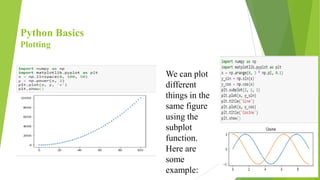
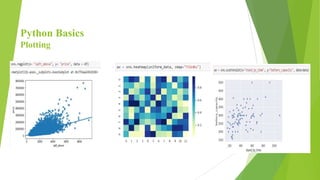
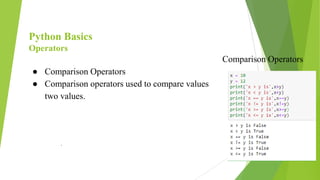
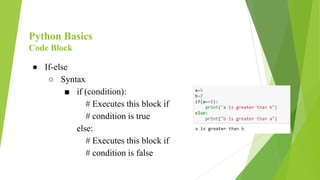
Python is a popular, high-level programming language that is used for a variety of tasks including web development, machine learning, and data science. It has a simple syntax and is readable. Python has built-in data types like integers, floats, booleans, strings, lists, tuples, and dictionaries. It also supports object-oriented programming. Common operations in Python include conditional statements, loops, functions, packages, file handling, classes, and data visualization using libraries like NumPy, Matplotlib, and Seaborn.





















![Python Basics
Functions
● Any input parameters or arguments should be placed within these
parenthesis. We can can also define parameters inside these
parentheses.
● The code block within every function starts with a colon (:) and is
indented.
● The statement return [expression] exits a function, optionally passing
back an expression to the caller. A return statement with no
arguments is the same as return None.
● We can call the function by function name followed by parenthesis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonbasics2-210214123816/85/Introduction-to-Python-programming-Language-24-320.jpg)