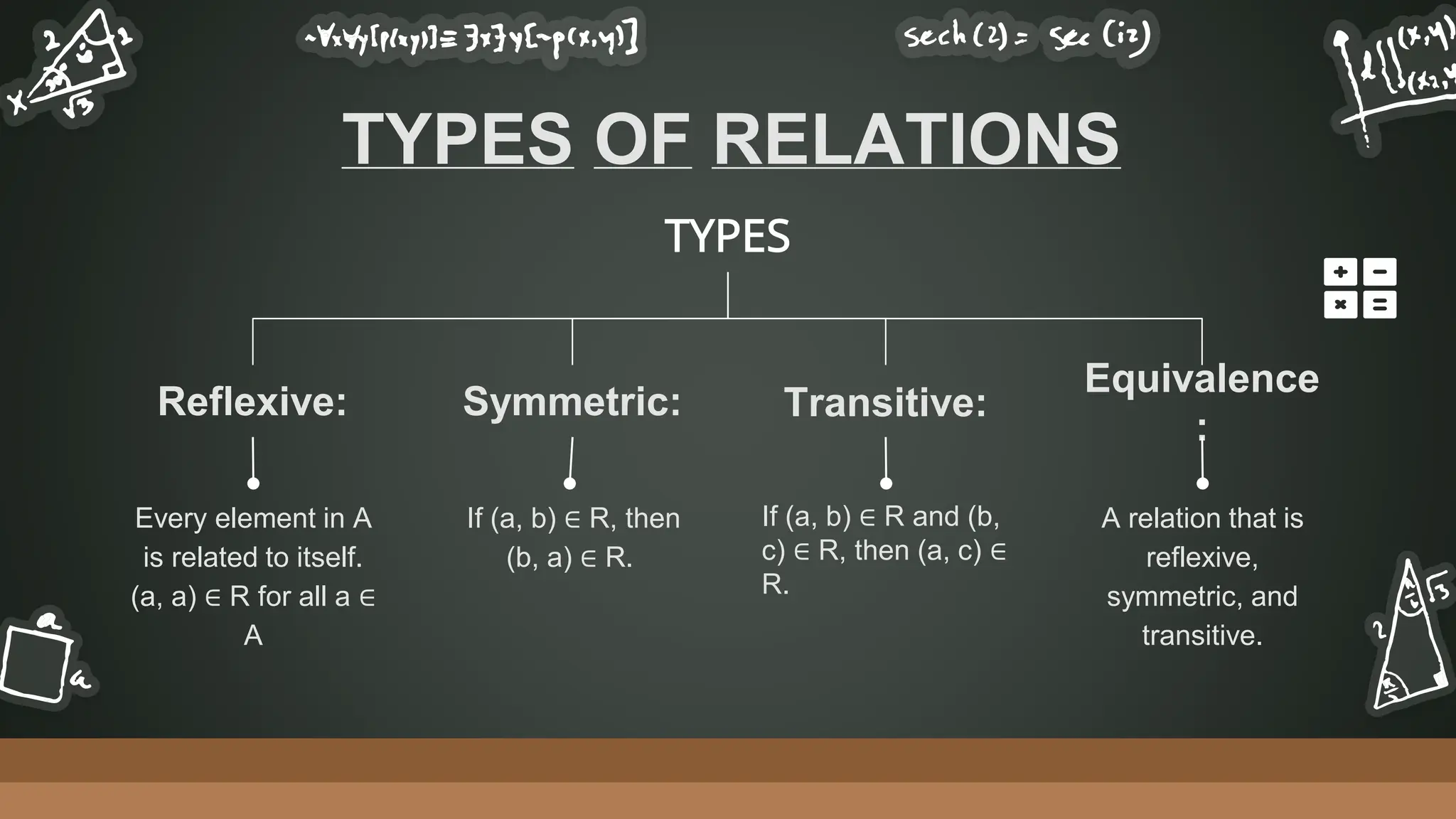
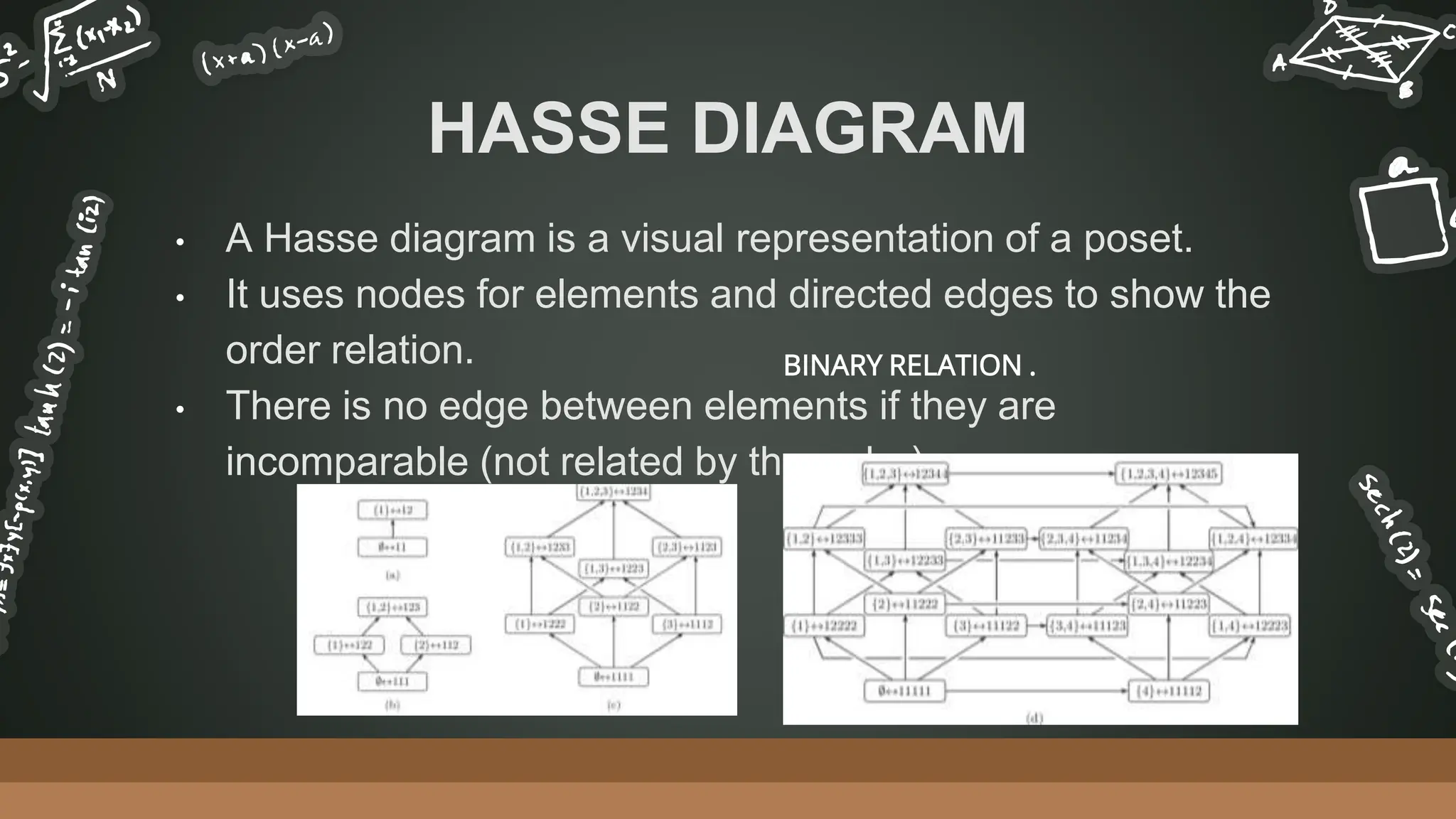
This document defines and explains different types of relations. It begins by defining a binary relation as a subset of the Cartesian product of two sets that specifies which ordered pairs are related. It then discusses various types of relations like reflexive, symmetric, transitive, and equivalence relations. The document also covers inverse relations, composite relations, equivalence classes, partitions of sets, partial order relations, partially ordered sets, and Hasse diagrams.