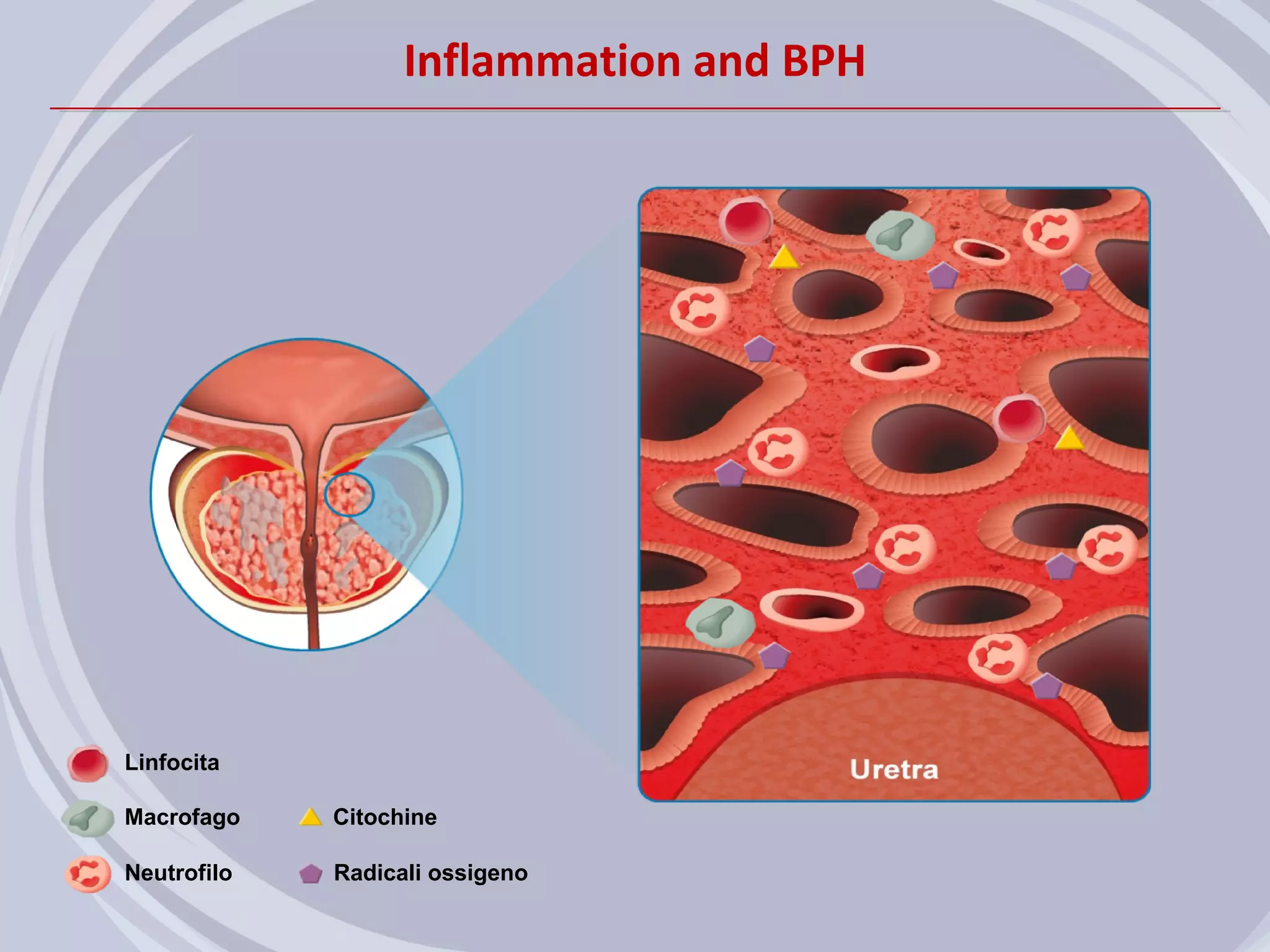
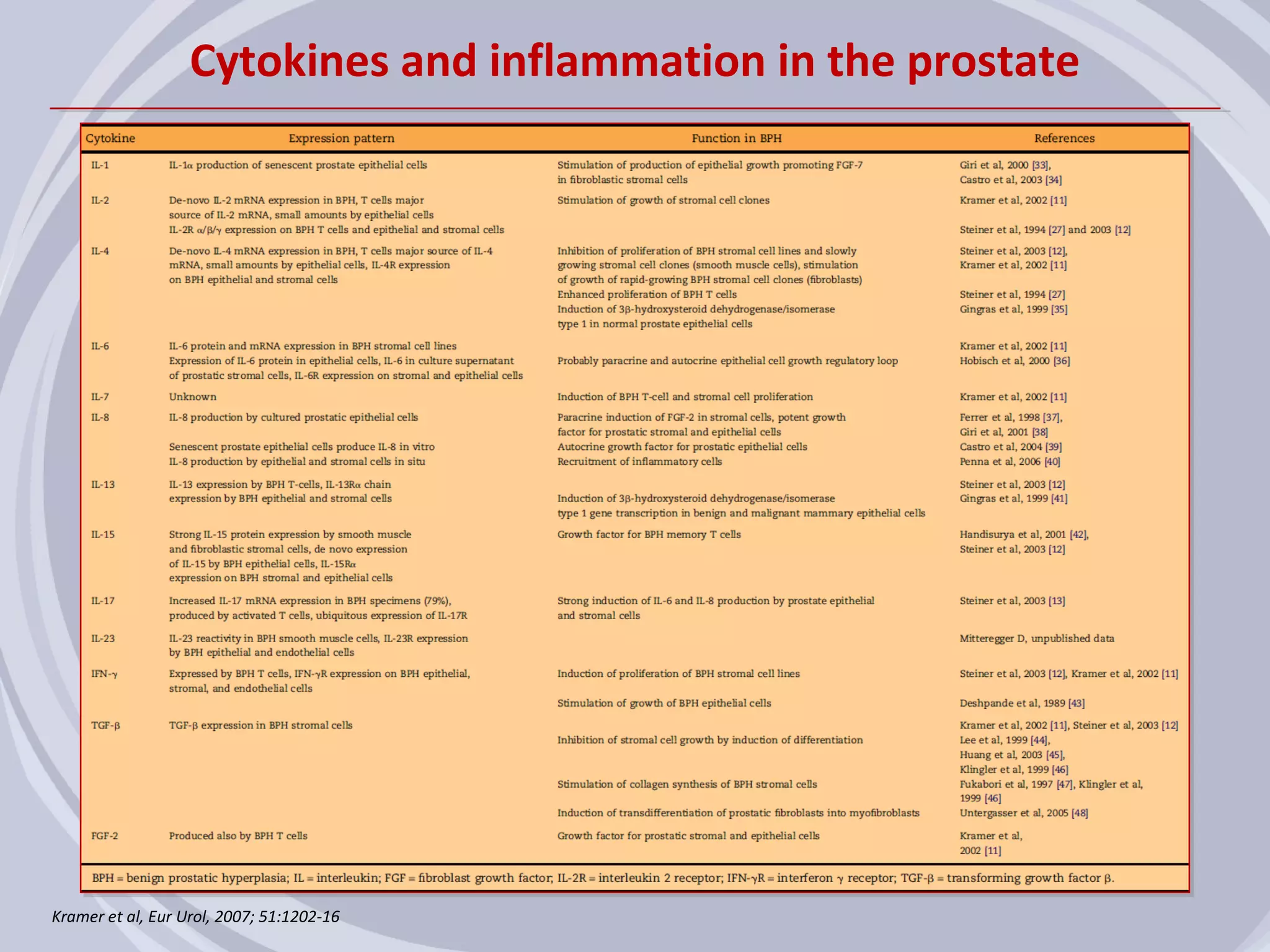
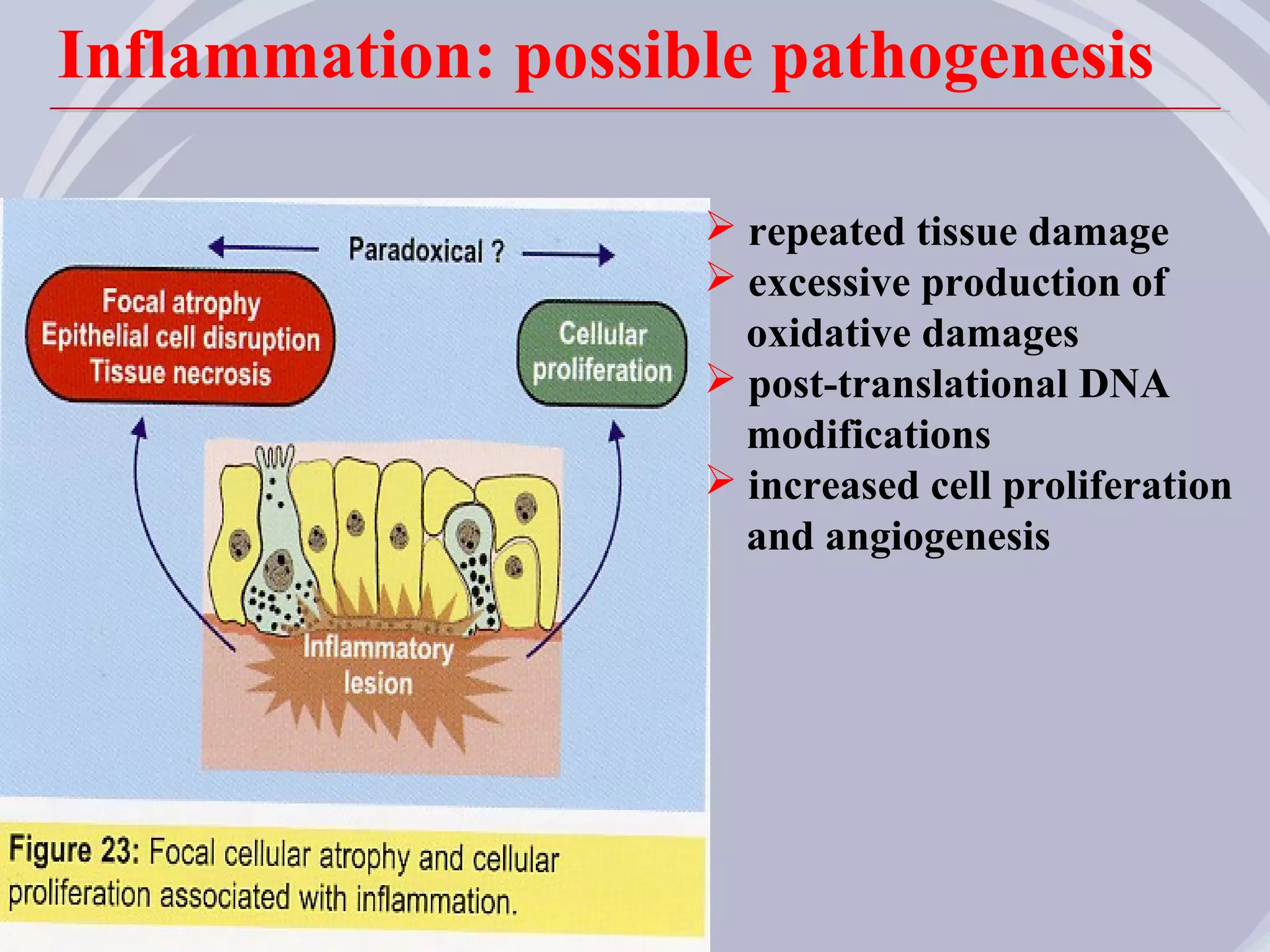
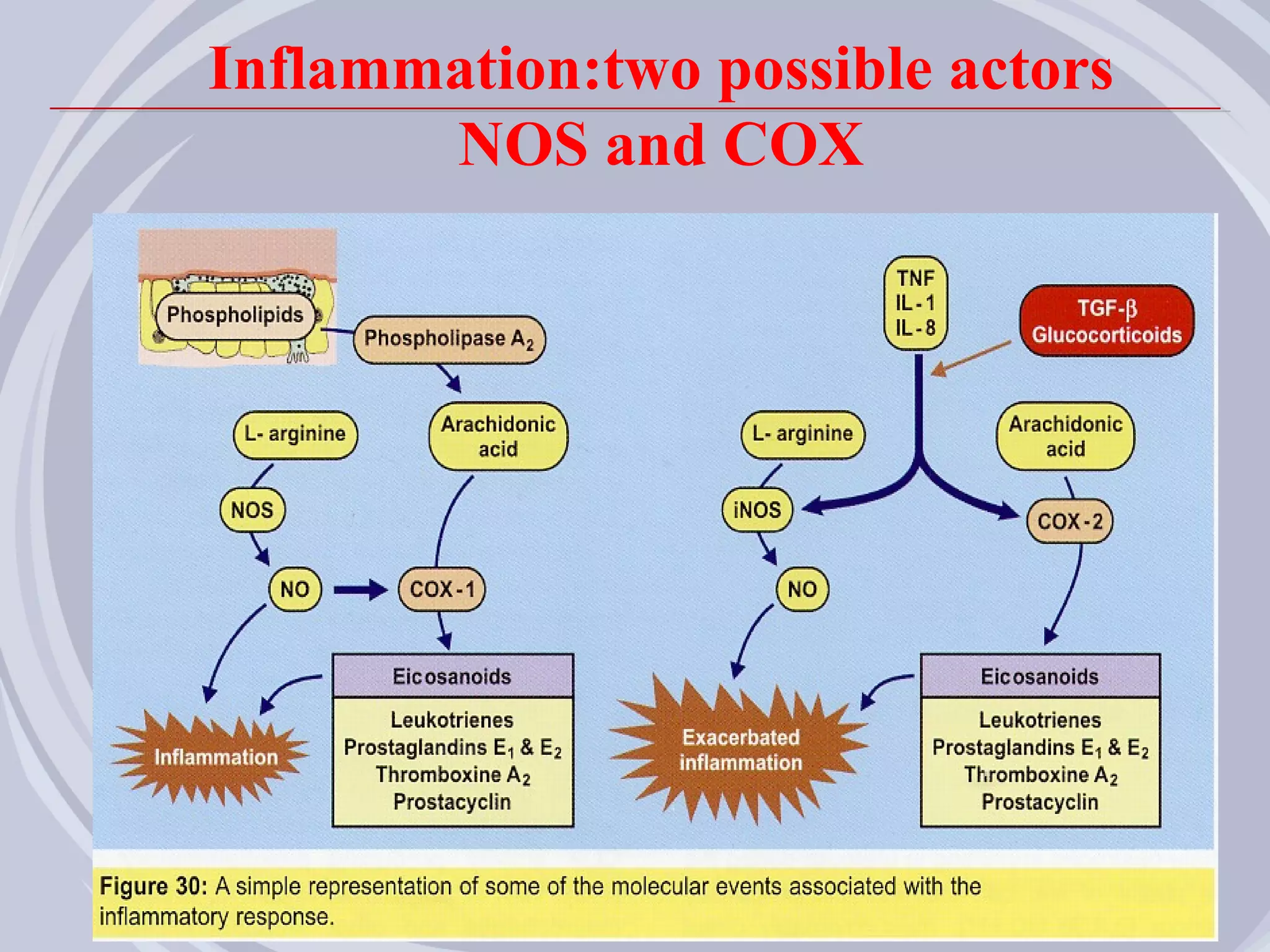
