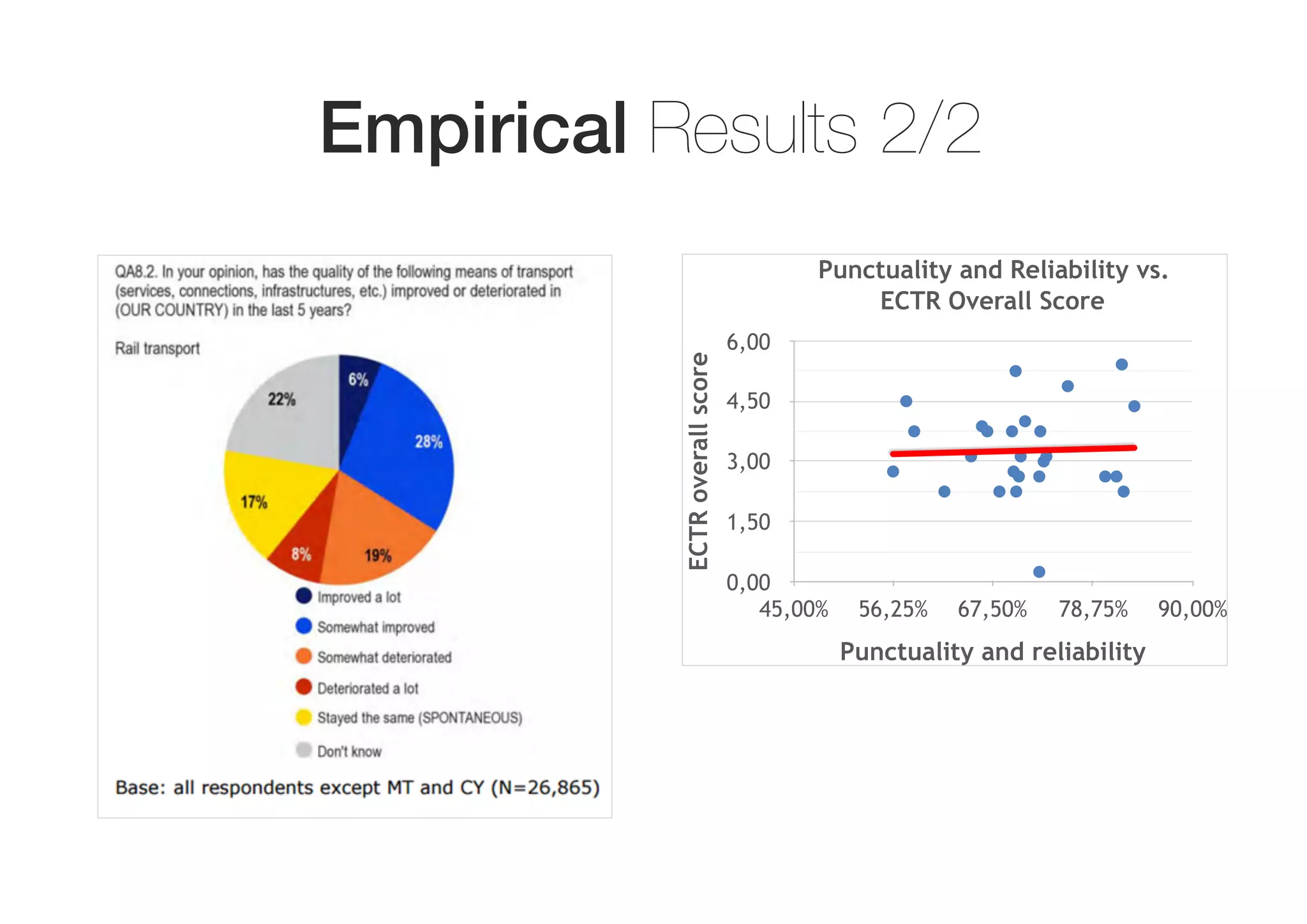
The document summarizes the current state of the rail sector in Europe. It discusses the EU's regulatory actions to liberalize and reform rail through measures like unbundling infrastructure from services and creating a single market. Implementation has varied by country, with some maintaining state control over ownership, network management and operations. Empirical analysis found a negative correlation between passenger rail prices and levels of regulation and privatization. However, regulation was not correlated with perceptions of service quality, which still varied across countries. State-owned enterprises continue to play an important role in rail.