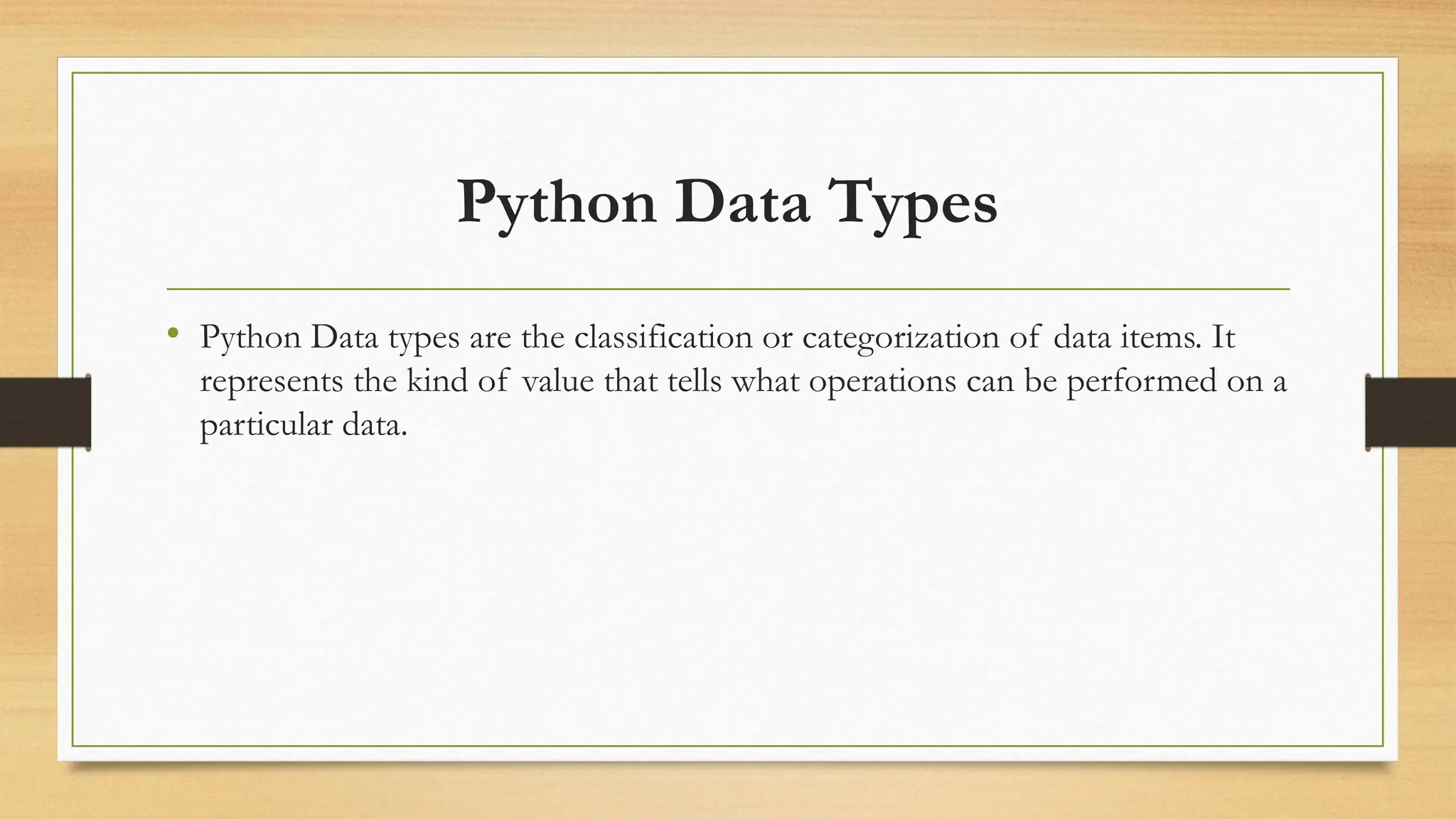
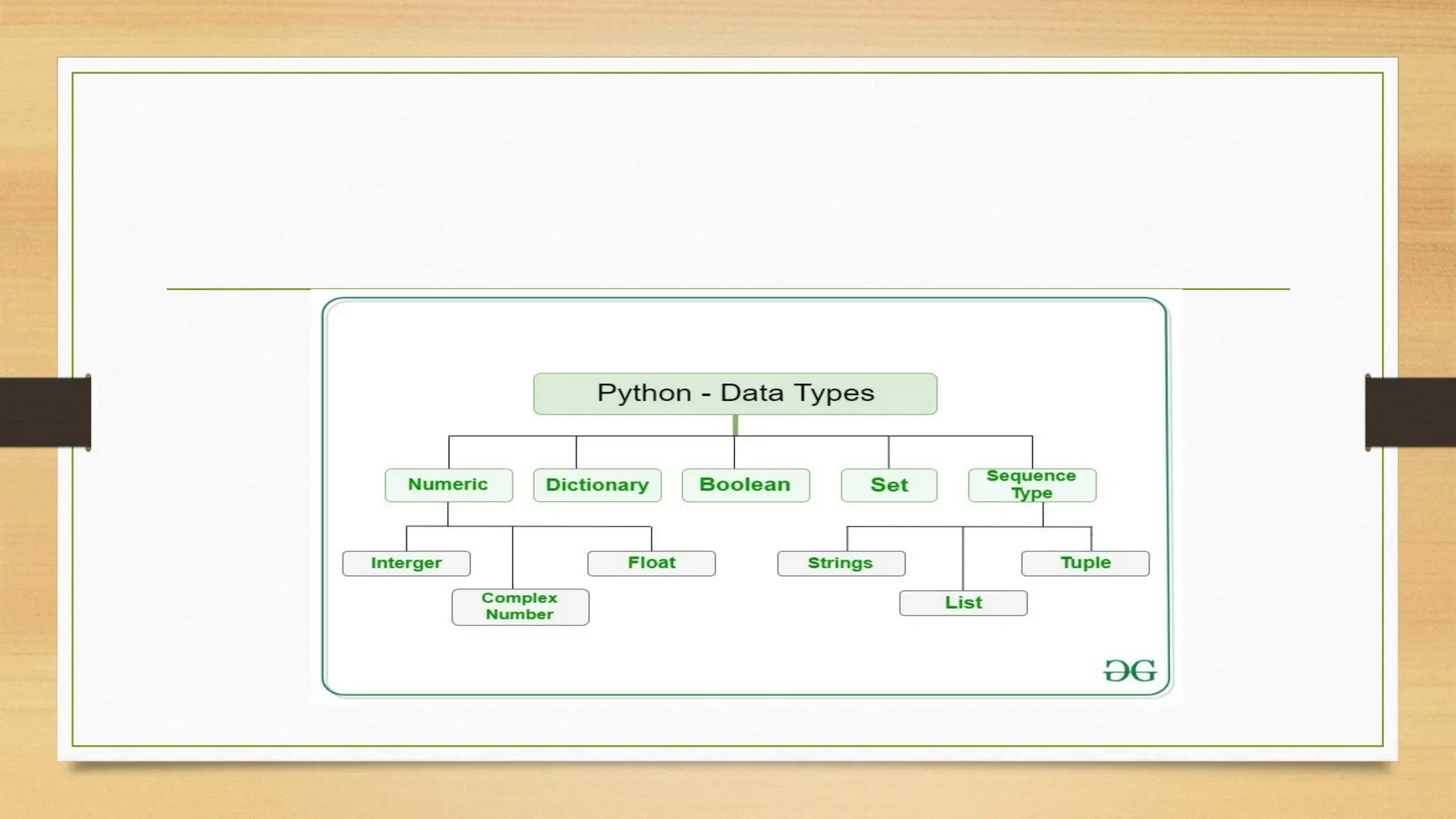
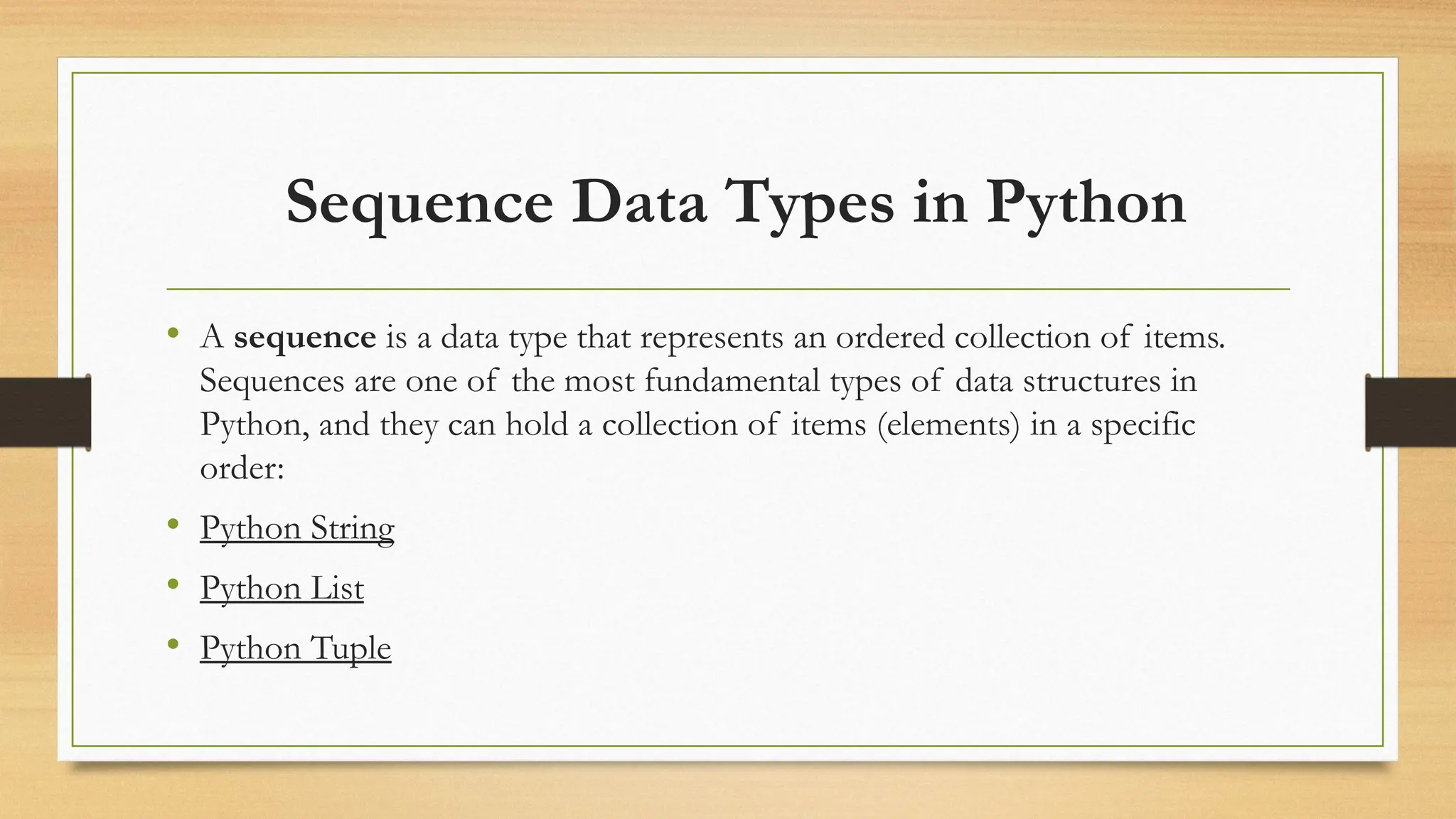
The document provides an overview of Python's features and its built-in data types, including numeric, sequence types, boolean, sets, dictionaries, and binary types. It details the definition, behavior, and examples of numeric types (integers, floats, and complex numbers) and sequence types such as strings and lists, highlighting their creation and manipulation. Additionally, it illustrates list operations including accessing, modifying, adding, and removing elements.








![• List are just like arrays, declared in other languages which is an ordered
collection of data. It is very flexible as the items in a list do not need to be of