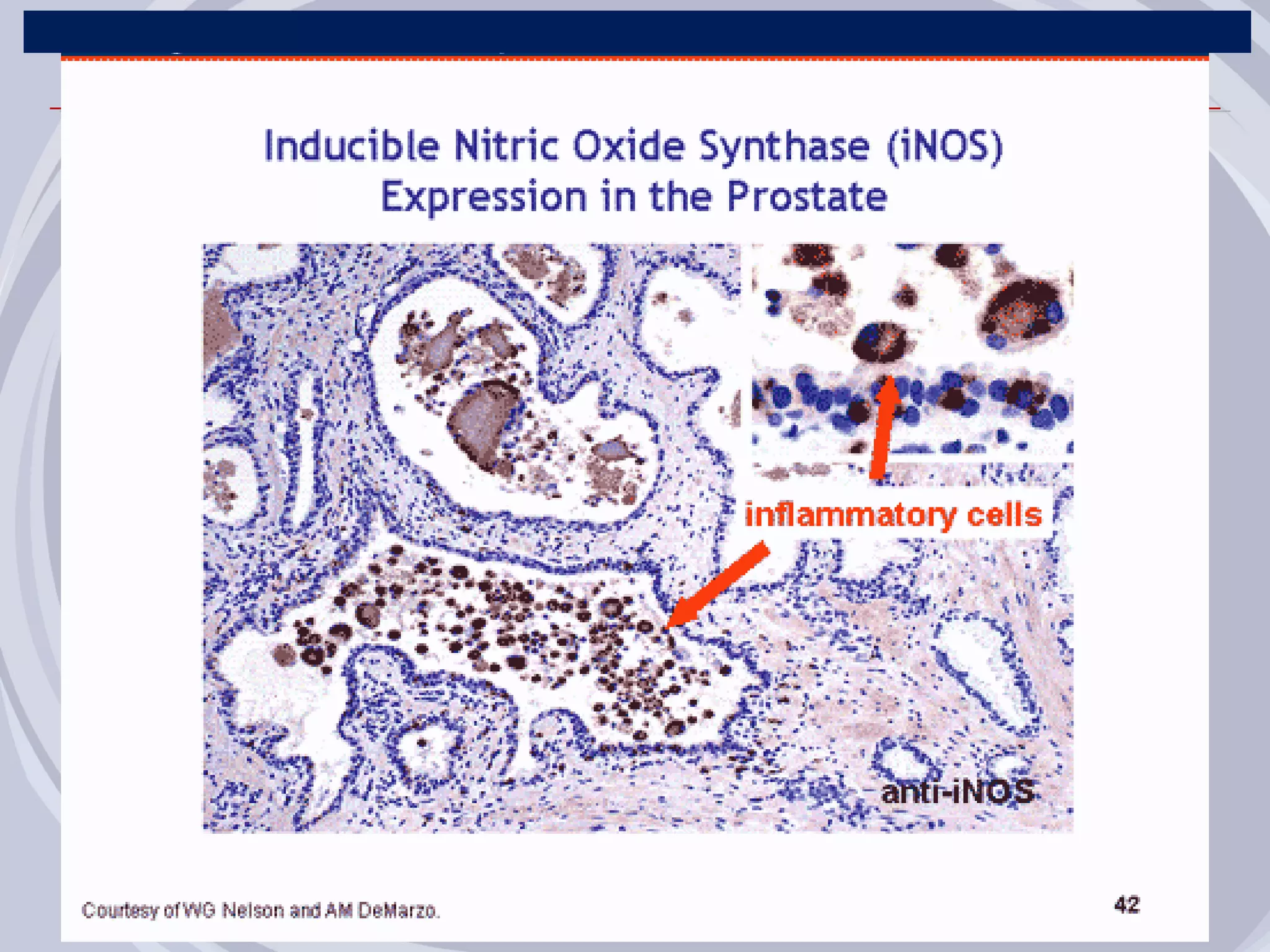
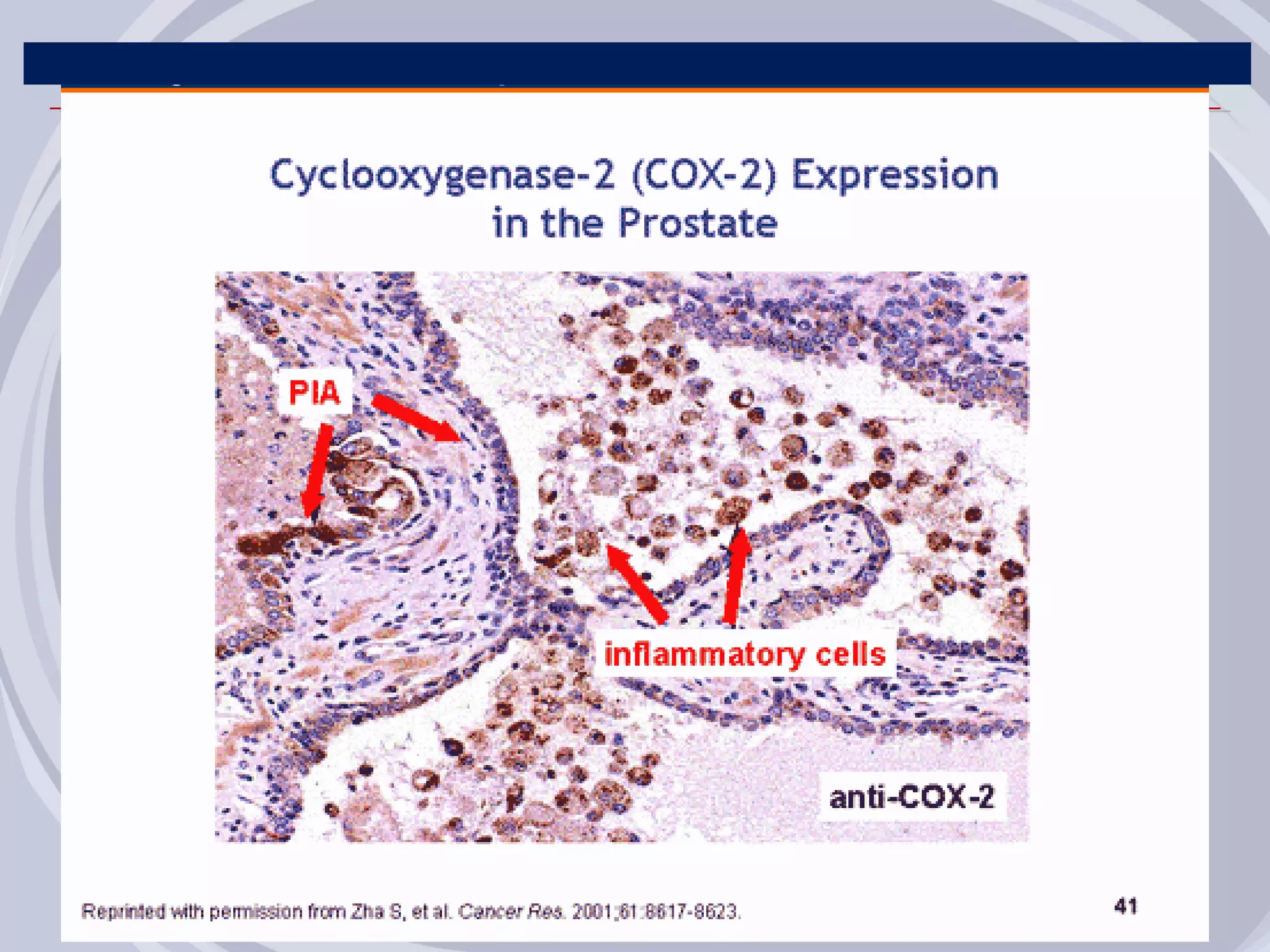
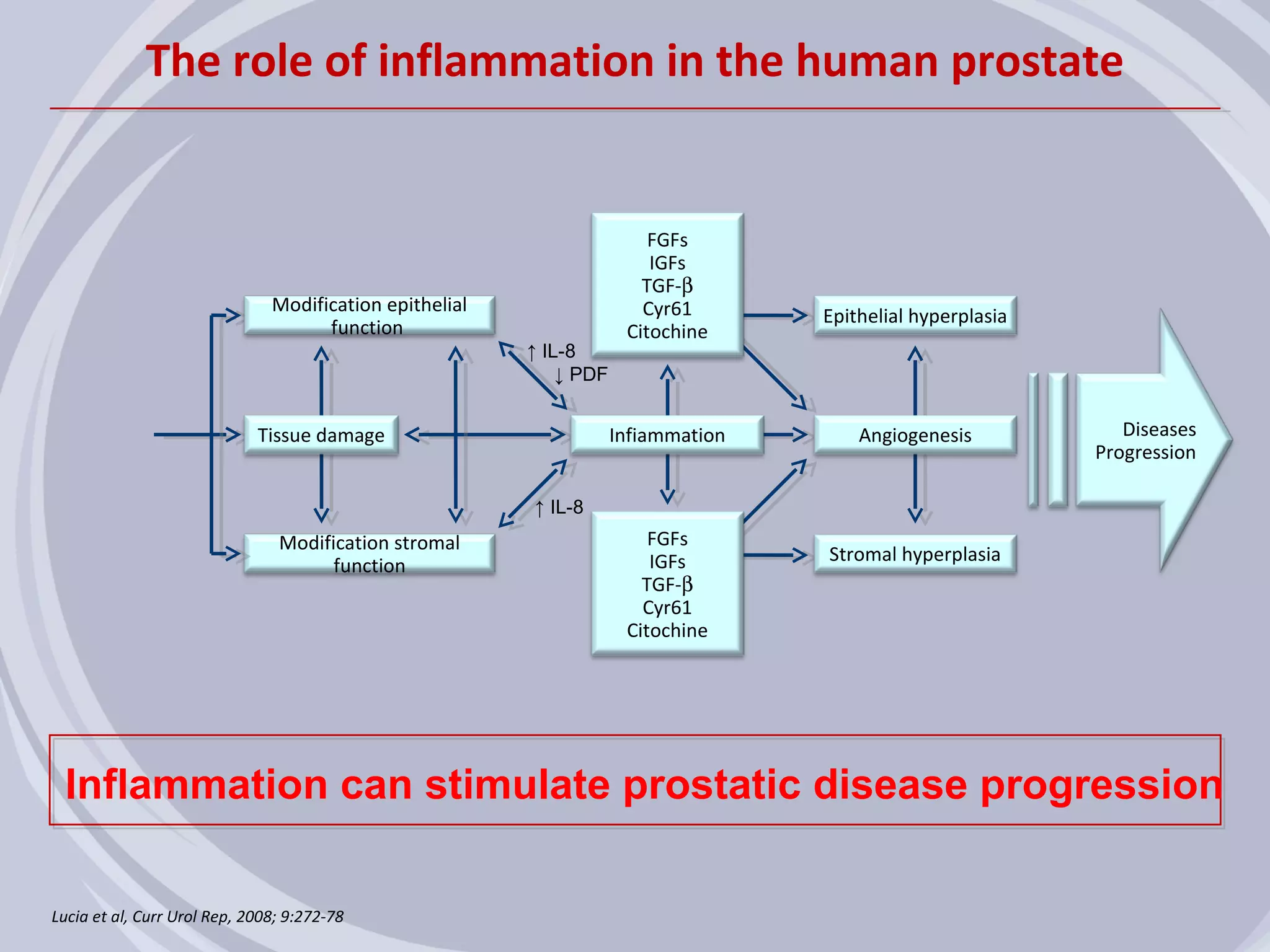
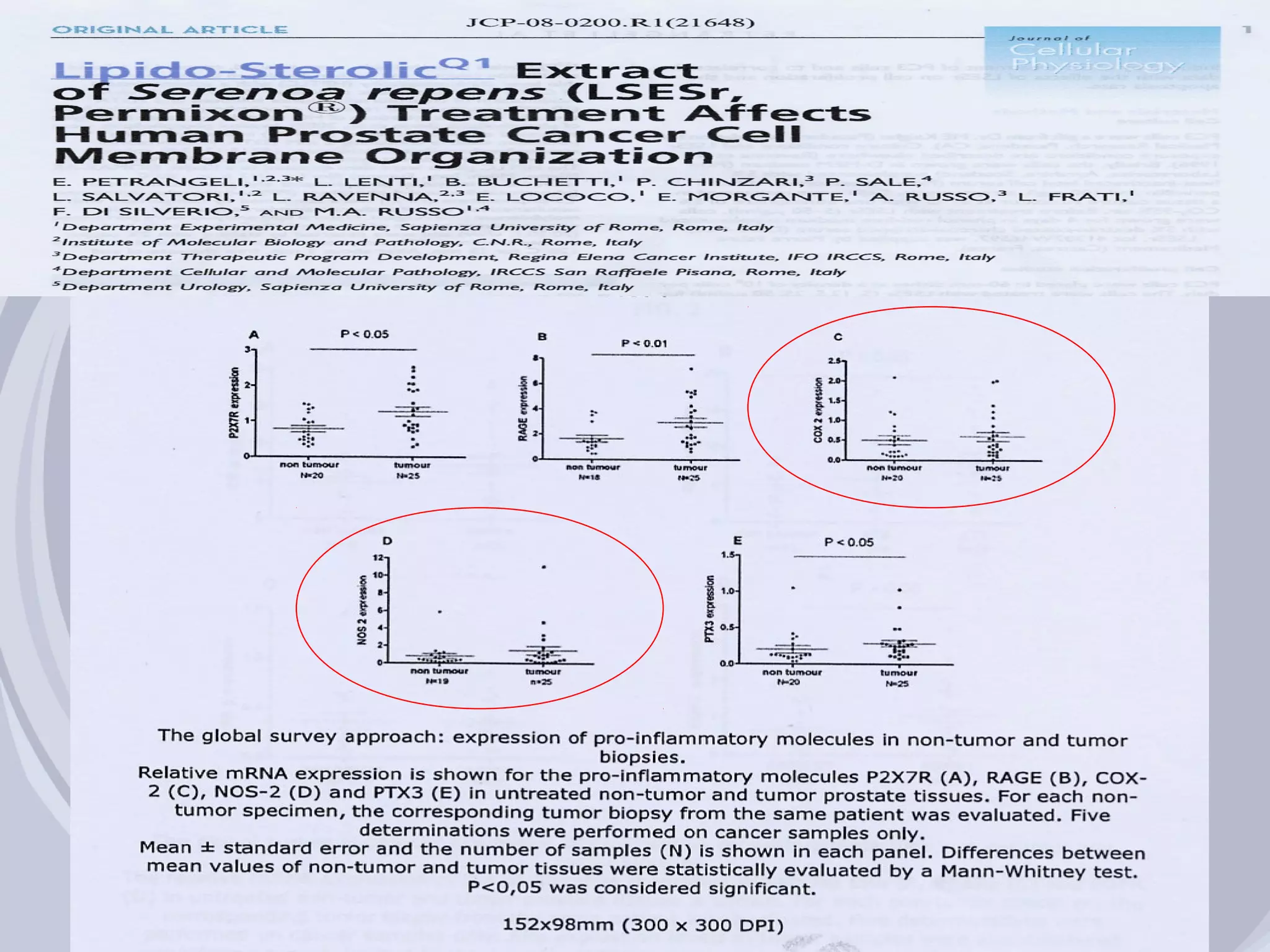
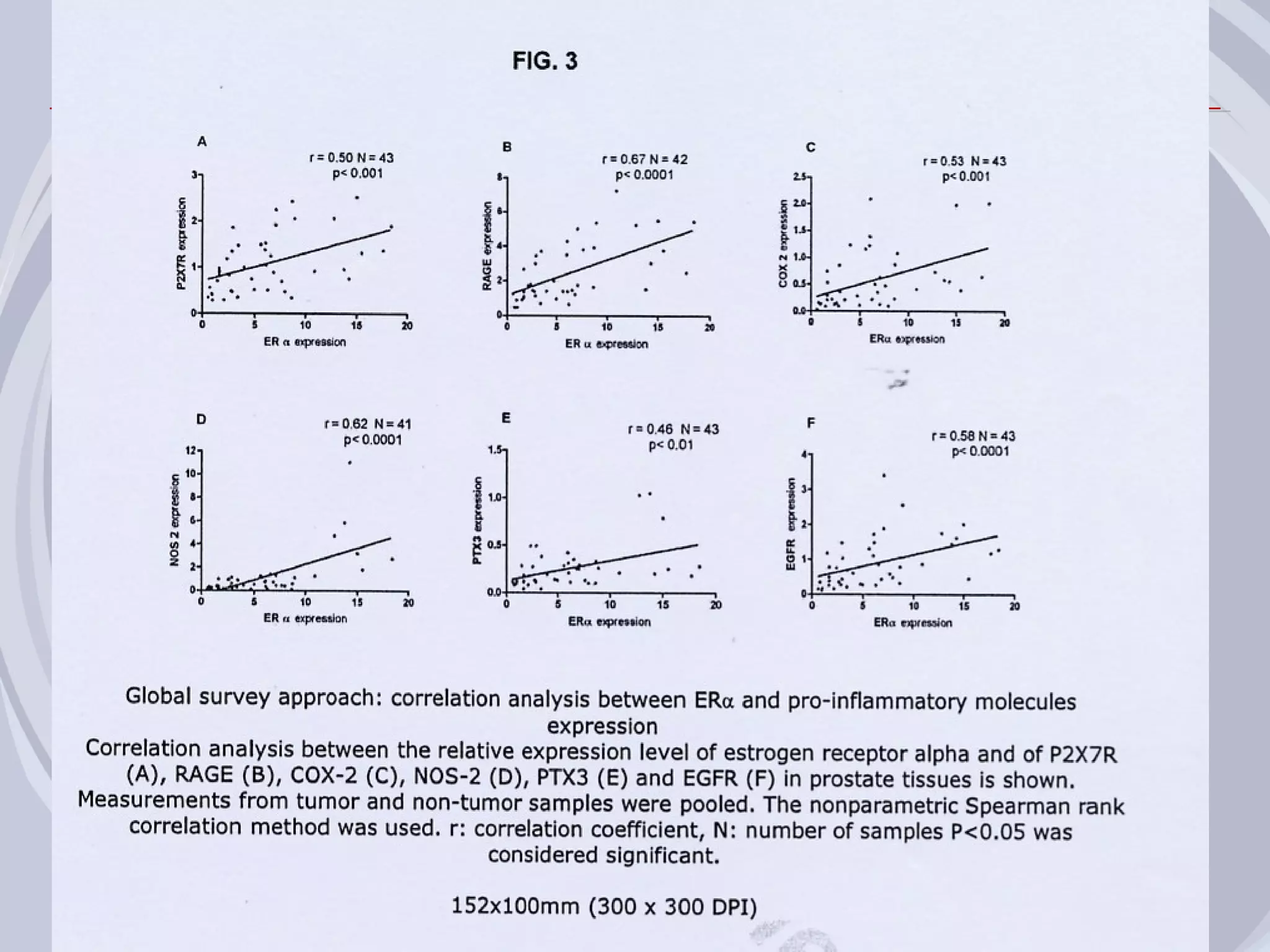
