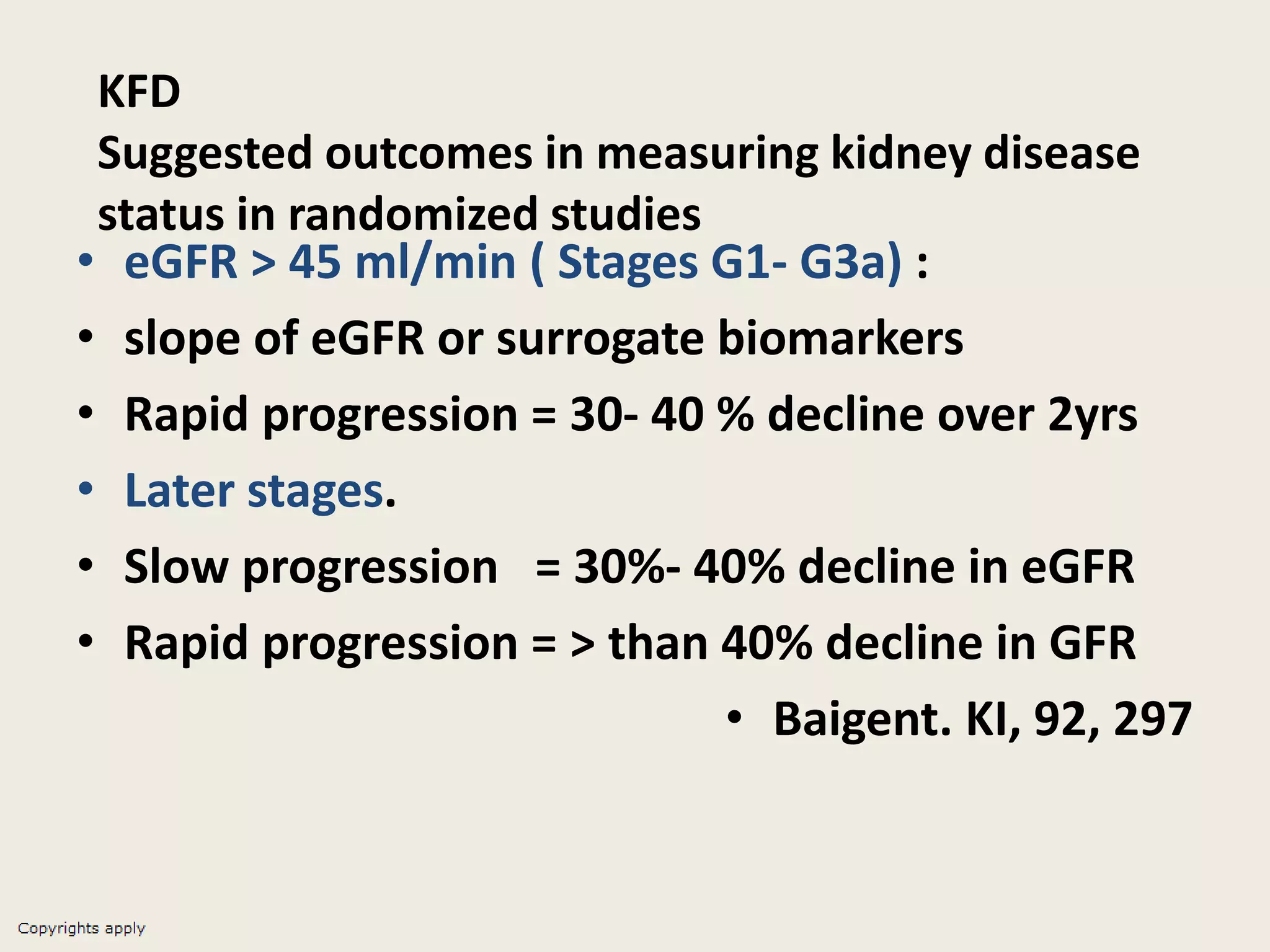
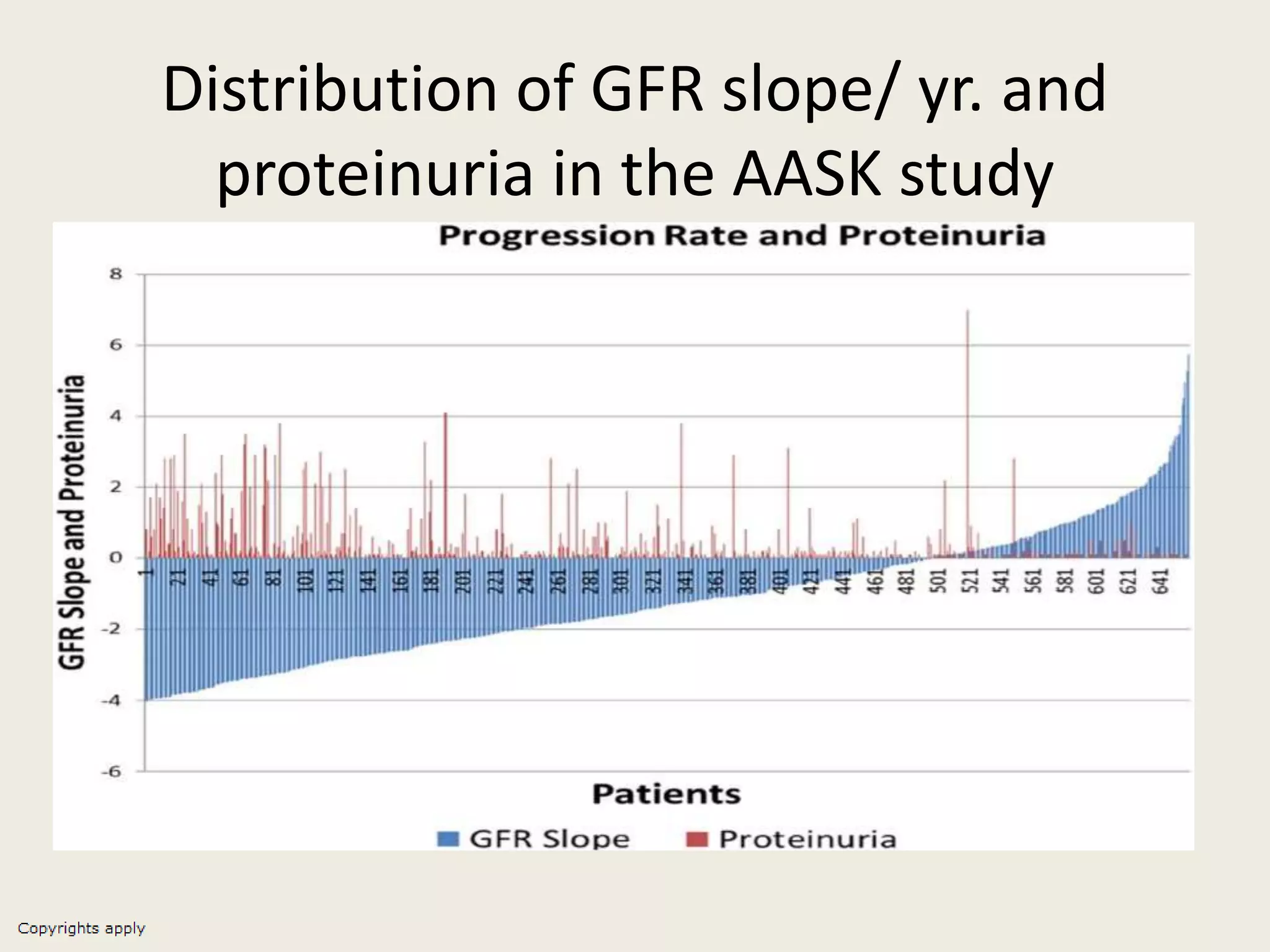
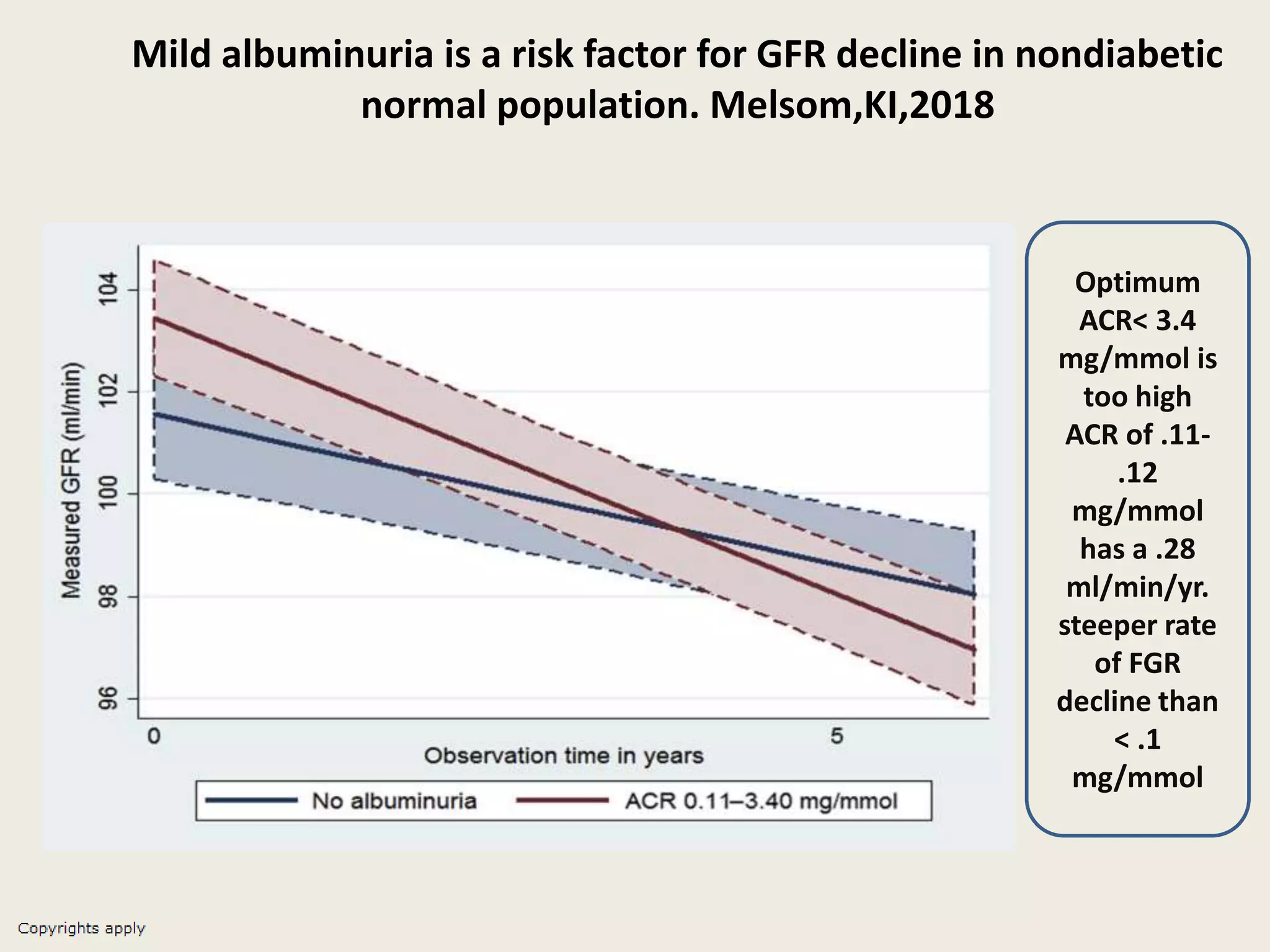
