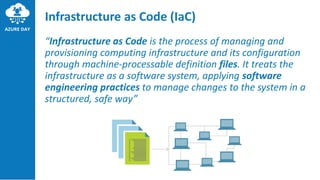
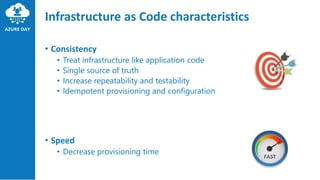
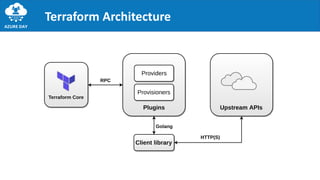
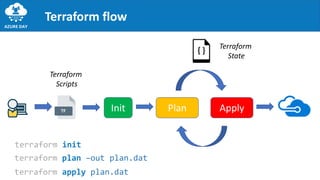
The document discusses provisioning on Azure using Terraform and Azure DevOps, highlighting key concepts like Infrastructure as Code (IaC), Terraform architecture, and workflows. It covers the benefits and characteristics of IaC, the core ideas of Terraform, and various features such as providers, resources, and modules. Additionally, it provides tips and best practices for using Terraform effectively, including version control and testing frameworks.









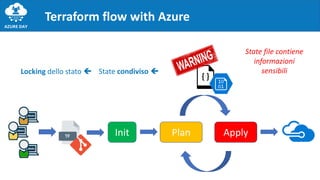




![✓ Use a VCS
✓ Use remote state and access policy
❑ e. g. use a single build server
✓ Avoid user credentials in Terraform code
✓ Naming convention
❑ e. g. "${var.shortname}-{var.env}"
✓ Use VSCode with following extensions:
❑ Terraform [mauve.terraform] by Mikael Olenfalk
❑ Terraform doc snippet [run-at-scale.terraform-doc-
snippets] by Brandon O'Connor
Terraform tips and tricks](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slideazuredayreloaded20191129terraform-191206095105/85/Provisioning-with-Terraform-AzureDay-Reloaded-25-320.jpg)



