This document summarizes topics that will be covered by a group of EXTC students in 2022-2023 for their Random Signals Analysis course. The topics include: ergodicity, Markov chains, and statistical learning and its applications. Ergodicity concepts such as mean ergodic processes and correlation ergodic processes will be discussed. Markov chains will be defined and different classifications will be examined. Statistical learning techniques like simple and multiple regression analysis will also be explored, along with comparing correlation and regression.











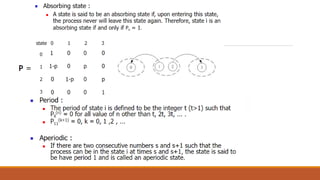
![Definition :- If, for all n,
P[ Xn = an/Xn-1 = an-1,Xn-2=an-2…..,X0=0 ]
= P [ Xn = an/Xn = an-1, then process [Xn], n = 0,1,2…. Is called a Markov Chain.
States of Markov Chain :-
(a1,a2,an,….) are called the States of The Markov Chain.
Transition Probability Matrix :-
When the system changes from ith stage to jth stage with probability Pij , the
probability is called transition probability .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/randomsignalsanalysispdf-230309054705-bbc42a66/85/RANDOM-SIGNALS-ANALYSIS-pdf-pdf-12-320.jpg)