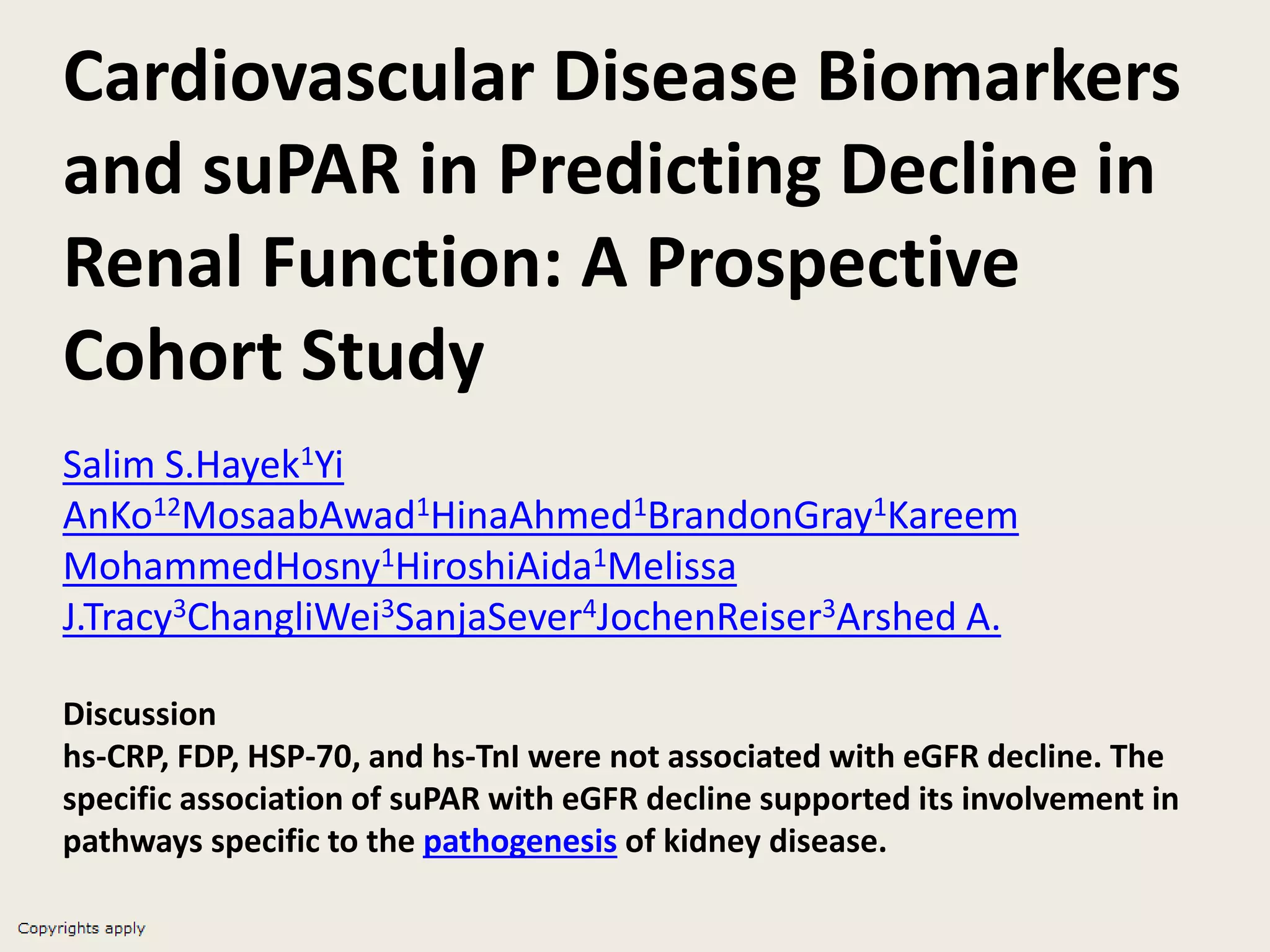
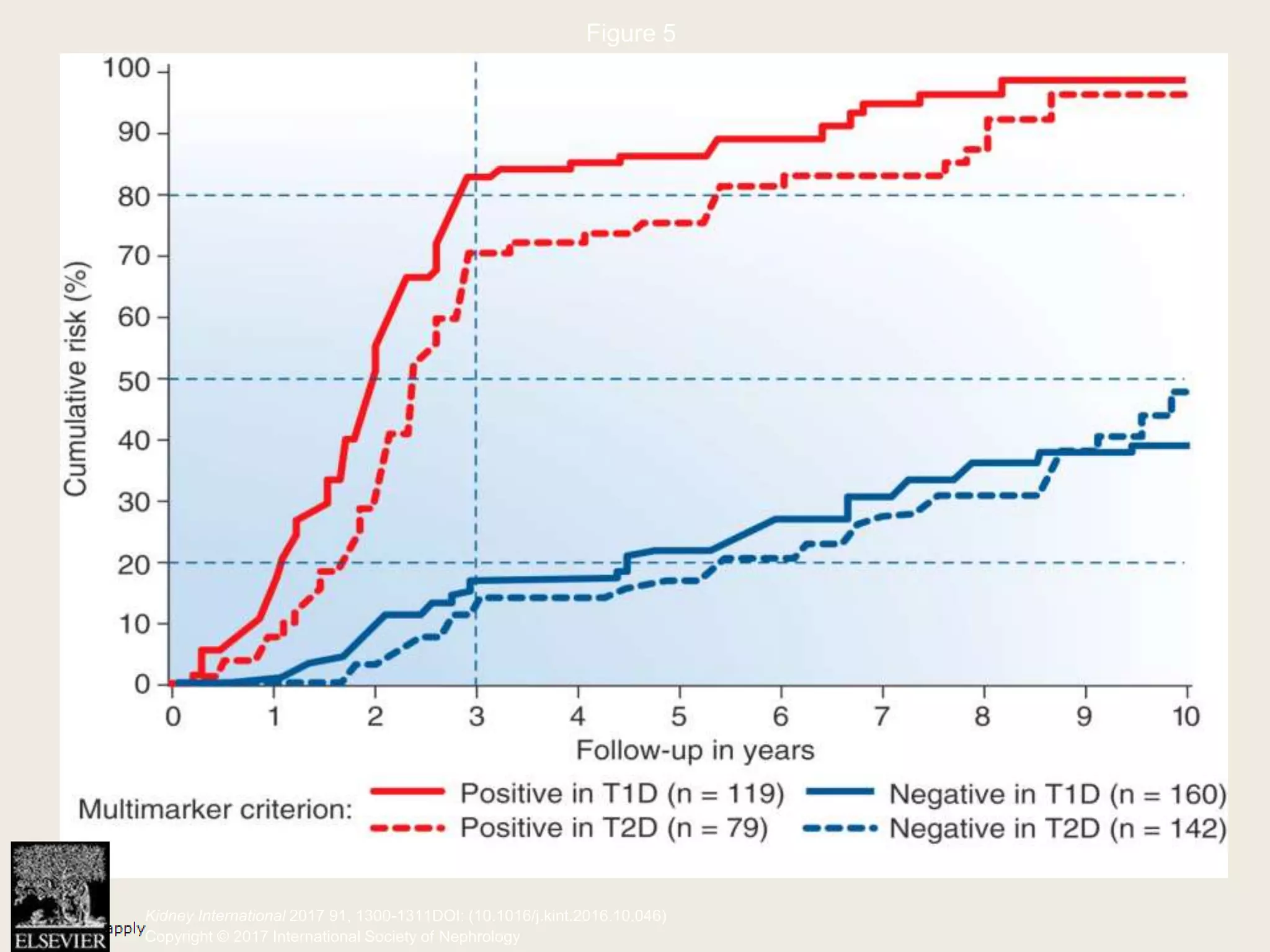