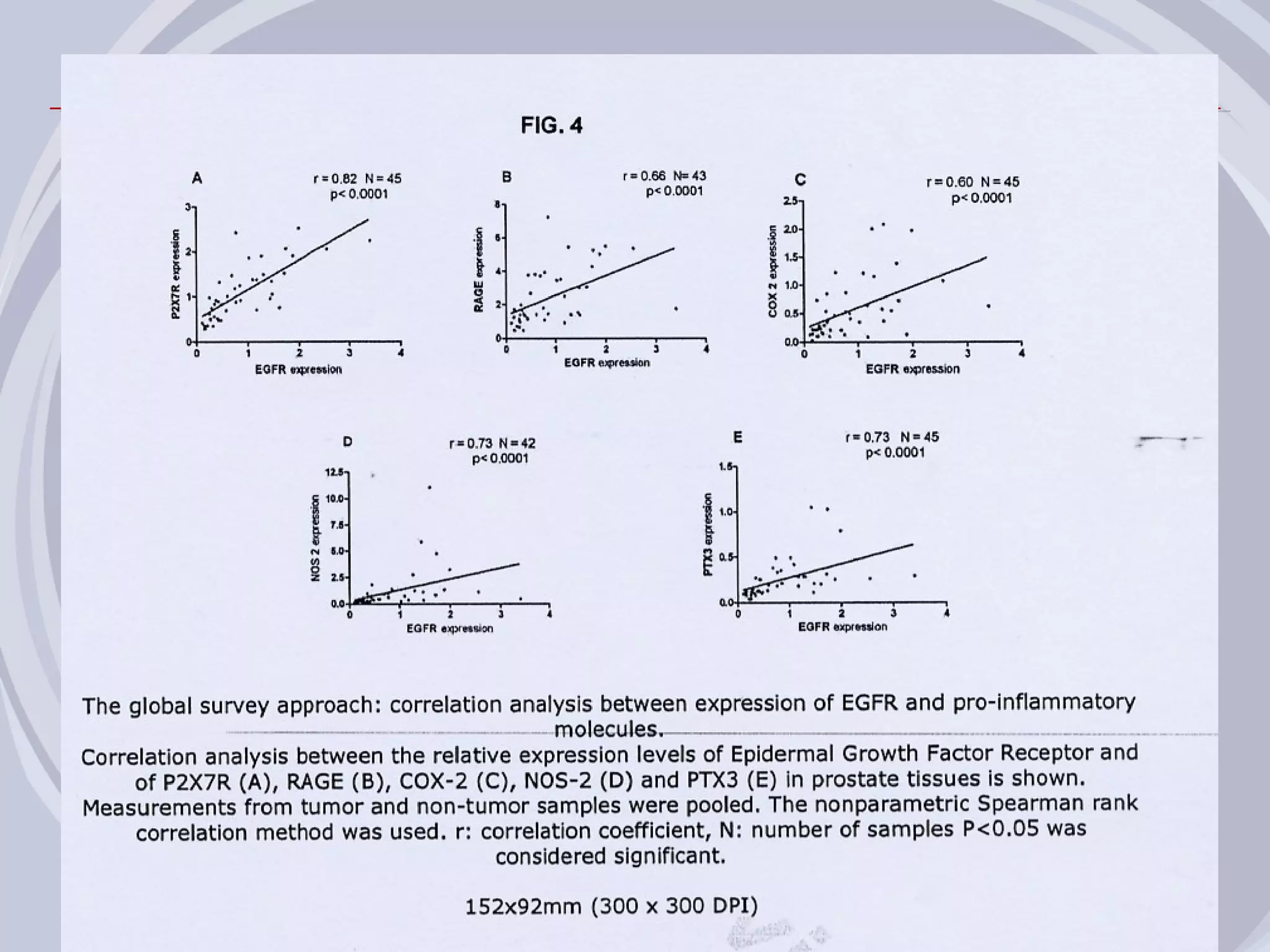
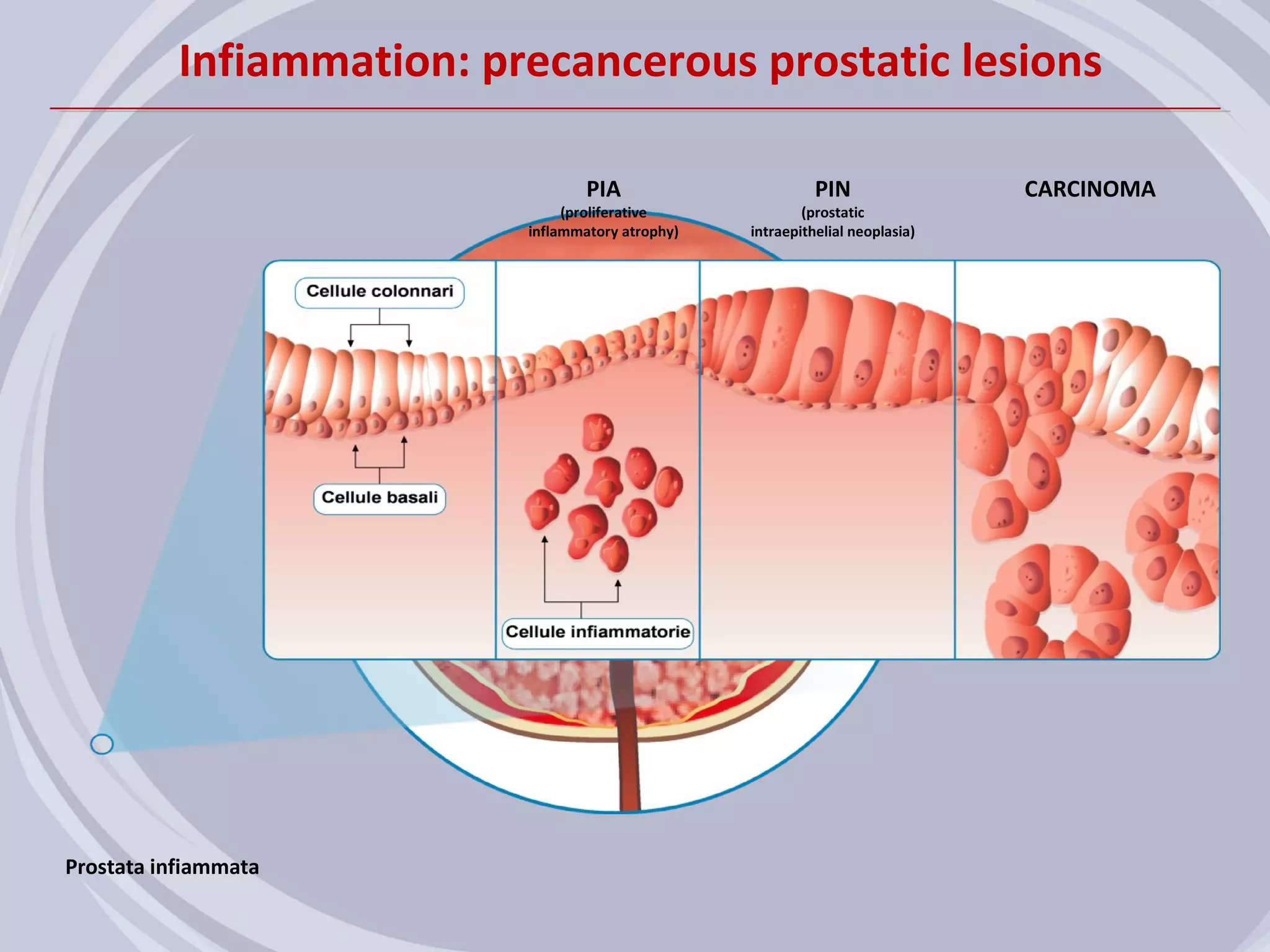
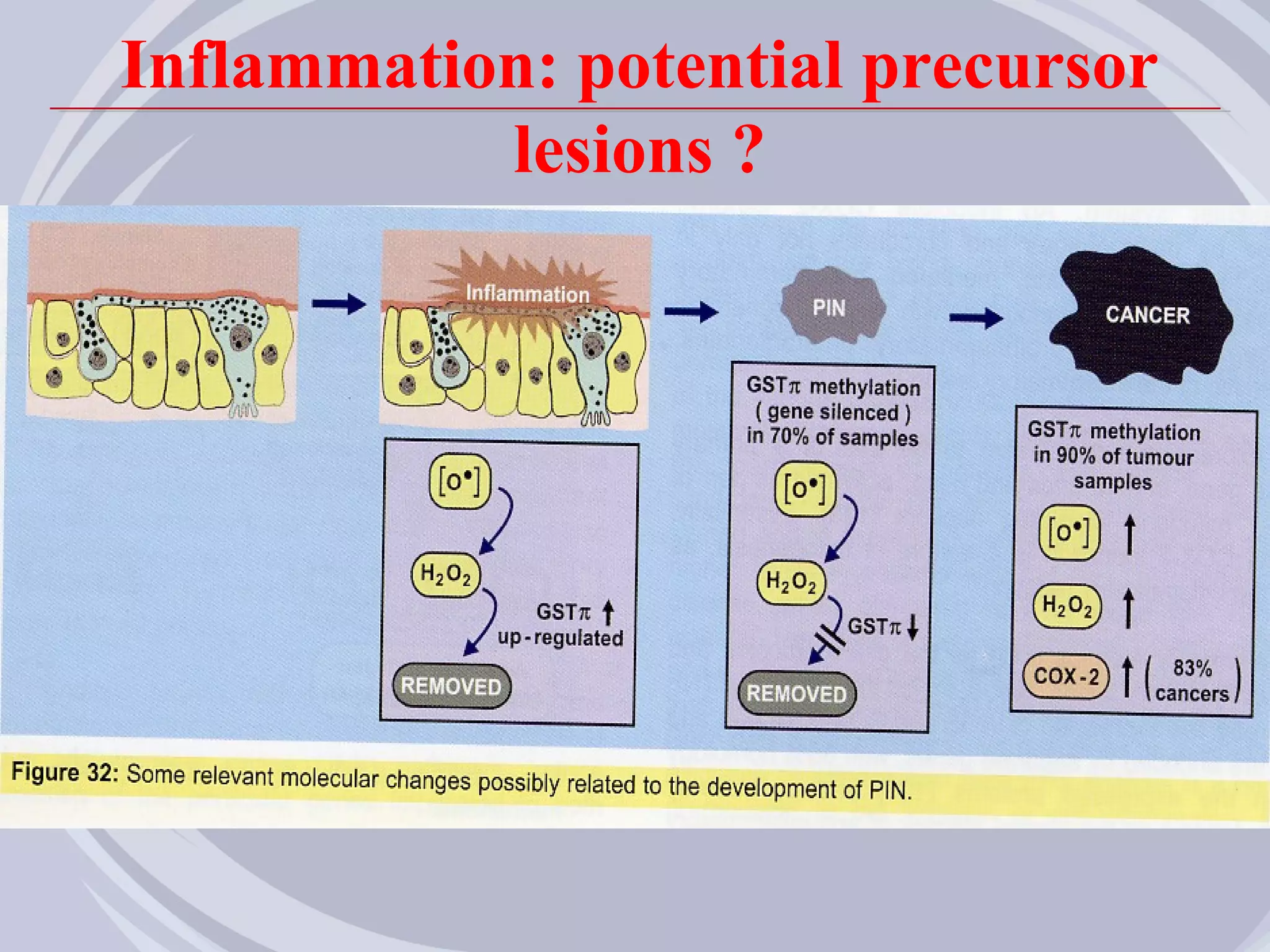
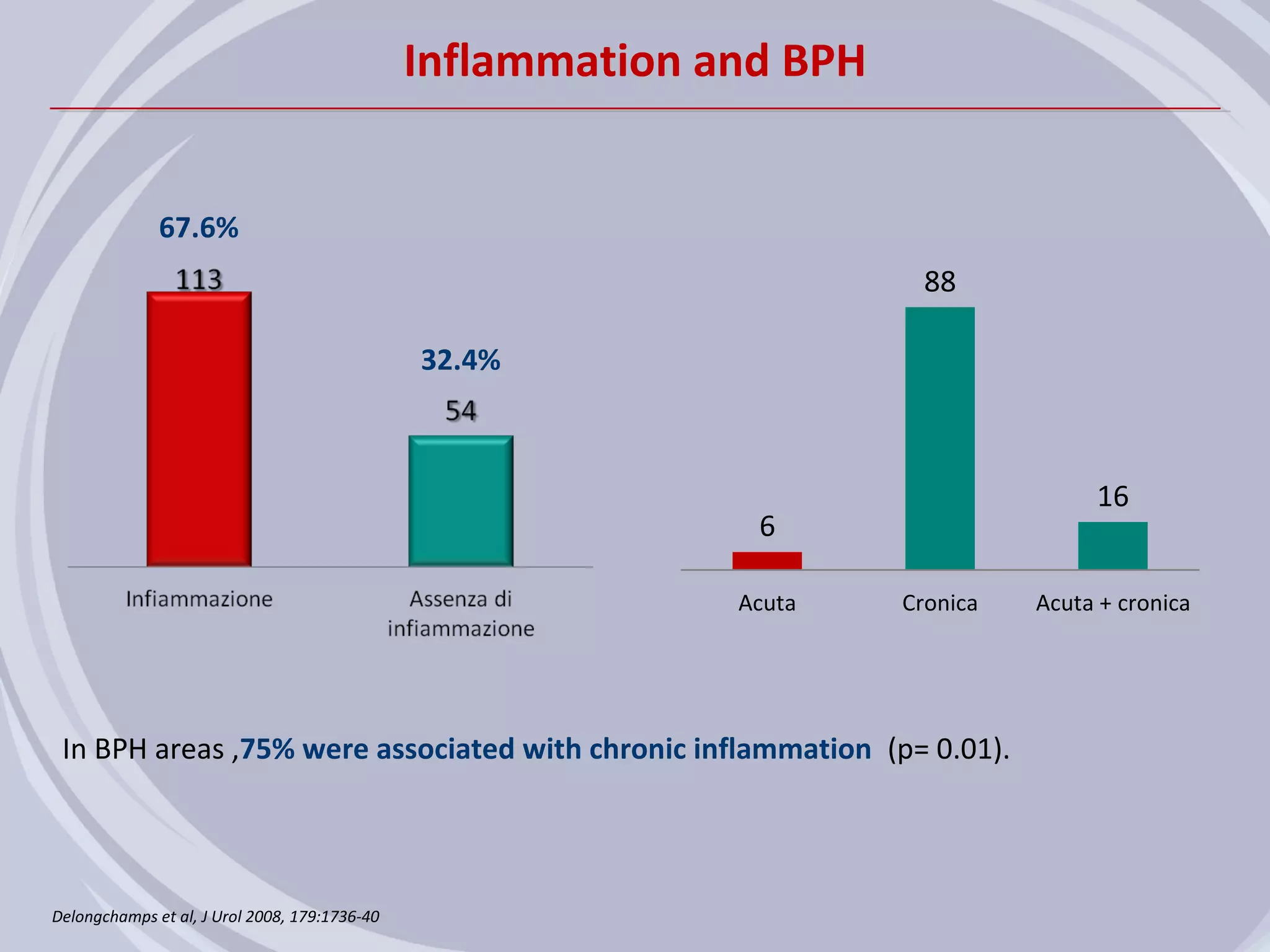
