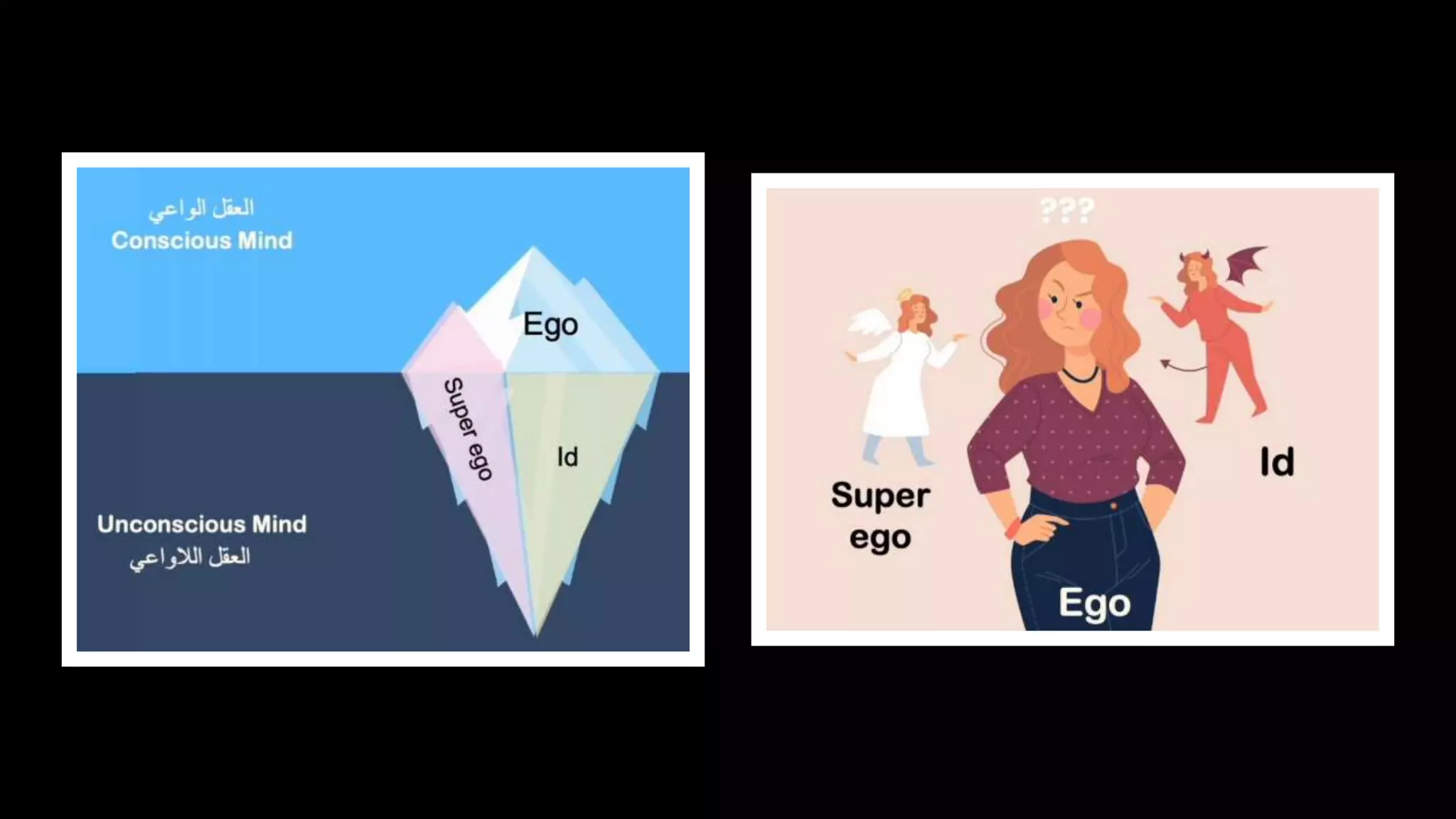
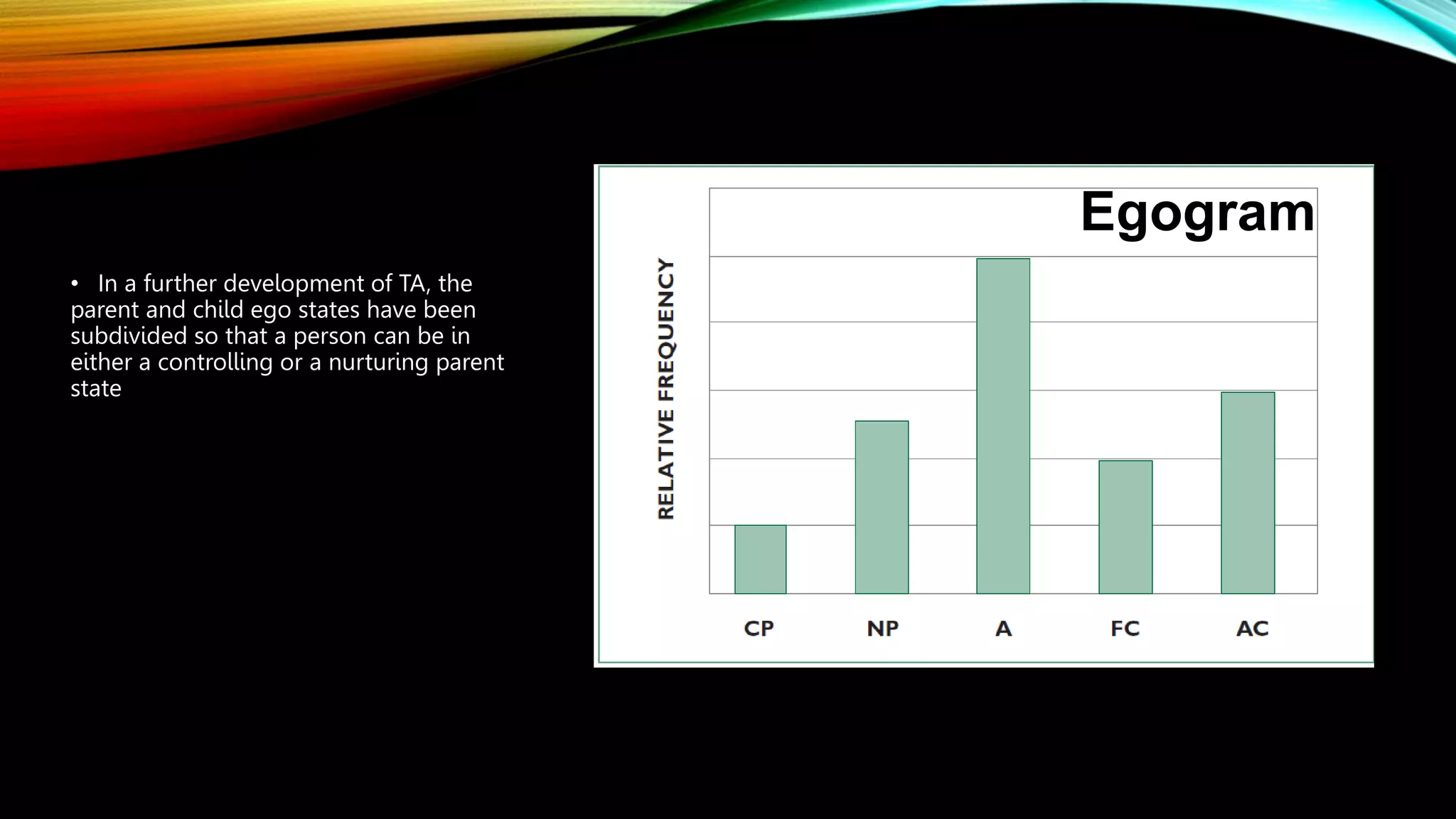
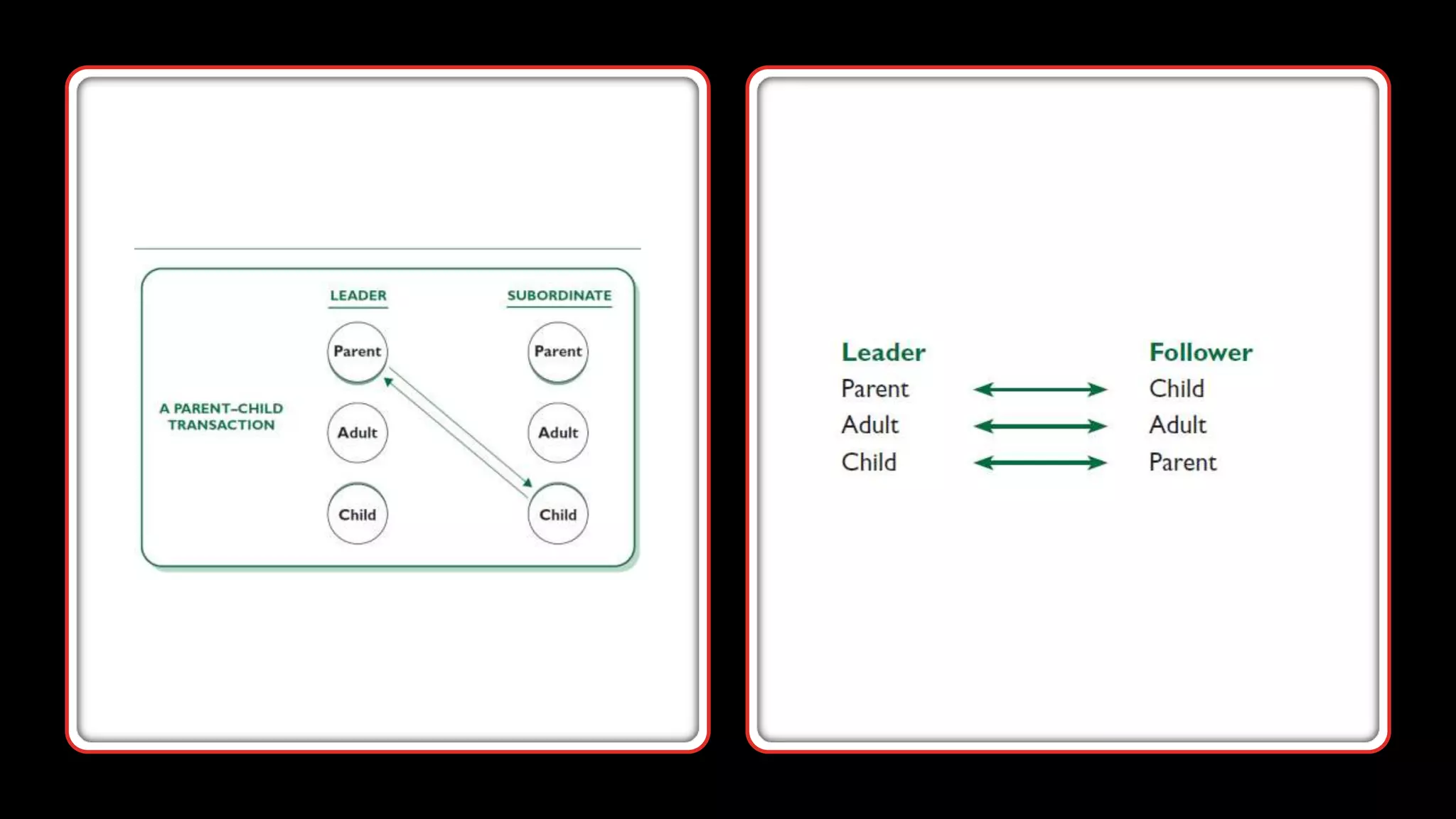
The psychodynamic approach examines leadership through the lens of personality and relationships between leaders and followers. It assumes that personality traits are deeply ingrained and behavior stems from prior experiences and the unconscious. Key aspects include Freud's theories of personality types, Jung's four dimensions of personality, and Transactional Analysis' three ego states. The approach aims to raise awareness of personality types and their implications for work relationships in order to improve communication and effectiveness. Its greatest strength is analyzing the leader-follower relationship, while its main criticism is its basis in clinical observation rather than organizational factors.