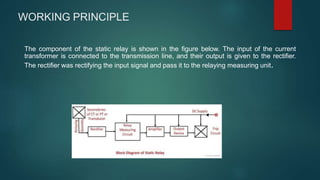
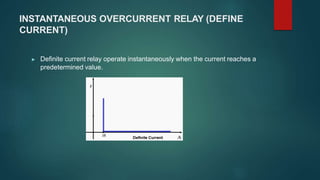
This document provides an introduction to static relays used in microprocessor-based protective relay systems. It discusses how static relays use solid-state components like transistors and diodes rather than moving parts to create the relay characteristic. The working principle is described where the current transformer input is rectified and compared to a threshold value, with the output actuating an electromagnetic trip coil if the threshold is reached. Advantages of static relays include less power consumption, quick response time, high reliability and accuracy. Limitations include sensitivity to electrostatic discharge and voltage transients. Static relays are applied in high-speed protection of EHV transmission lines and overcurrent and earth fault protection schemes.