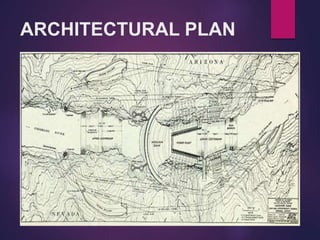
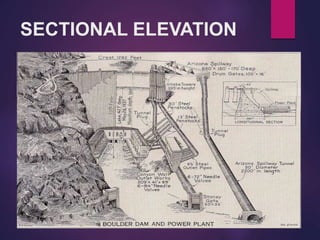
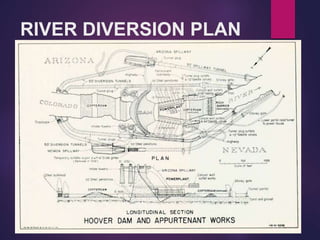
A dam is a barrier that impounds water and creates reservoirs. Dams suppress floods and provide water for uses like irrigation, power, and navigation. The Hoover Dam is a concrete arch-gravity dam on the Colorado River between Nevada and Arizona. It was constructed between 1931-1936 to control floods and generate hydroelectric power. Over 4 million cubic yards of concrete were used to build the dam, which stands 726 feet tall and created Lake Mead. The dam continues to provide flood control and power to millions in the Southwest United States.