the same type
• In Python, list is a collection data type that is ordered, mutable (changeable), and
allows duplicate elements.
• Creating a List in Python
• Lists in Python can be created by just placing the sequence inside the square
brackets[]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythondatatype-241014075036-14af8a9f/75/PYTHON-DATA-TYPE-in-python-using-v-pptx-13-2048.jpg)
![• # Creating a list of fruits
• fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "date"]
• # Accessing elements of the list
• print(fruits[0]) # Output: apple
• print(fruits[2]) # Output: cherry
• # Modifying an element in the list
• fruits[1] = "blueberry"
• print(fruits) # Output: ['apple', 'blueberry', 'cherry', 'date']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythondatatype-241014075036-14af8a9f/75/PYTHON-DATA-TYPE-in-python-using-v-pptx-14-2048.jpg)
![• # Adding elements to the list
• fruits.append("elderberry")
• print(fruits) # Output: ['apple', 'blueberry', 'cherry', 'date', 'elderberry']
• # Removing an element from the list
• fruits.remove("date")
• print(fruits) # Output: ['apple', 'blueberry', 'cherry', 'elderberry']
• # Slicing the list (extracting a portion of the list)
• sublist = fruits[1:3]
• print(sublist) # Output: ['blueberry', 'cherry']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythondatatype-241014075036-14af8a9f/75/PYTHON-DATA-TYPE-in-python-using-v-pptx-15-2048.jpg)