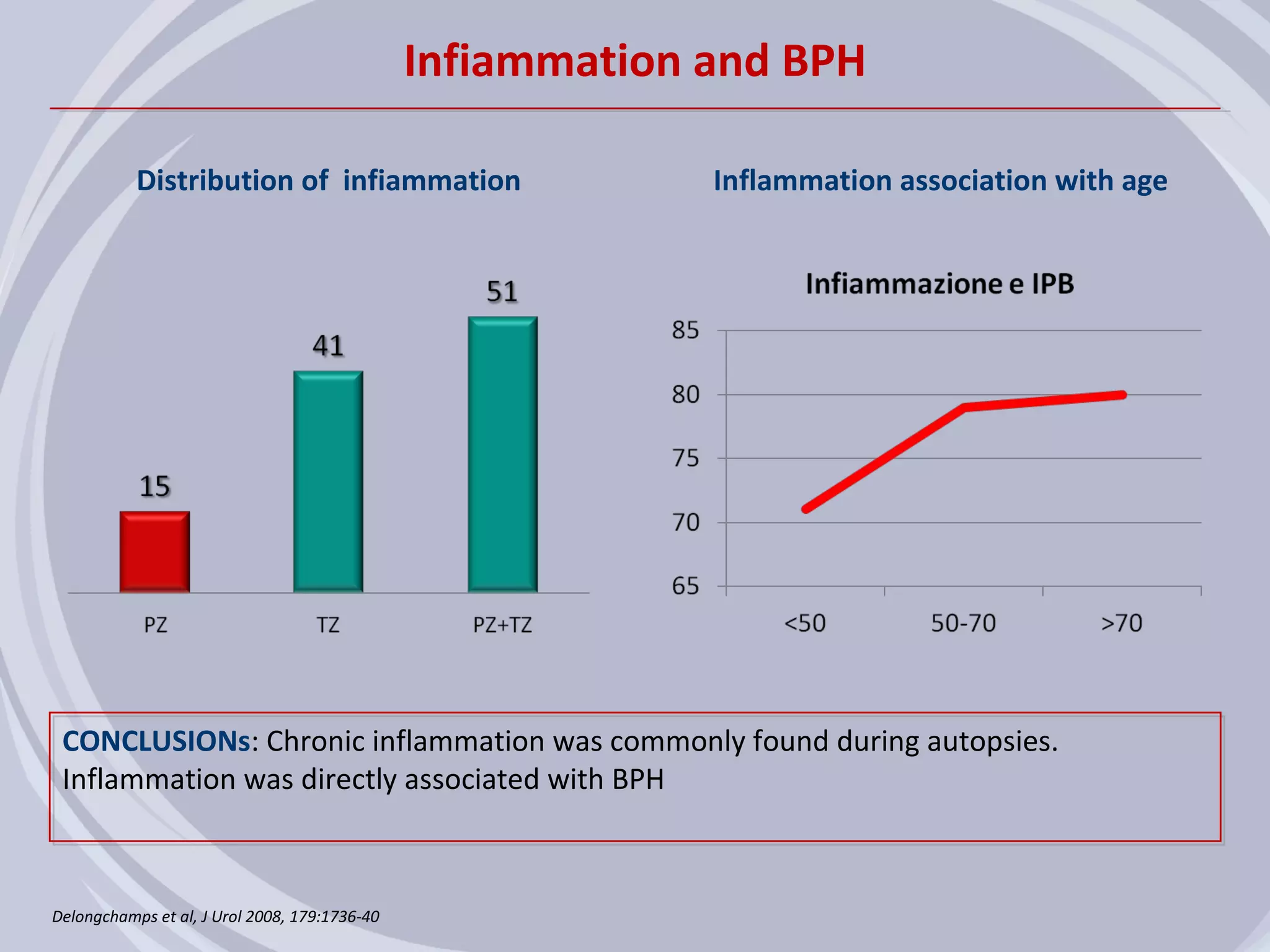
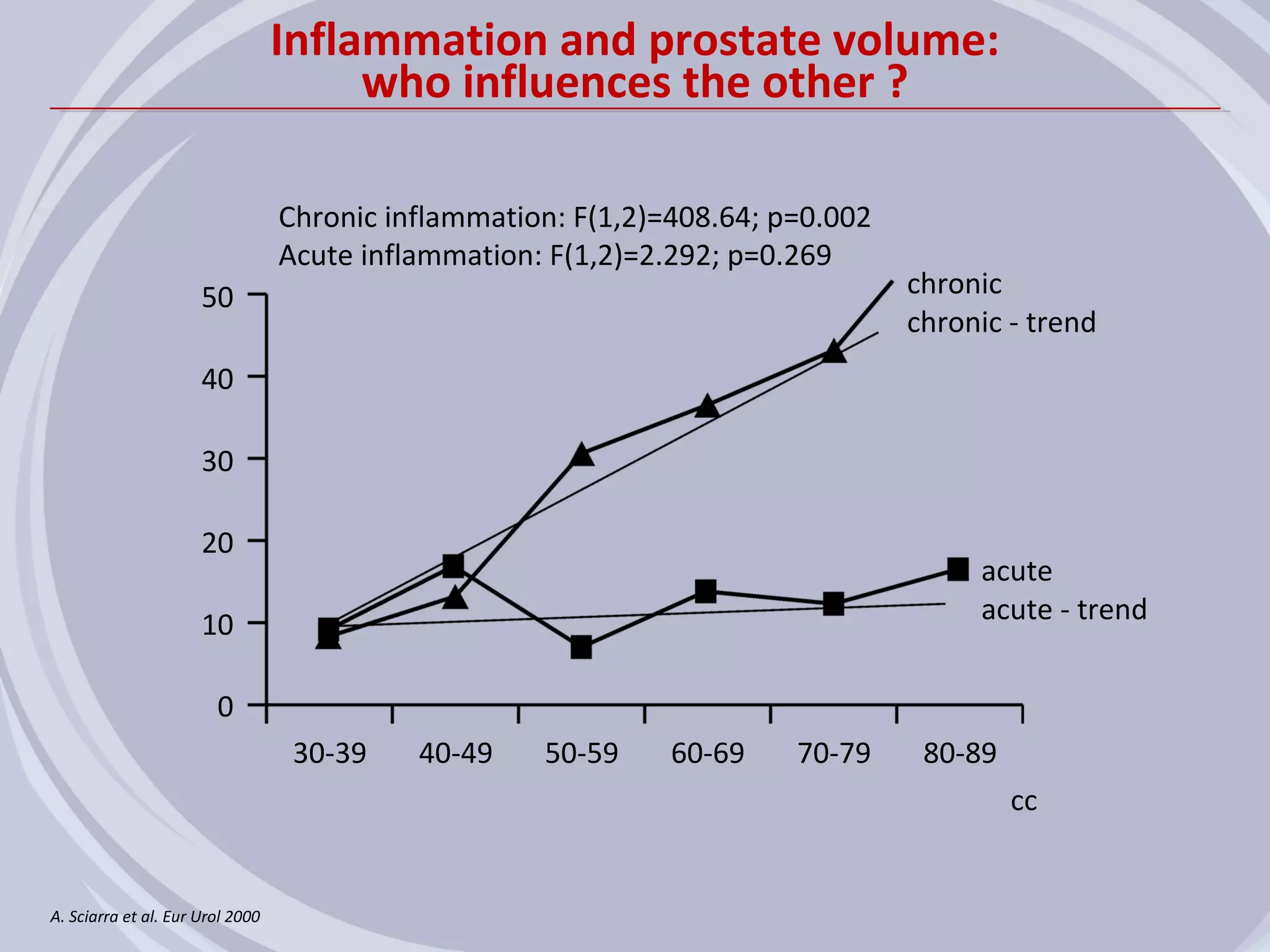
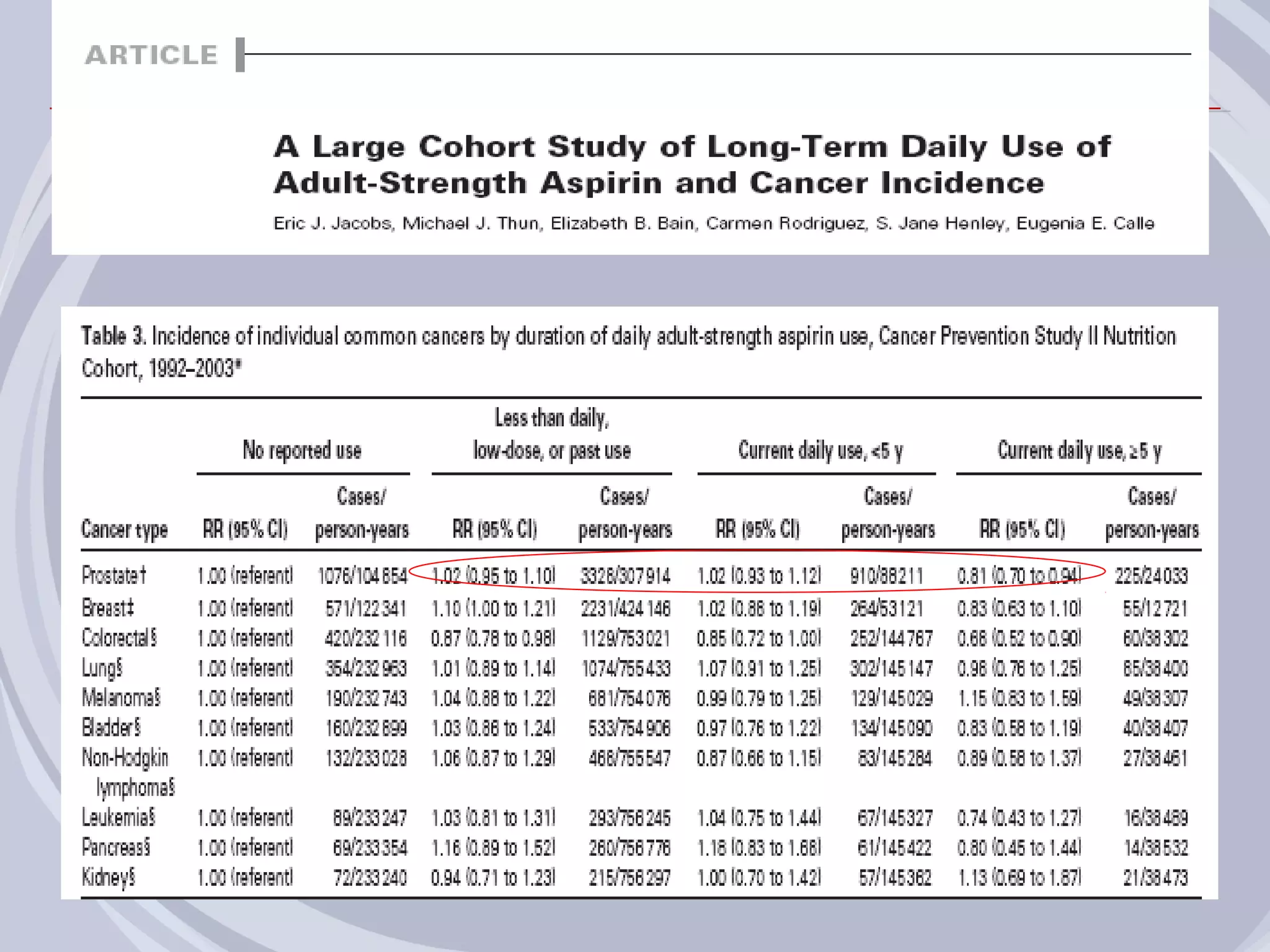
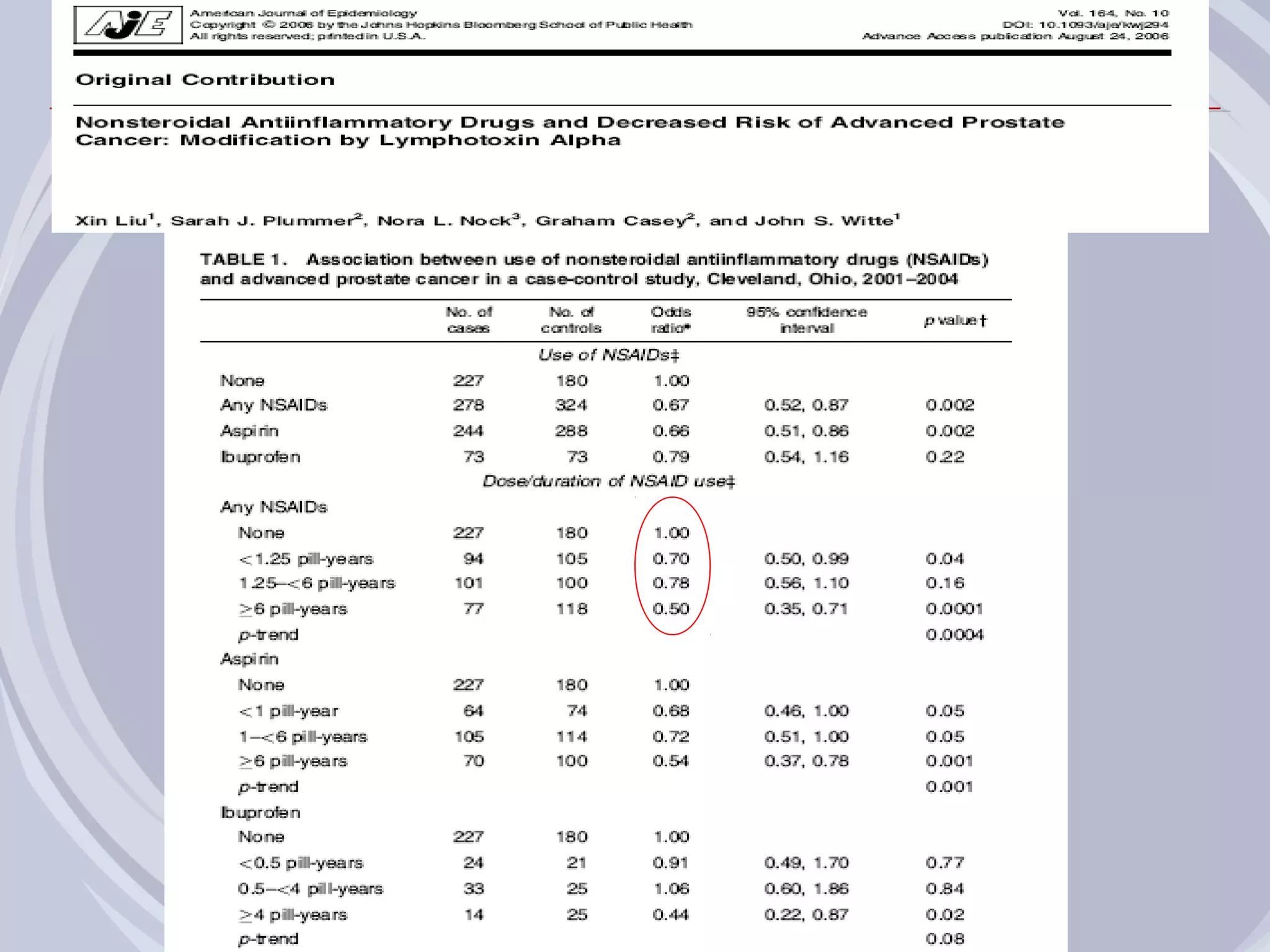