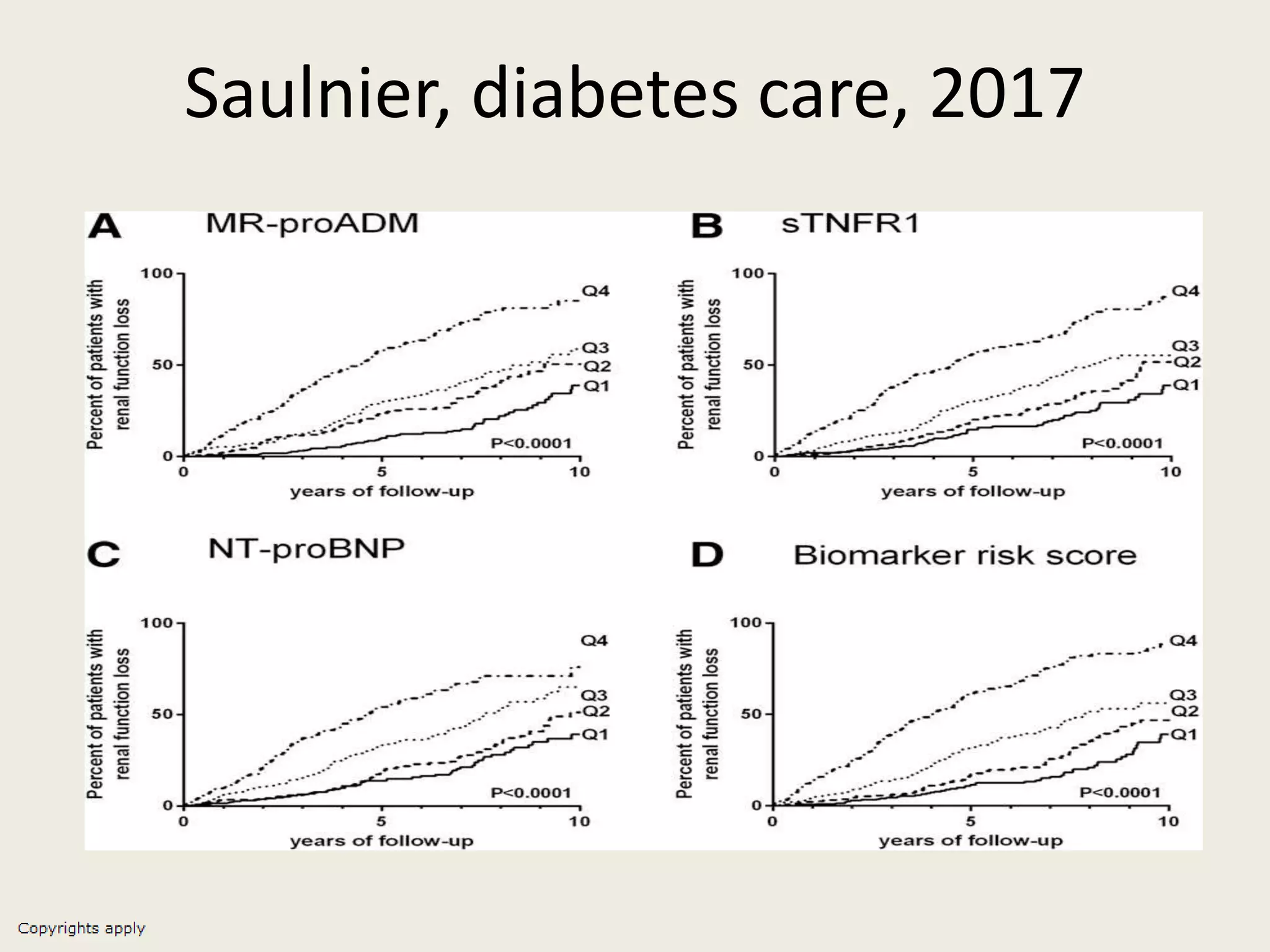
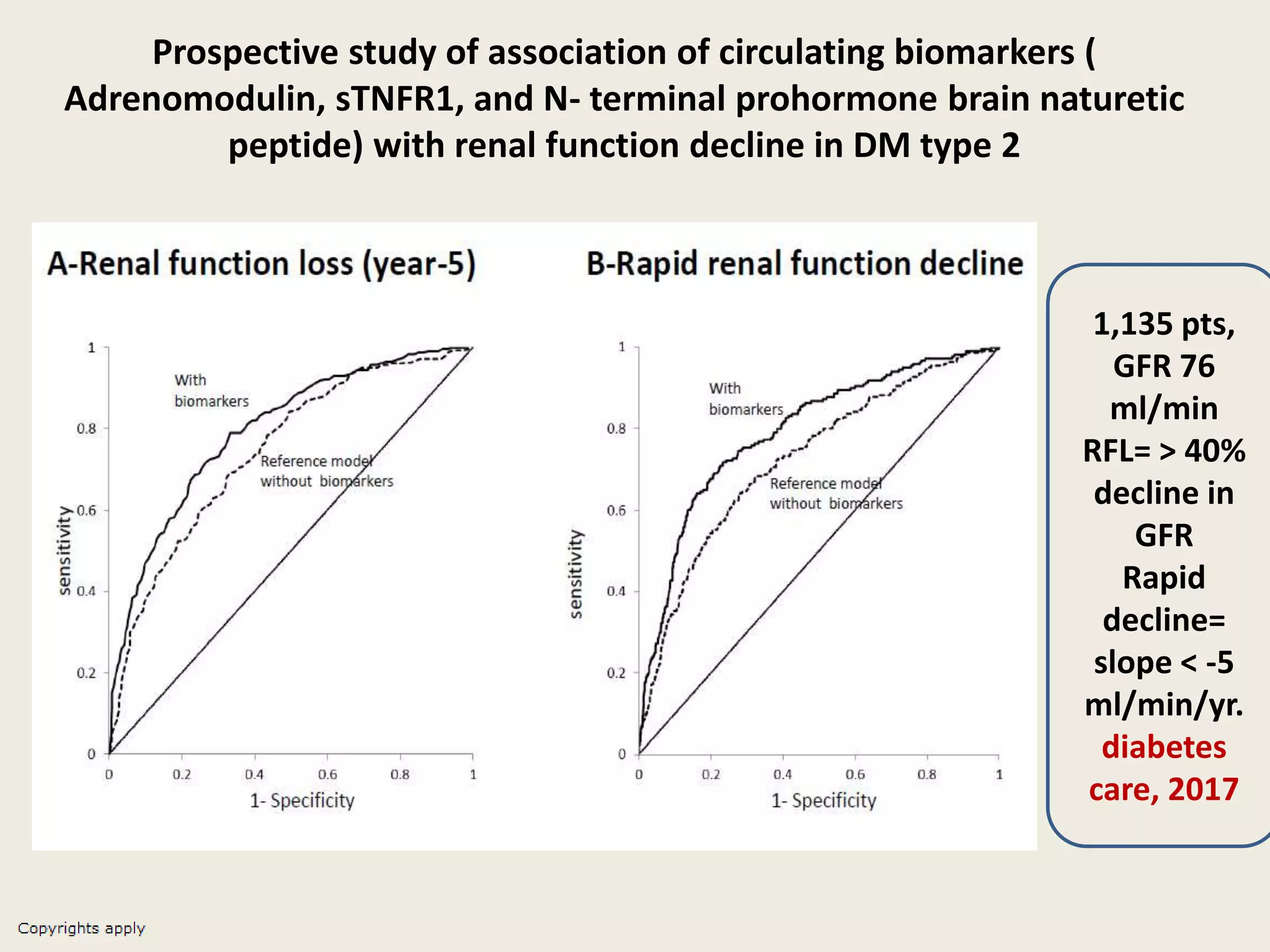
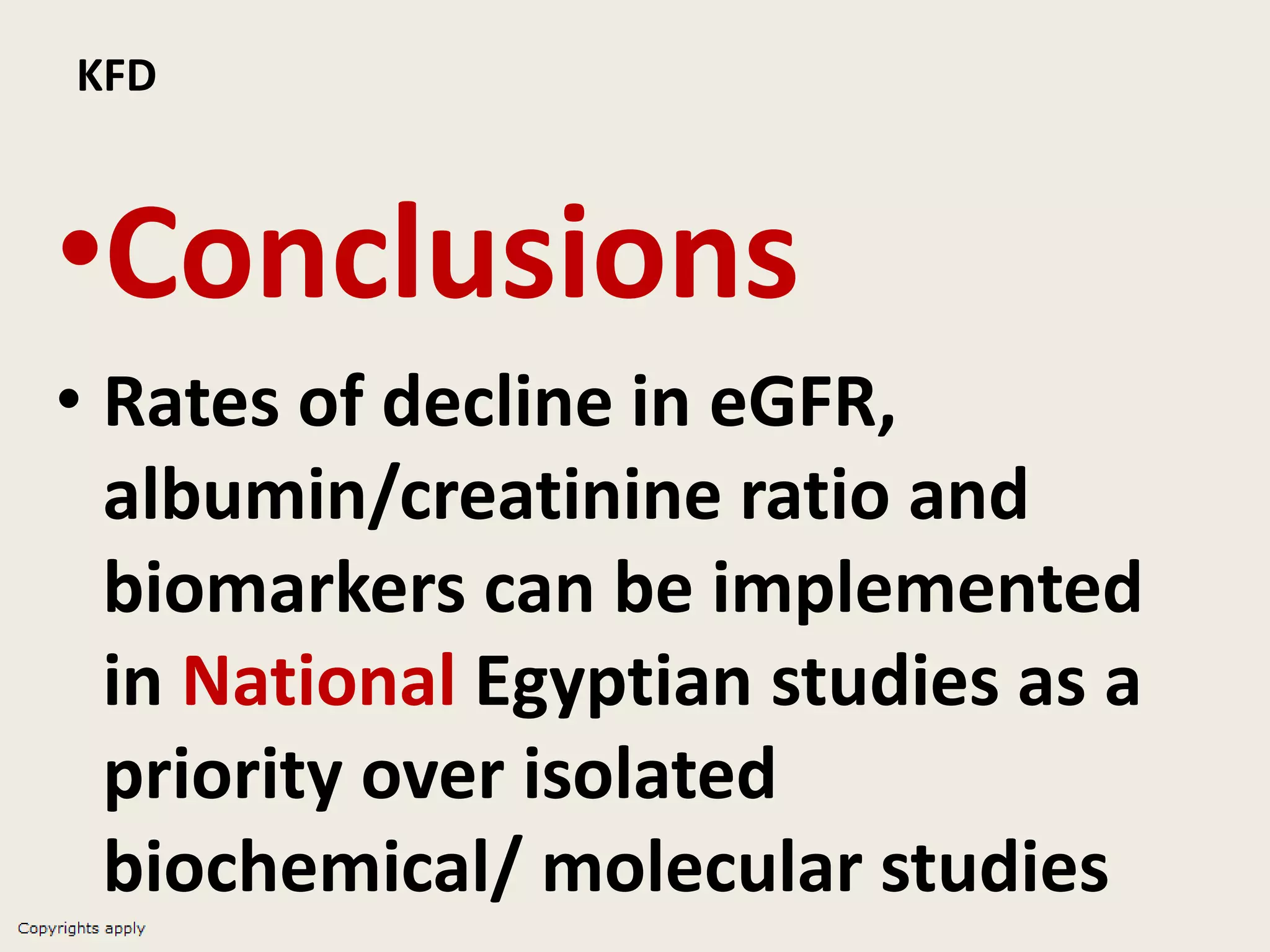
The document emphasizes the significance of the rate of kidney function decline (KFD) as a predictive measure for chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) while discussing various factors influencing CKD in Egypt. It highlights recommendations from the 2016 ISN Global Kidney Health Summit regarding monitoring CKD prevalence, potential therapeutic targets, and the importance of early intervention. The analysis includes the variable decline rates in eGFR among different CKD stages and the need for standardized outcome measures in clinical studies.