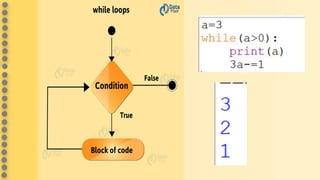
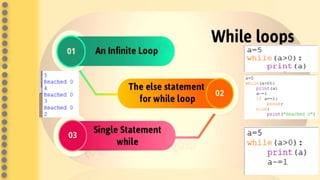
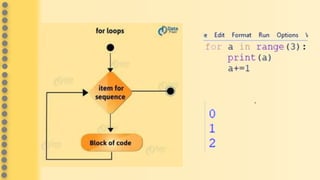
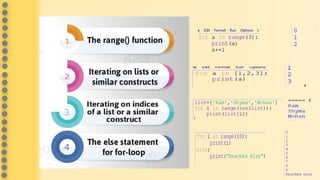
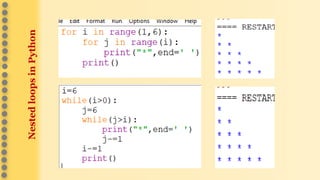
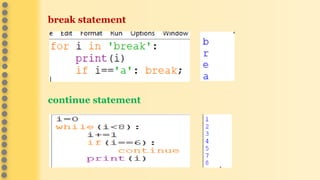
This document provides an overview of computer science concepts in Python including tokens, keywords, identifiers, data types, operators, statements, and control flow. It defines tokens like keywords and identifiers. It lists Python's main data types like integers, floats, strings, lists, tuples, dictionaries, and sets. It describes different types of operators like arithmetic, relational, assignment, logical, and bitwise operators. It also covers statements, blocks of code, and control flow structures like if/else conditionals, loops, break and continue statements.














![Punctuators
Punctuators are symbols (‘ “ () [ ] { } @ , : ‘ =) that are
used in programming language to organize sentence
structure and indicate the rhythm and emphasis of
expressions, statements and program structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonrevisiontour-ii-210816033107/85/Python-revision-tour-I-20-320.jpg)





![02
04
01
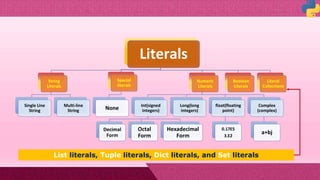
NUMBERS
a. Integers
a. Integers
b. Boolean
b. Floating Point Numbers
c. Complex Numbers
LIST
A list in Python represents a group of comma-
separated values of any data type between
square brackets []
TUPLE
Tuple is represented as a group of
comma-separated values of any data
type withing parenthesis ().
STRING
All strings in Python 3.0 are sequence of pure
Unicode. Unicode is a System designed to
represent every character from every
language. String can hold any type of known
character
Data Types
DICTIONARY
Dictionary is an unordered set of
comma separated key:value pairs,
within { } . No two keys can be same.
06
SET
A Set is a mutable data type which is created
like lists { }. It can take values of different
types.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonrevisiontour-ii-210816033107/85/Python-revision-tour-I-26-320.jpg)