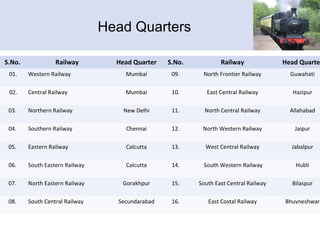
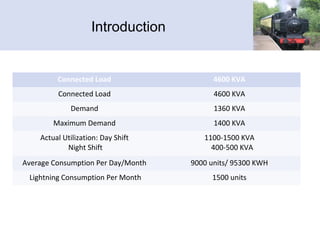
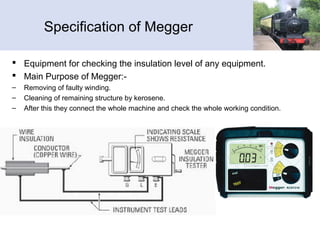
The document provides information about Pradeep Vyas's practical training at the Northern-Western Railway Workshop. It discusses the various shops within the workshop including the power shop, air conditioning shop, train lighting shop, and production and control department. It describes the key equipment and processes used in each shop's operations for maintaining railway equipment. The workshop provides basic training to engineering graduates and technicians to develop their skills.