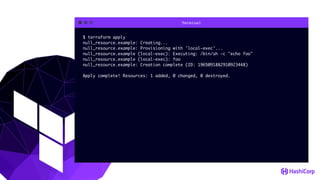
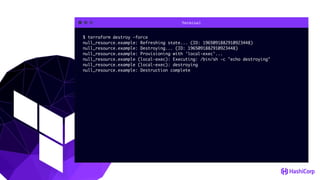
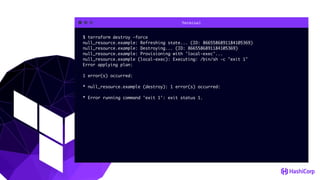
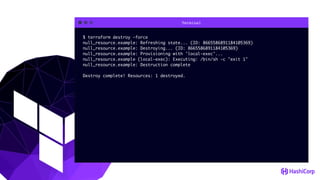
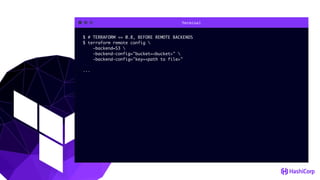
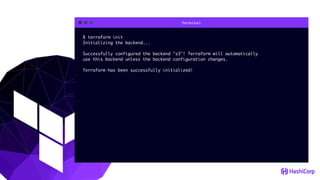
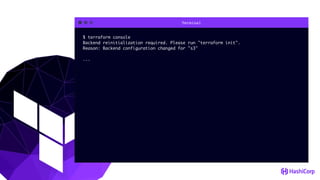
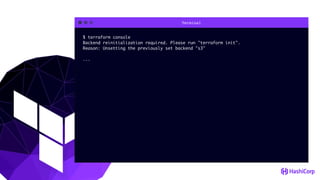
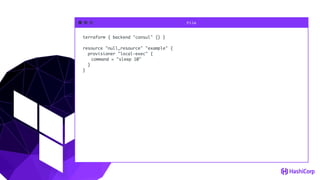
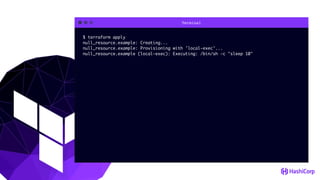
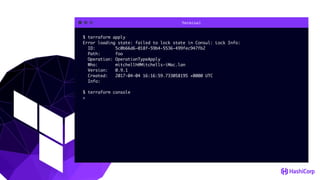
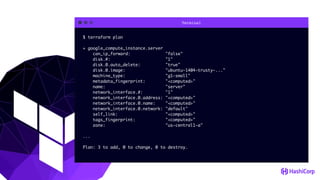
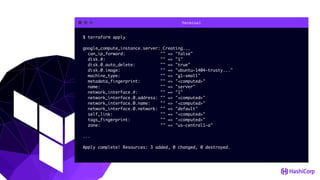
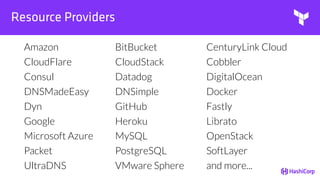
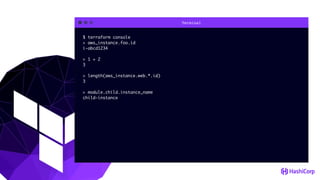
This document provides an overview of Terraform, an open-source infrastructure as code tool. It discusses Terraform's goals of providing a unified view of infrastructure, composing multiple tiers of infrastructure from IaaS to PaaS to SaaS, and safely changing infrastructure over time with one workflow. Key features highlighted include being open source, using infrastructure as code, resource providers that interface with cloud APIs, and the plan and apply workflow. The document also covers topics like collaboration and version history in Terraform Enterprise, file examples, the plan and apply commands, resource providers, and new features in recent Terraform versions like destroy provisioners, remote backends, state locking, and state environments.






![Terraform Features
• Open Source
• Infrastructure as Code
• Resource Providers
• Plan and Apply
• Collaboration, History [Enterprise]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terraform-hug2017-170412150237/85/London-HUG-12-4-7-320.jpg)
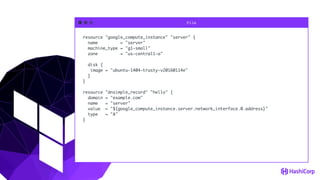














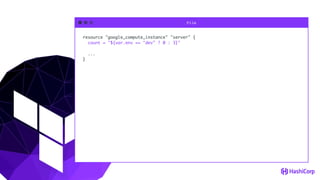








![File
data "vault_generic_secret" "rundeck_auth" {
path = "secret/rundeck_auth"
}
provider "rundeck" {
url = "http://rundeck.example.com/"
auth_token = "${data.vault_generic_secret.rundeck_auth.data["auth_token"]}"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/terraform-hug2017-170412150237/85/London-HUG-12-4-40-320.jpg)