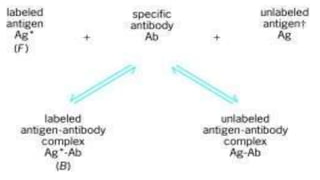
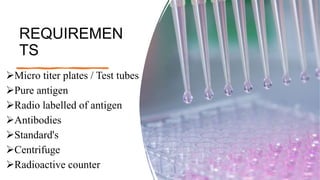
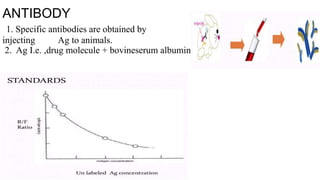
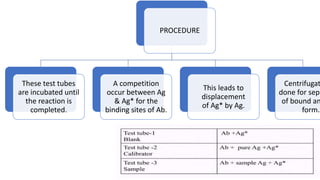
Radioimmunoassay is an immunological technique used to detect antigens in biological samples. It involves competitive binding between unlabeled antigen and radiolabeled antigen to antibodies. The sensitivity ranges from 0.0006-0.006 ug/ml, making it more sensitive than other immunoassays. It requires a pure antigen, radiolabeled antigen, antibodies, standards, and equipment like centrifuges and radioactive counters. The procedure involves incubating the antigen, radiolabeled antigen and antibody, then centrifuging to separate bound from unbound fractions. It is used to detect hormones, vitamins, drugs, and pathogens in plasma and has the advantages of being highly specific and an indirect analysis method.