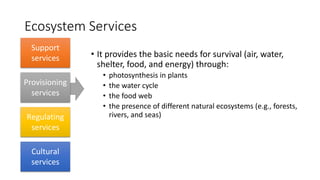
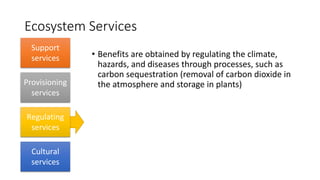
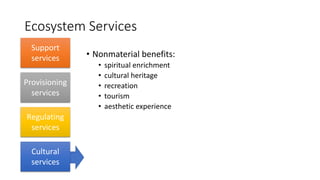
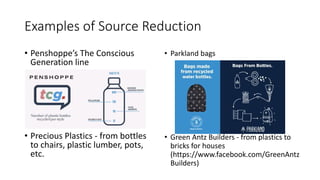
The document discusses human activities and their impact on the environment. It defines ecosystems and ecosystem services which include provisioning services that provide food, water and shelter; regulating services that influence climate and water cycles; and cultural services that provide spiritual and recreational benefits. It also defines different types of solid waste generated from municipal, agricultural, industrial and mining activities and various methods used for waste disposal like landfilling, incineration, composting, recycling and source reduction.