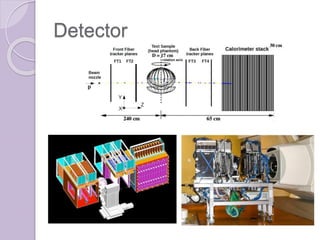
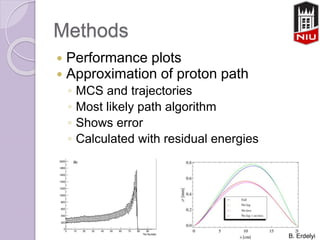
Proton computed tomography (pCT) is a new imaging technique that uses protons instead of photons to create images with improved accuracy over standard x-ray CT. pCT reduces radiation dose and range errors compared to x-ray CT, which is especially important for imaging near vital organs. The presented detector for pCT was built through collaboration and tracks proton trajectories using a fiber tracker and calculates residual energy using a scintillator stack to estimate proton path lengths and densities for improved treatment planning and delivery of proton therapy. Testing of the detector is ongoing to quantify the benefits of pCT compared to standard x-ray CT.