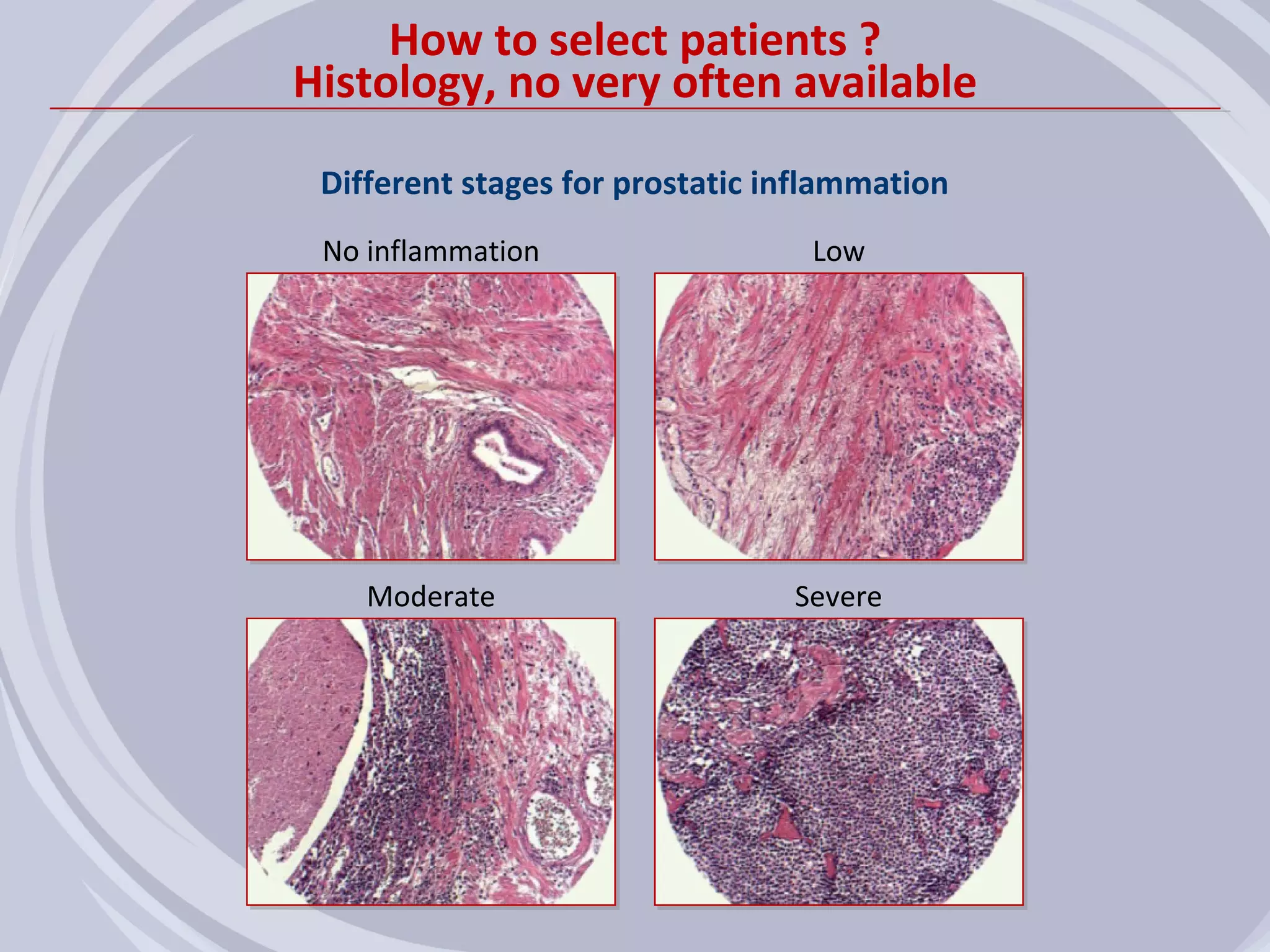
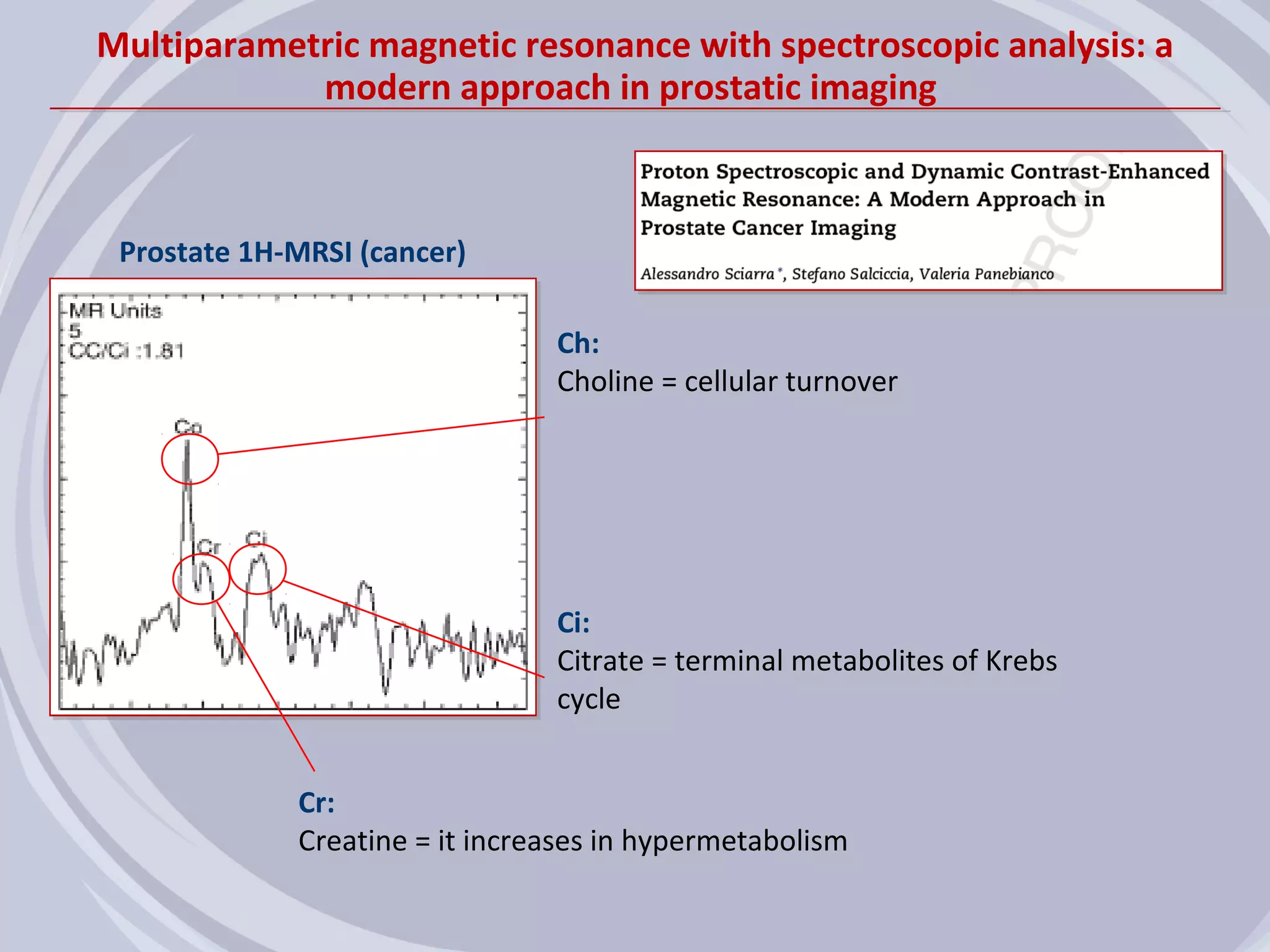
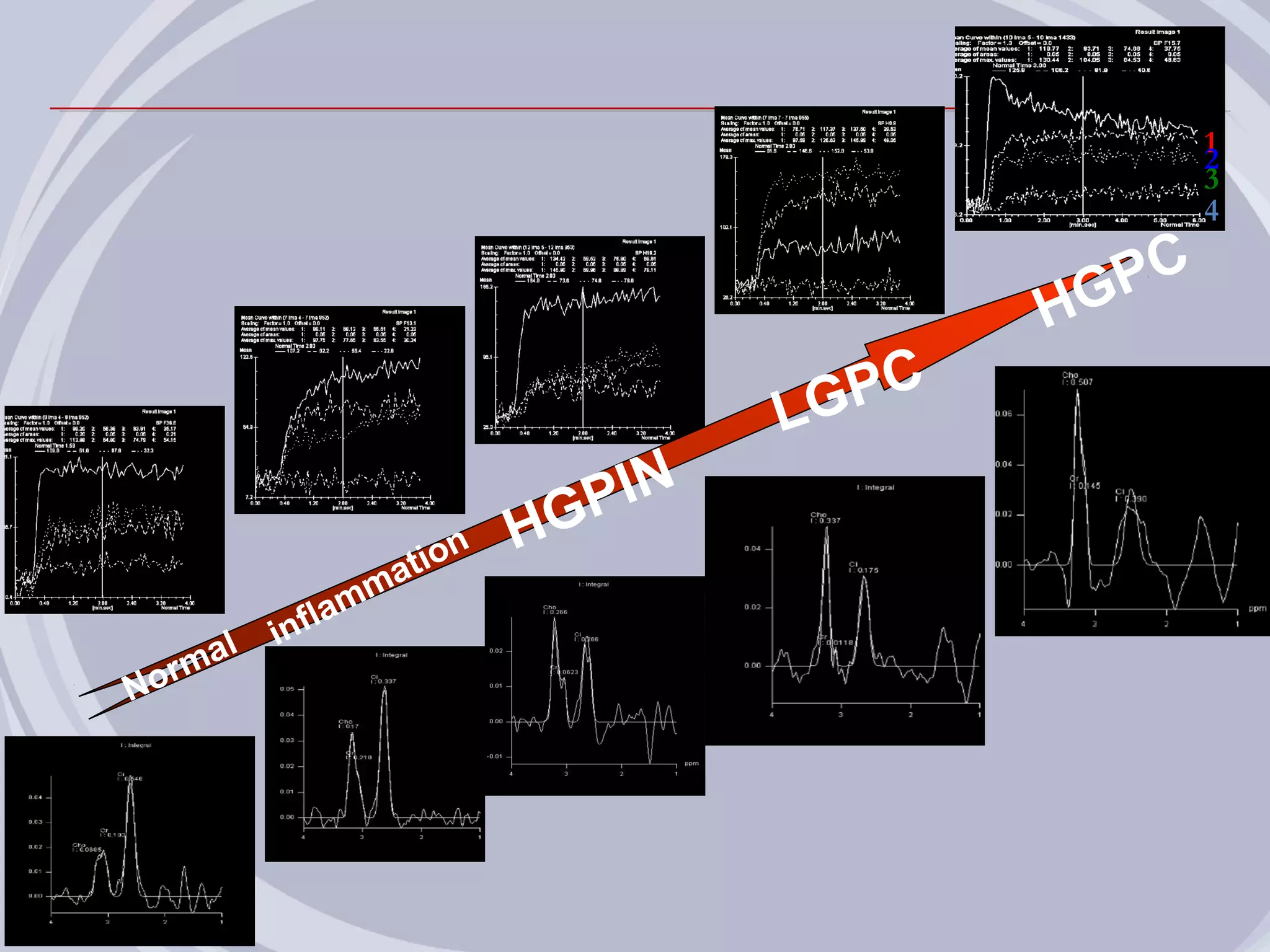
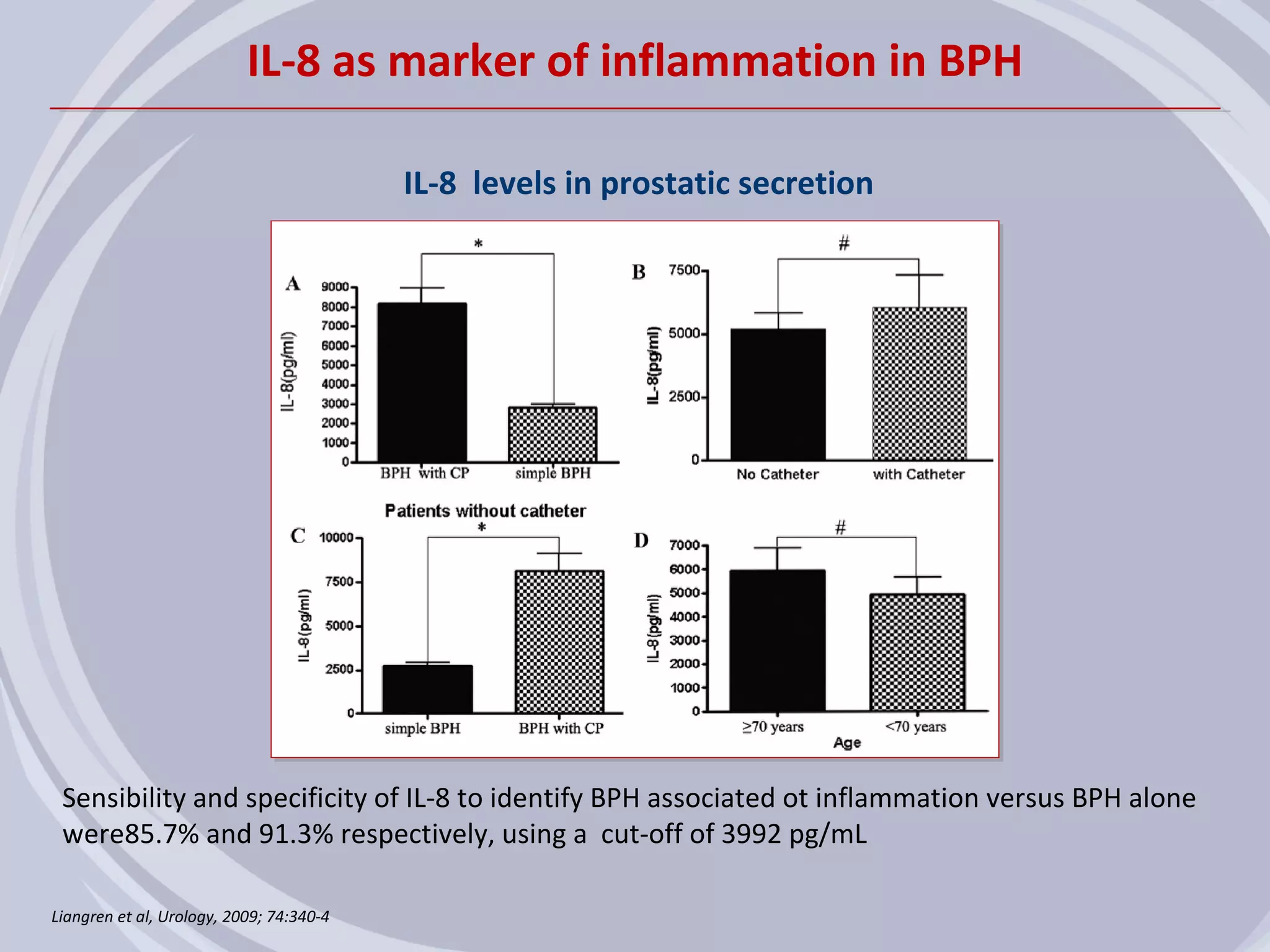
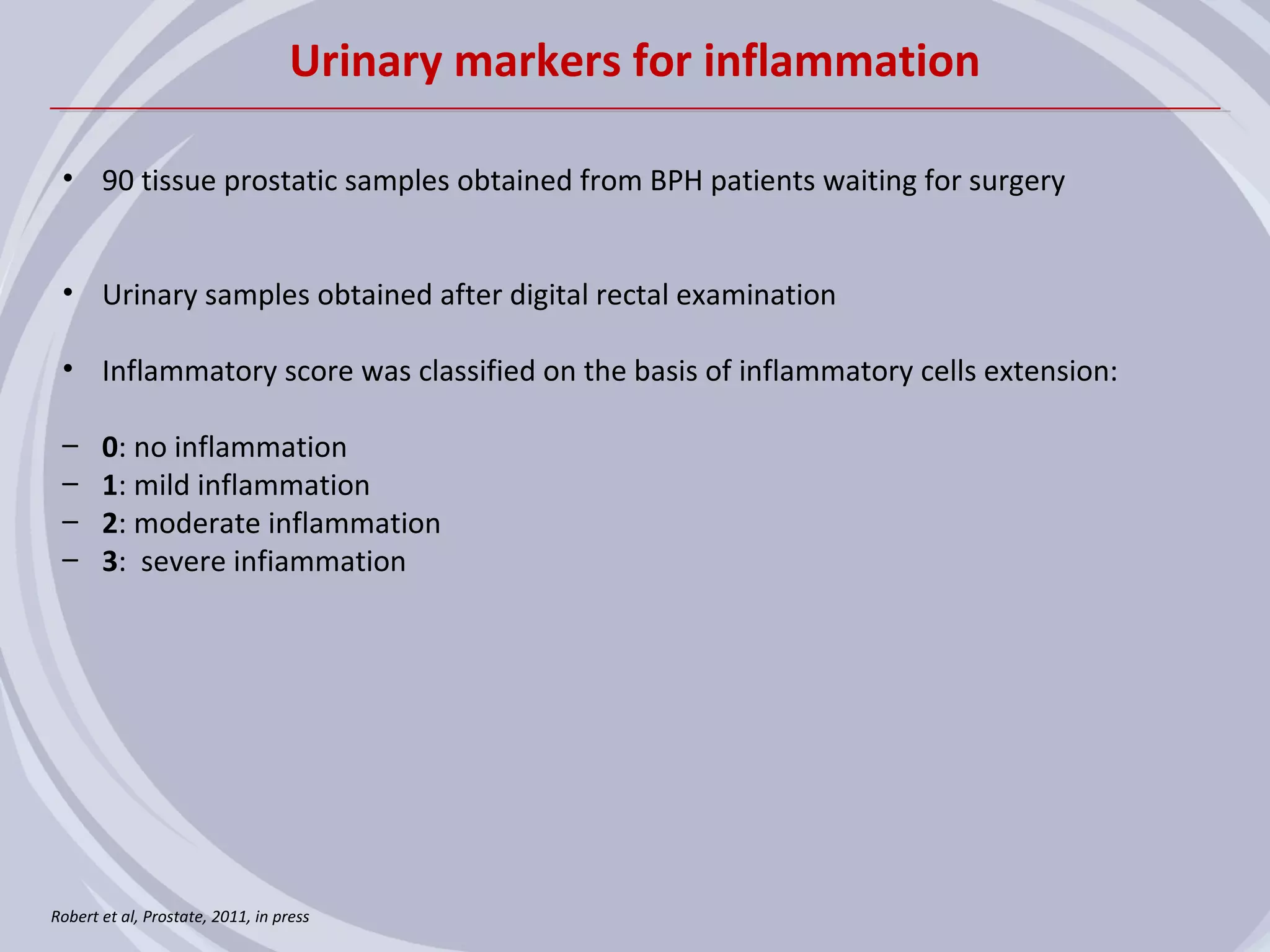
