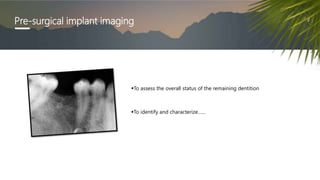
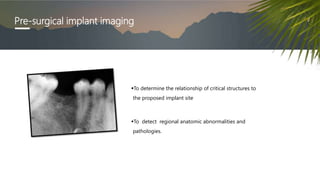
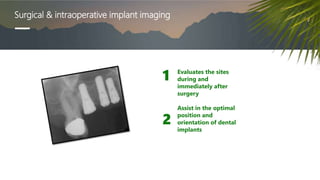
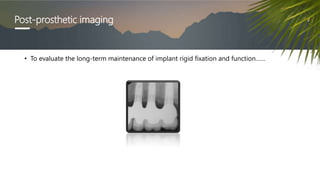
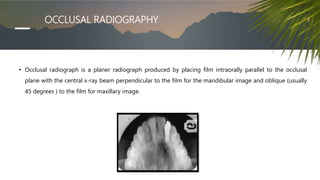
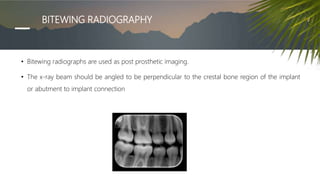
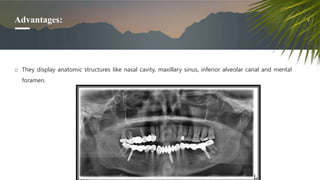
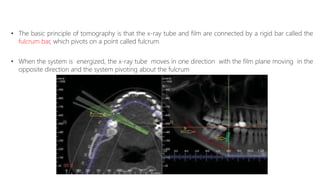
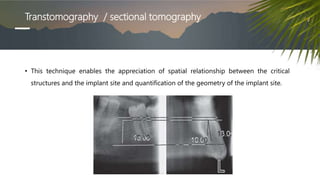
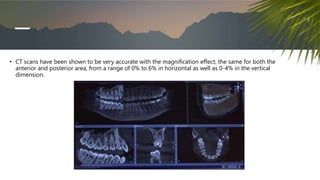
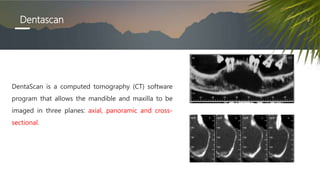
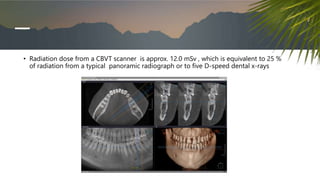
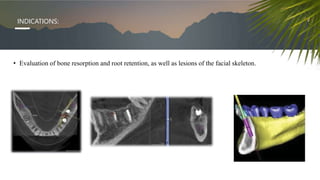
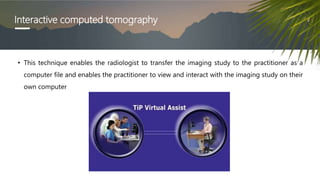
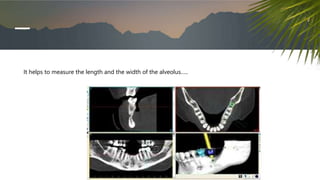
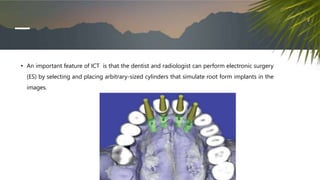
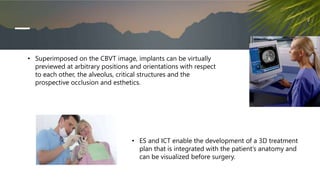
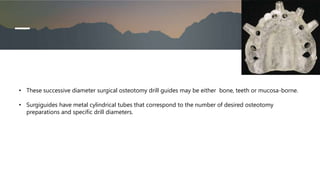
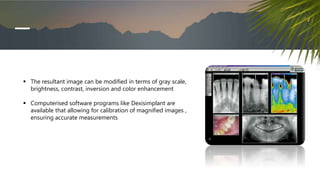
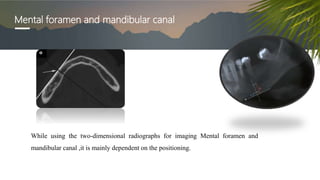
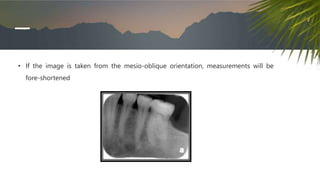
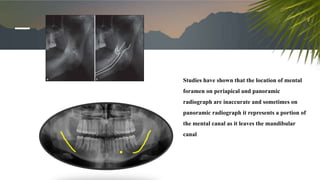
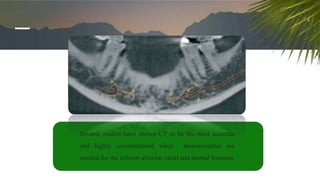
This document discusses various radiographic techniques used in dental implant planning and assessment. It describes the key phases of implant imaging as pre-surgical, surgical/intraoperative, and post-prosthetic. Various 2D and 3D imaging modalities are discussed, including periapical radiography, panoramic radiography, tomography, computed tomography, cone beam computed tomography, and interactive CT. The advantages and disadvantages of each technique are provided. Critical anatomic structures that require careful imaging for implant planning are also outlined.