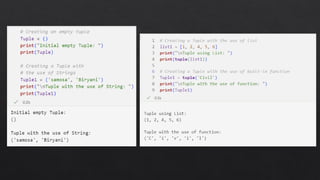
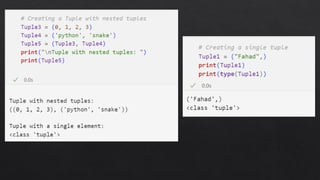
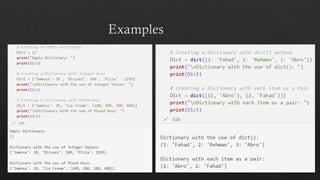
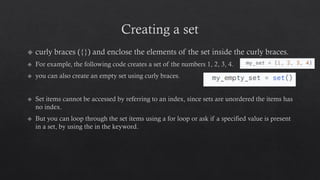
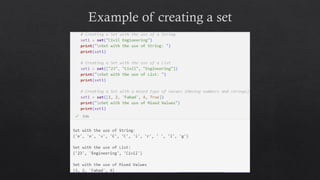
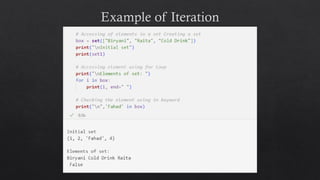
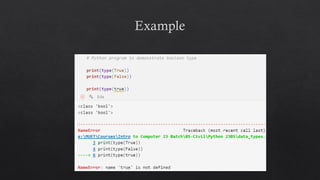
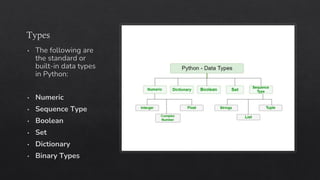
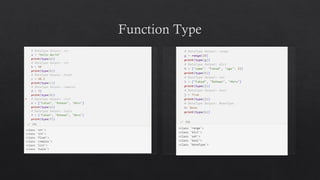
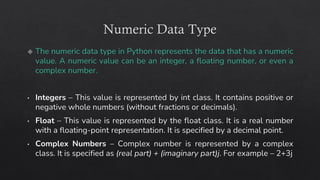
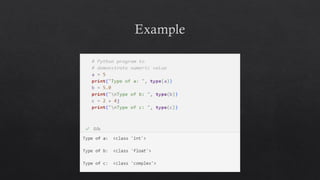
The document provides an introduction to Python data types, explaining their classification and operations. It covers numeric types (integers, floats, complex), sequence types (strings, lists, tuples), the dictionary type (key-value pairs), the set type (unordered collections), and boolean values. Examples and methods to create and manipulate these data types are also included.








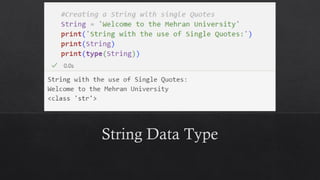
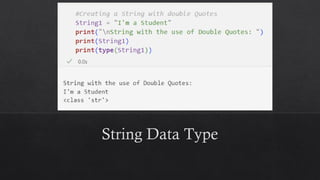
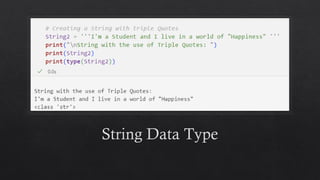
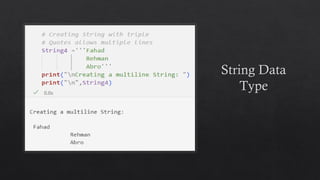
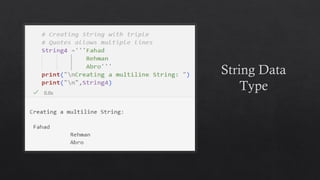

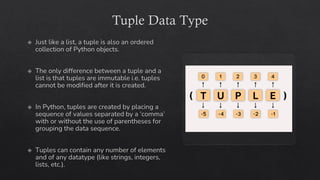
![List Data Type in Python
Mutable ordered sequence of elements. This
means that you can add, remove, and change the
elements of a list at any time.
Lists can store elements of any type, and the
elements can be different types.
To create a list in Python, you use square brackets
([]) and enclose the elements of the list inside the
square brackets.
For example, the following code creates a list of
the numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-dataanditstypes-240422153448-e7384965/85/13-Data-and-Its-Types-presentation-kafss-19-320.jpg)
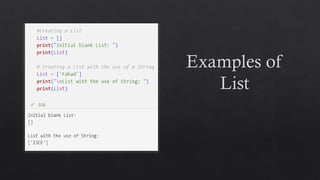
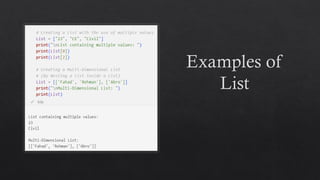
![List Data Type in Python
To access the list items, refer to the index
number.
Use the index operator [ ] to access an item in a
list.
Negative sequence indexes represent positions
from the end of the array.
Negative indexing means beginning from the
end, -1 refers to the last item, -2 refers to the
second-last item, etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/13-dataanditstypes-240422153448-e7384965/85/13-Data-and-Its-Types-presentation-kafss-22-320.jpg)