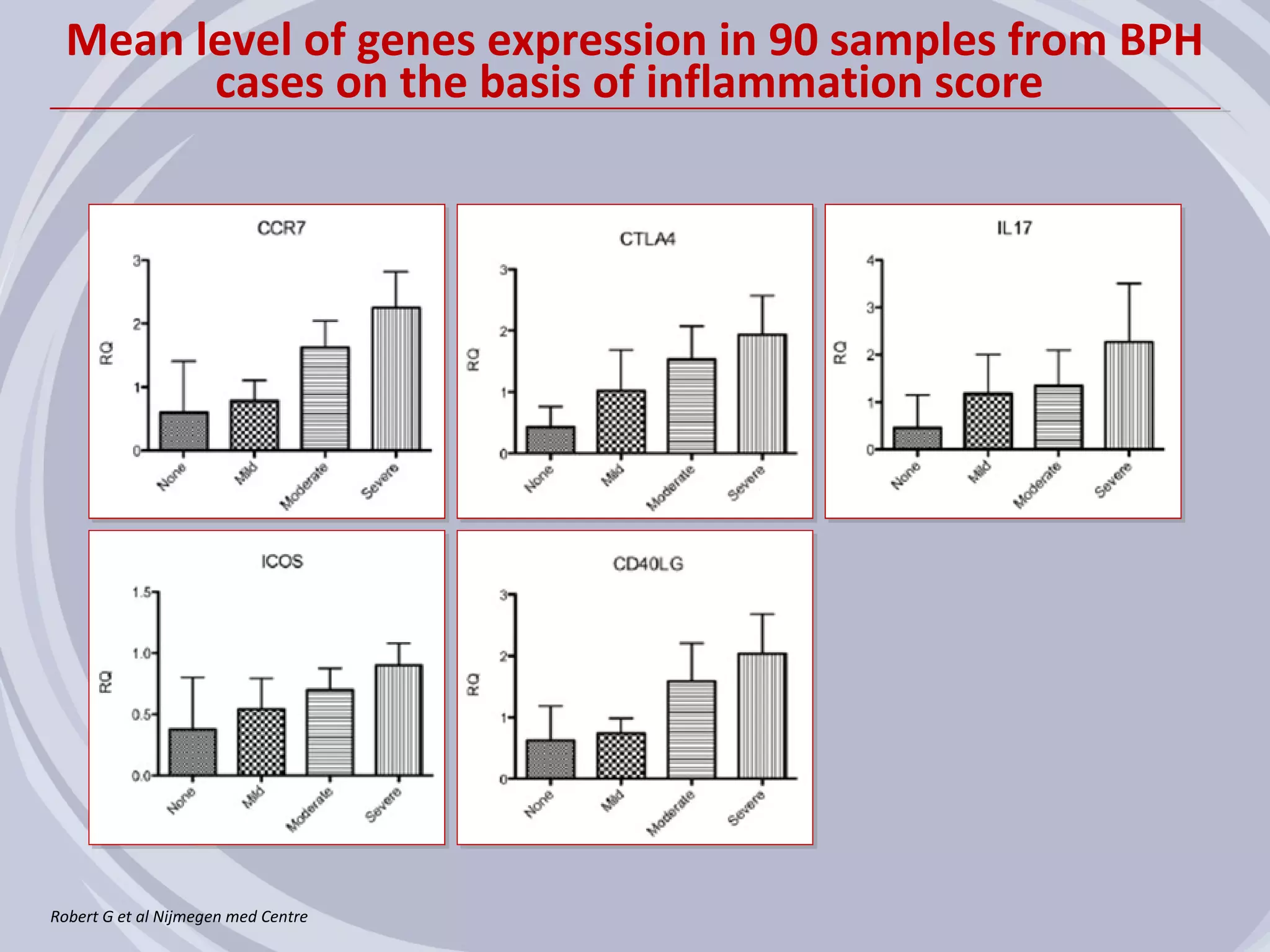
1. Inflammation may play a role in the development and progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer.
