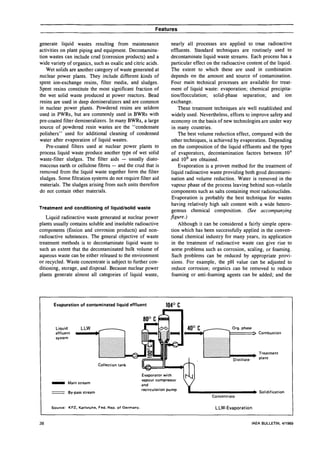
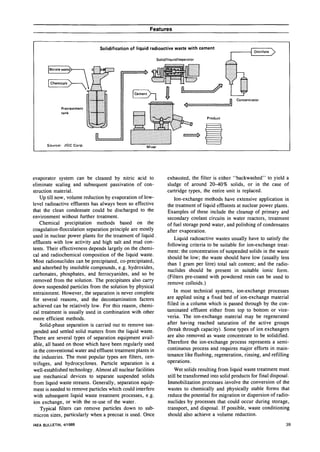
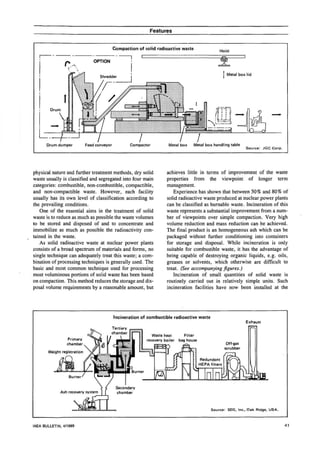
Radioactive waste is produced at nuclear power plants from contamination during operation and maintenance. Liquid waste is treated through evaporation, precipitation, filtration, and ion exchange to reduce volume and radioactivity before release or storage. Wet solid wastes from treatment are solidified through cementation, bitumenization, or polymerization. Gaseous wastes are filtered and held for decay before controlled release. Proper treatment and handling of wastes is important for safety and minimizing environmental impact.