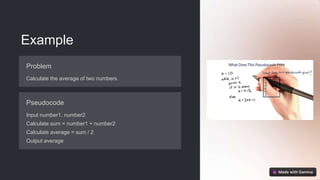
Pseudocode is a visual and readable representation of code that aids in understanding program logic. It facilitates communication among developers, helps with planning, debugging, and learning coding concepts. By breaking down problems into clear steps using plain language, pseudocode enhances efficiency, clarity, and flexibility in programming.





![Examples Across Languages
Language Example
Python num1 = input("Enter first number: ")
num2 = input("Enter second number: ")
sum = float(num1) + float(num2)
average = sum / 2
print("The average is:", average)
JavaScript let num1 = prompt("Enter first number: ");
let num2 = prompt("Enter second number:
");
let sum = parseFloat(num1) +
parseFloat(num2);
let average = sum / 2;
alert("The average is: " + average);
Java import java.util.Scanner;
public class AverageCalculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter first number: ");
double num1 = input.nextDouble();
System.out.print("Enter second number: ");
double num2 = input.nextDouble();
double sum = num1 + num2;
double average = sum / 2;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pseudocode-a-visual-guide-240729063936-e48a6de5/85/Pseudocode-A-Visual-Guide-for-new-learners-7-320.jpg)