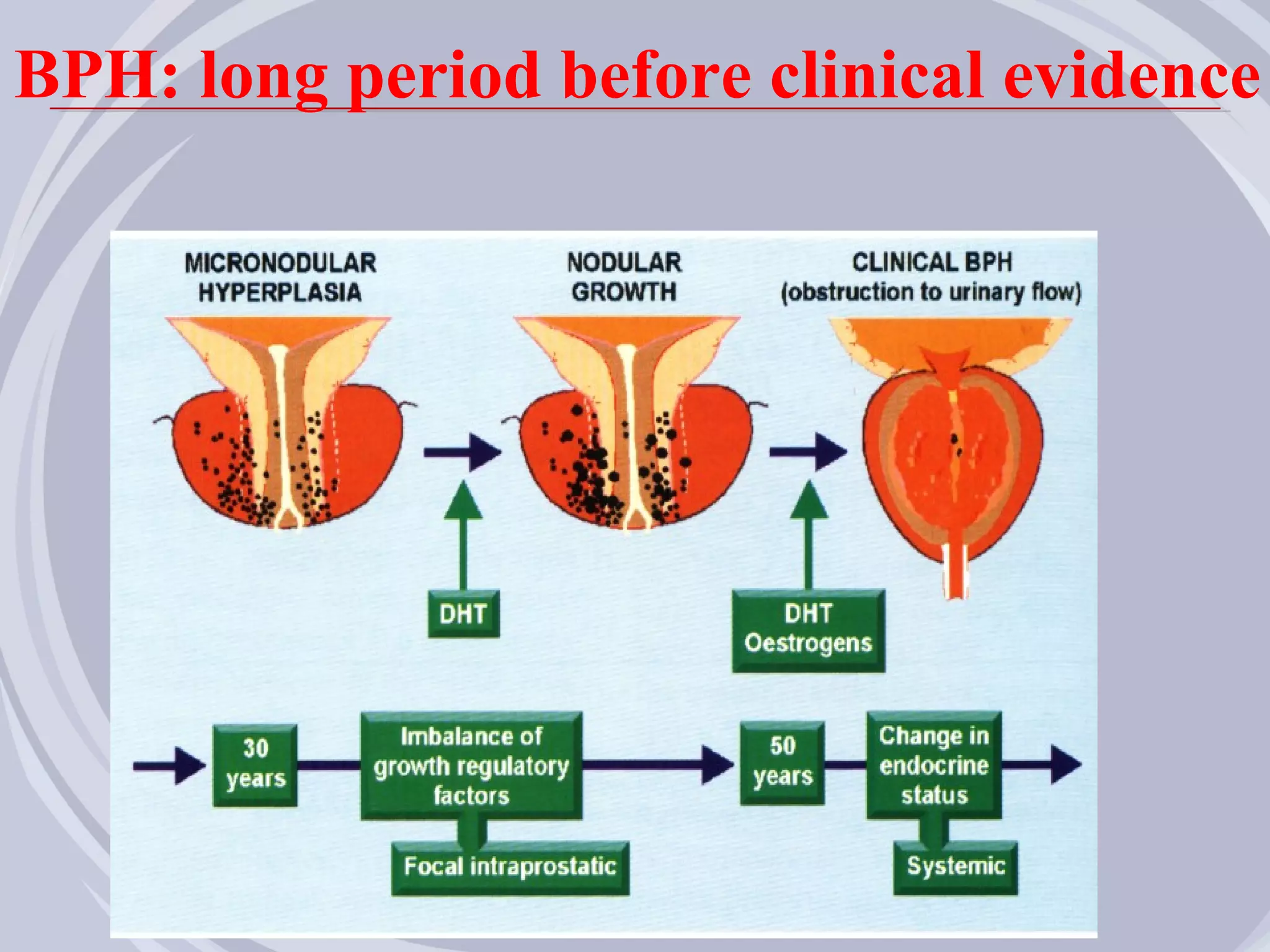
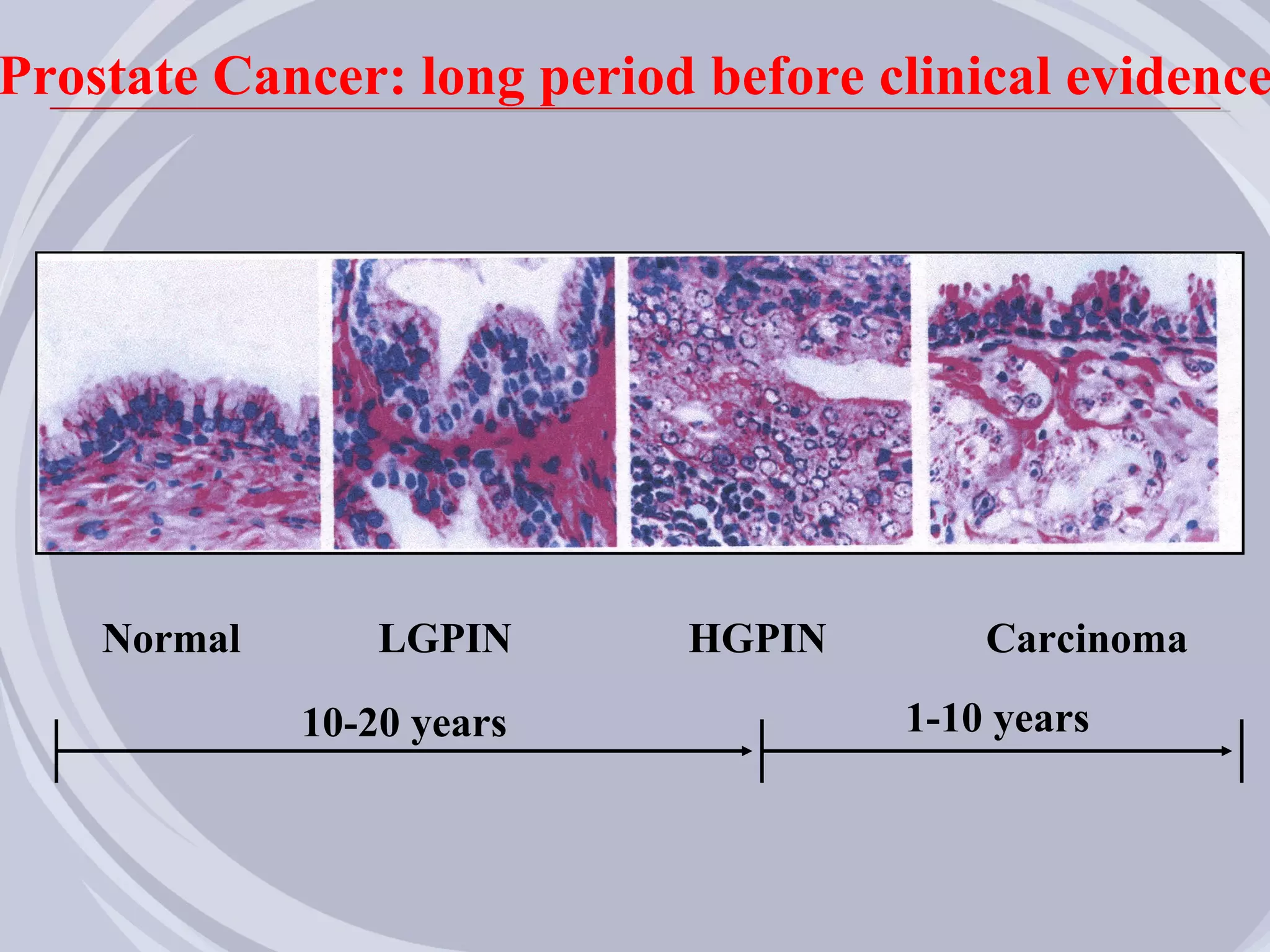
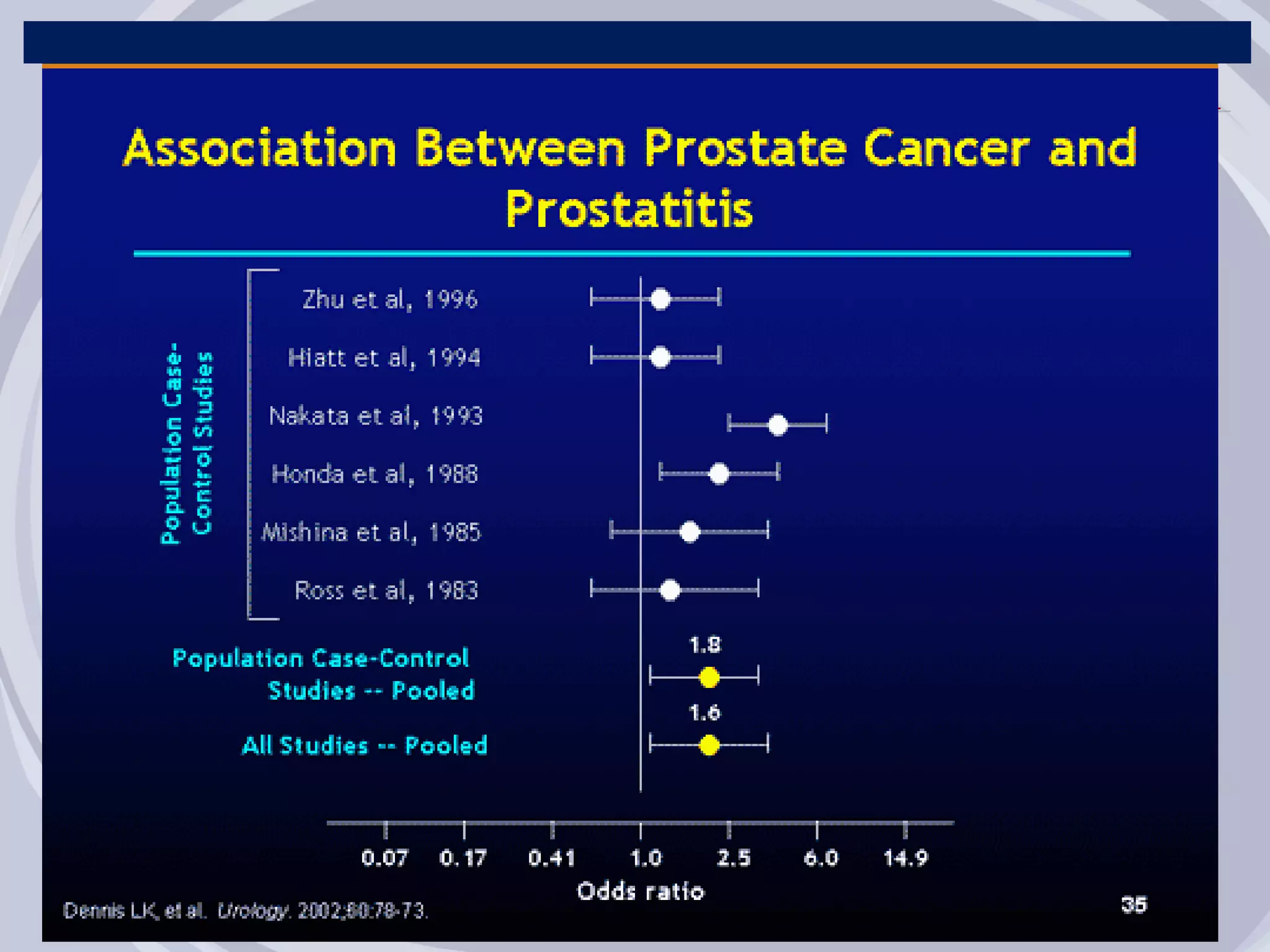
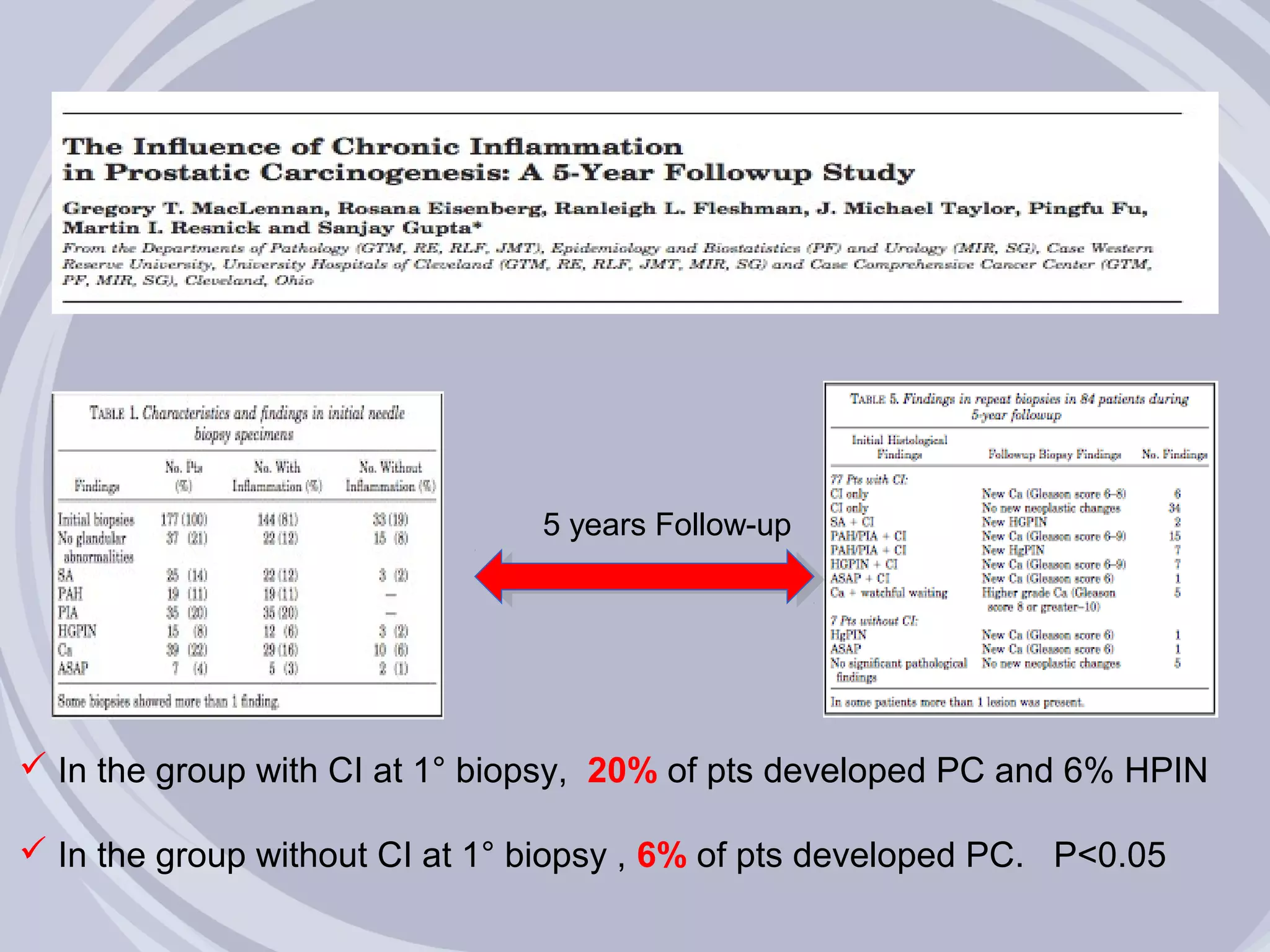
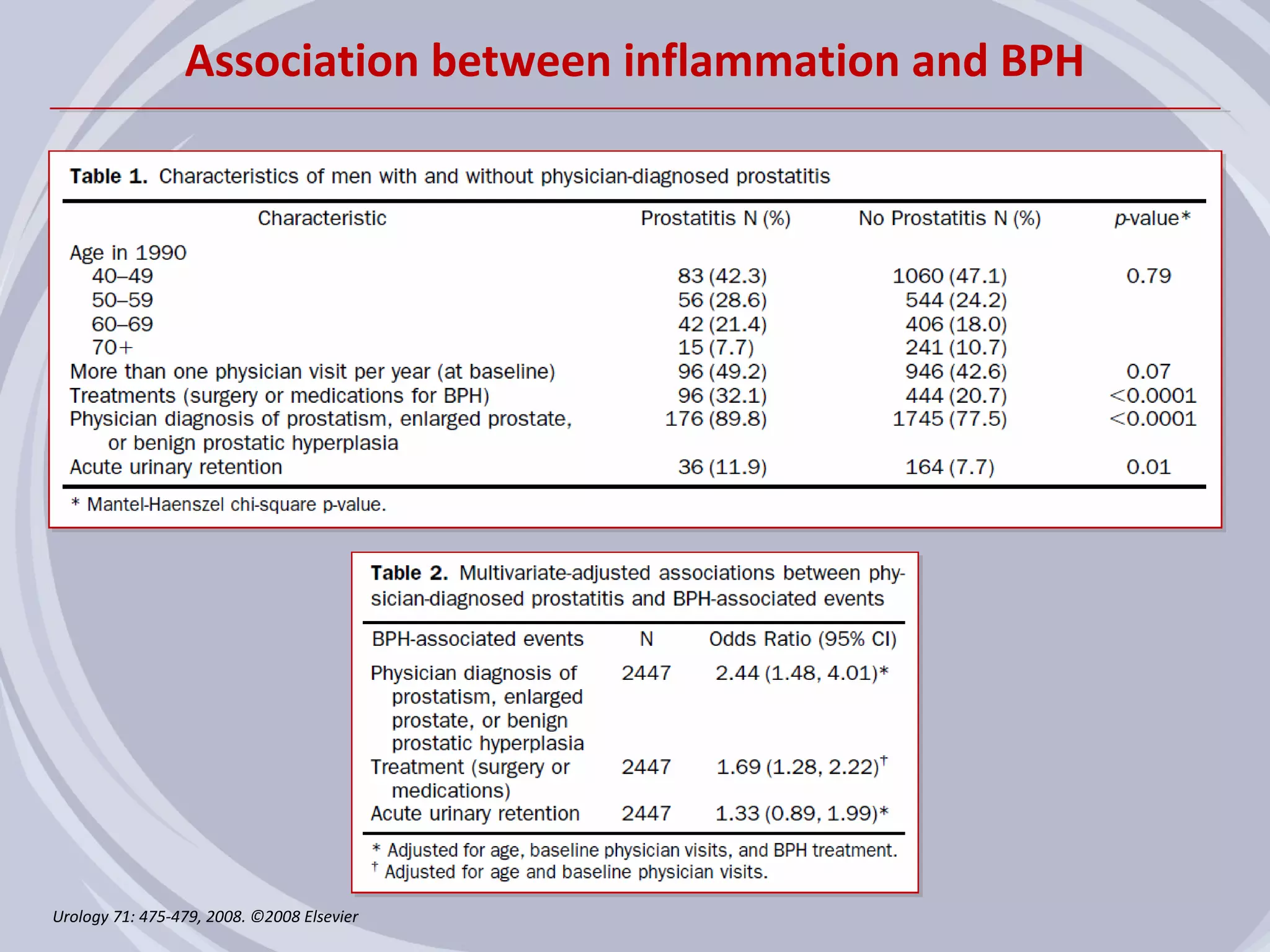
