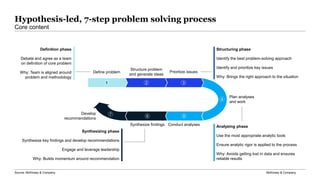
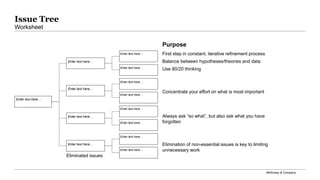
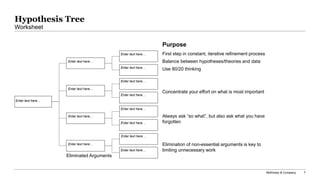
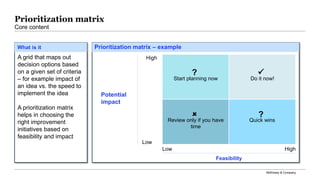
The document outlines a problem-solving toolkit developed by McKinsey & Company, which involves a structured, seven-step process for identifying and resolving business challenges. It emphasizes the importance of synthesizing findings, developing SMART problem definitions, and engaging leadership to create actionable recommendations. Additionally, it includes tools such as worksheets for problem statements, prioritization matrices, and insights into stakeholder involvement and criteria for success.