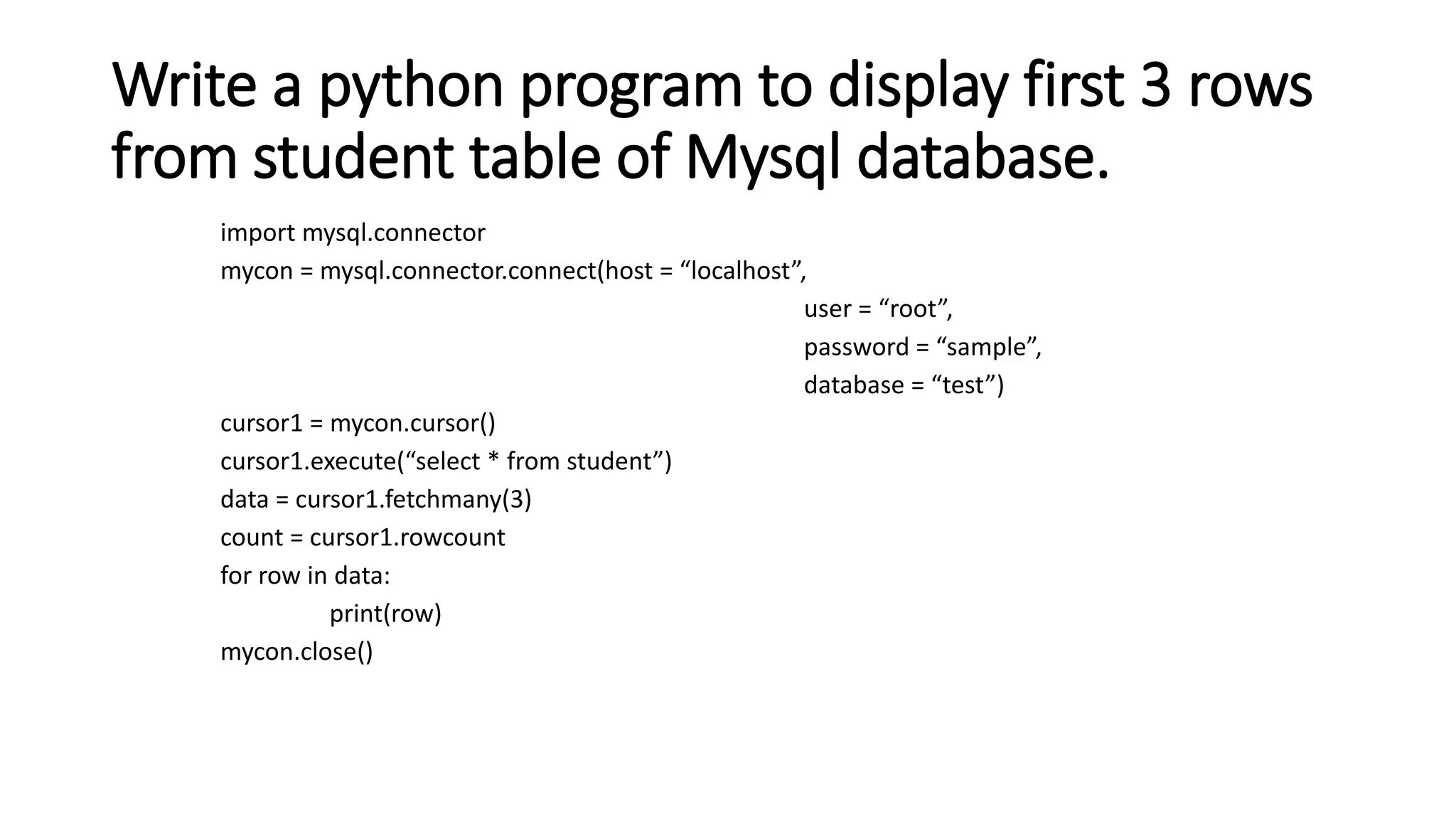
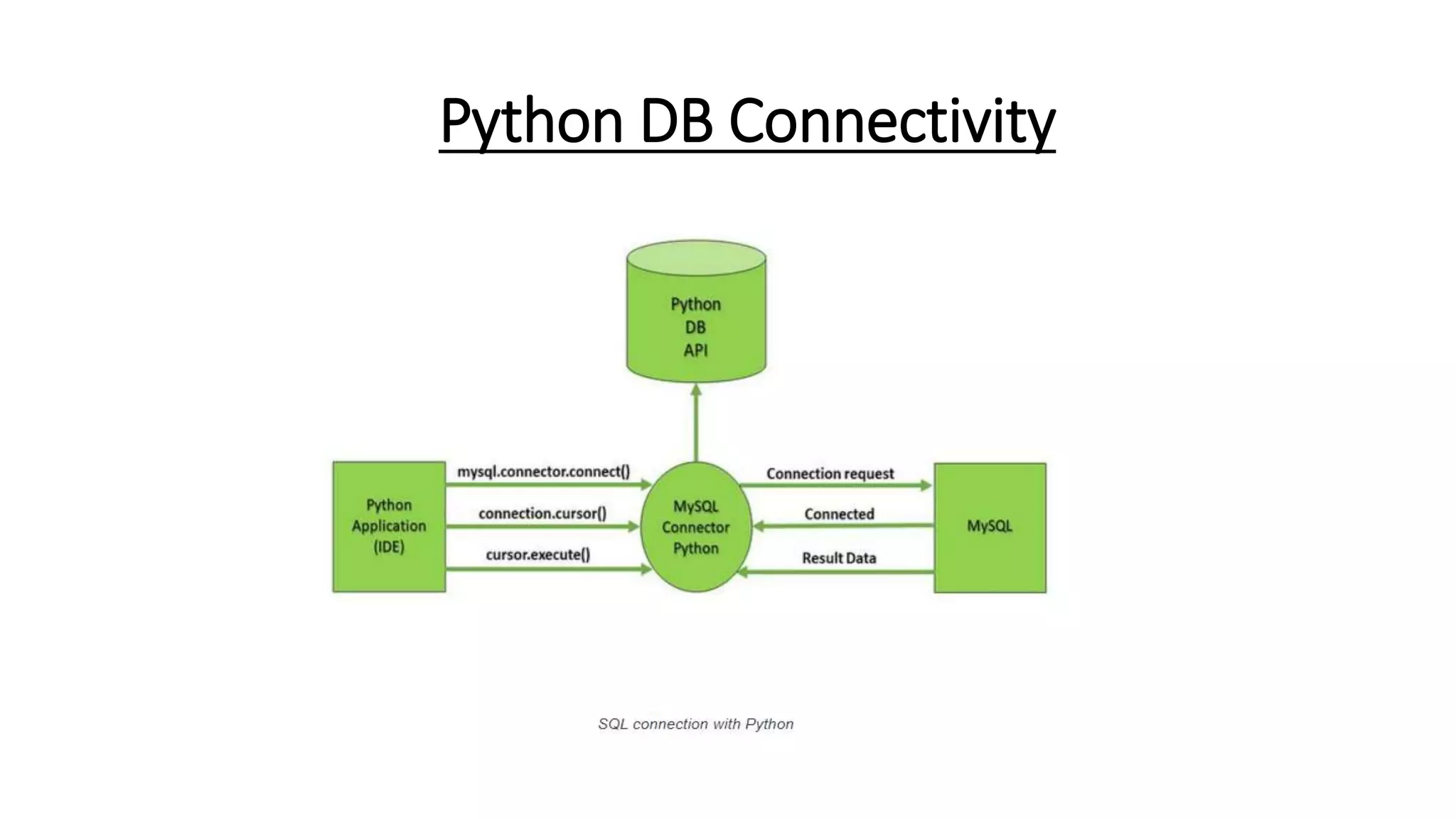
This document discusses connecting to and querying databases in Python. It outlines 7 steps to connect to a MySQL database: 1) start Python, 2) import database packages, 3) open a connection, 4) create a cursor, 5) execute queries, 6) extract data, and 7) clean up. It provides examples of connecting to MySQL and retrieving the first 3 rows from a student table.





![Step 3:Open a connection to database
syntax :connect()
Connection-Object= mysql.connector.connect(host = <host-
name> , user = <username> , passwd = <password>[,database=,
database name>] )
Example:
#Create the connection object
mycon = mysql.connector.connect(host = "localhost", user = "roo
t",passwd = "google", database = "mydb")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/python-db-221225103912-7abc76e5/75/Python-db-pptx-7-2048.jpg)