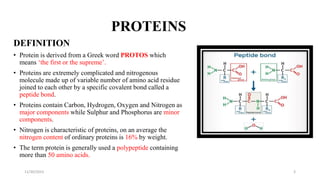
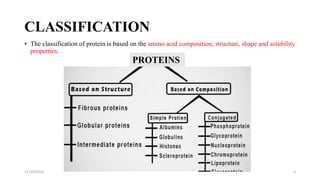
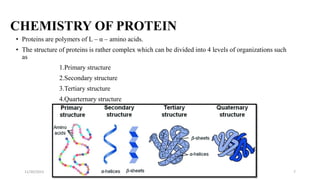
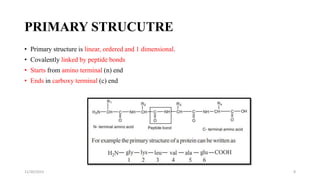
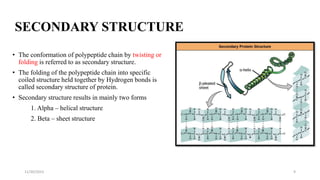
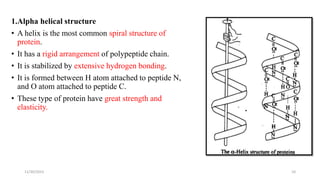
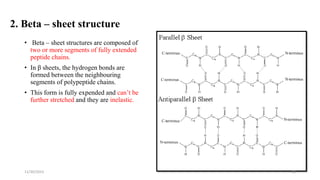
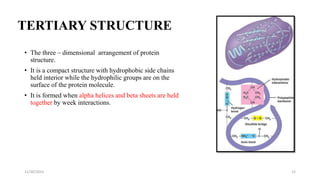
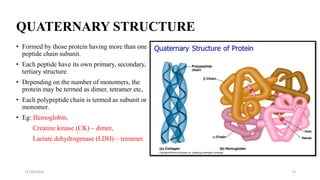
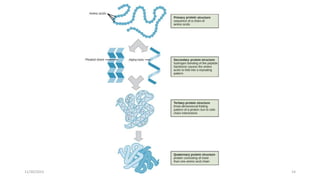
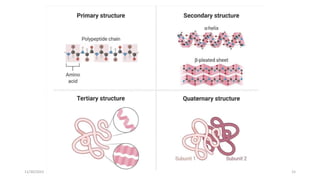
Proteins are polymers of amino acids and can be classified based on their structure, shape and solubility. They have four levels of organization - primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure. The primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Secondary structure involves folding into alpha helices or beta sheets held by hydrogen bonds. Tertiary structure is the compact 3D structure formed by interactions between secondary structures. Quaternary structure refers to proteins with more than one polypeptide chain subunit.