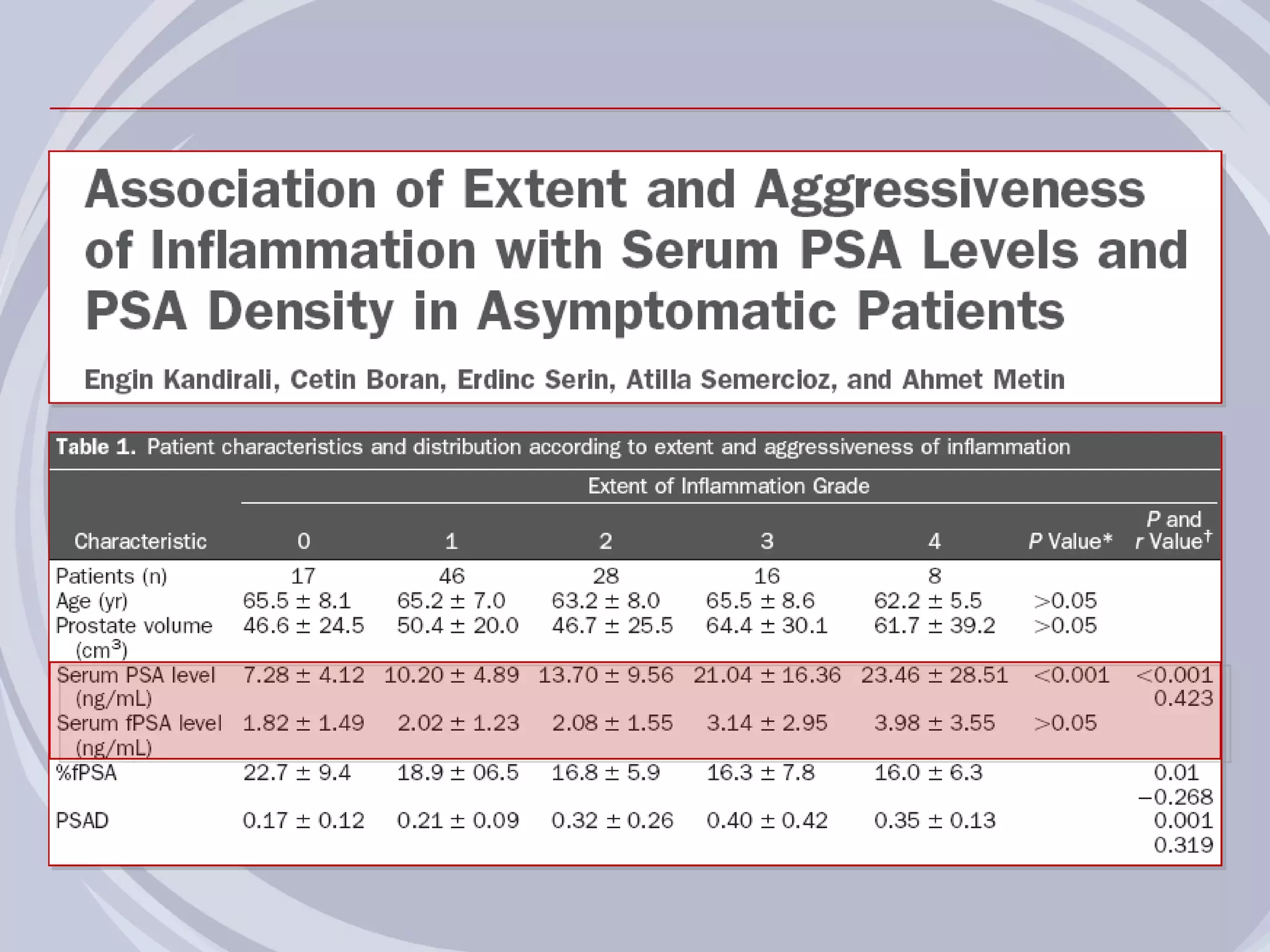
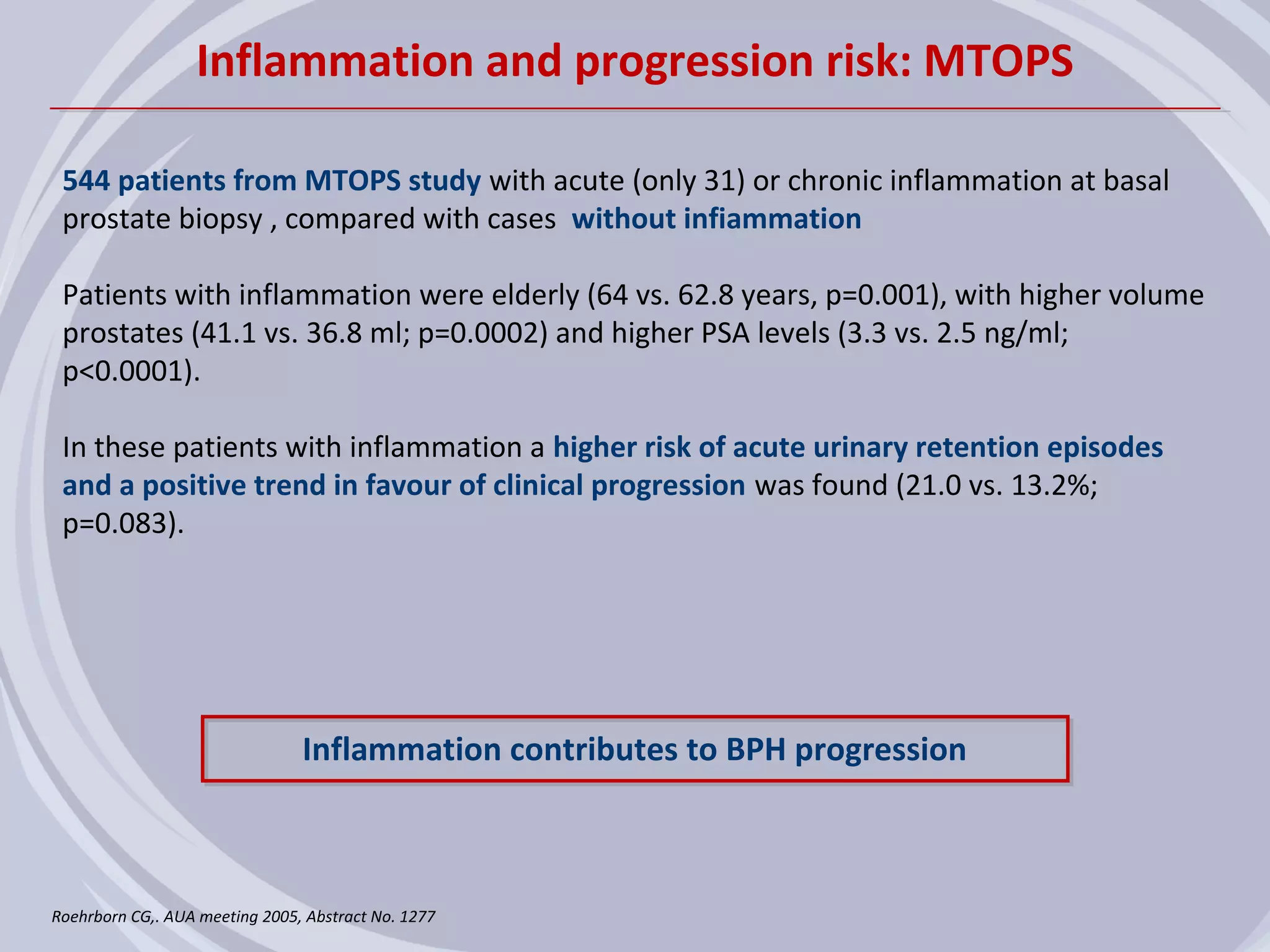
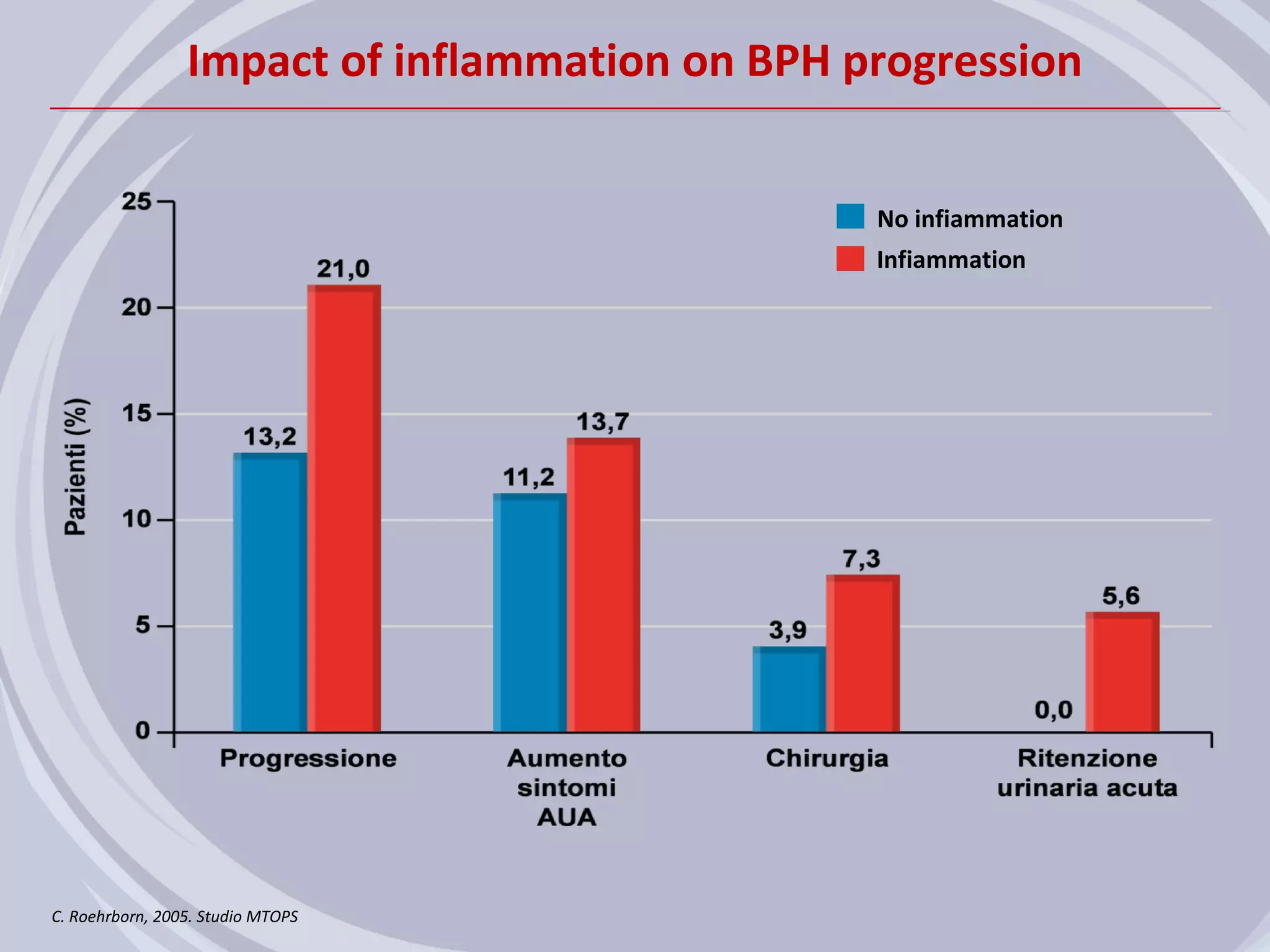
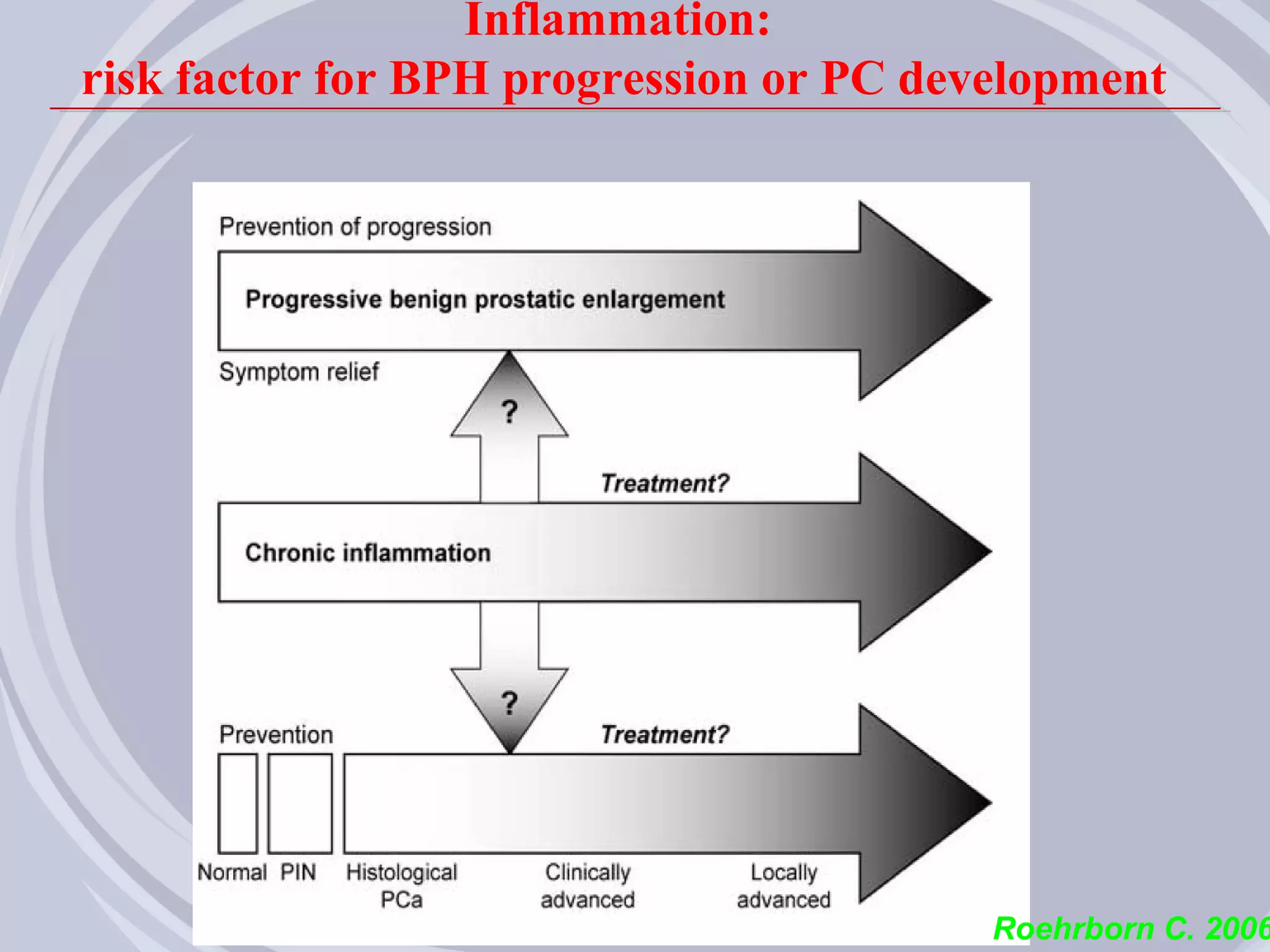
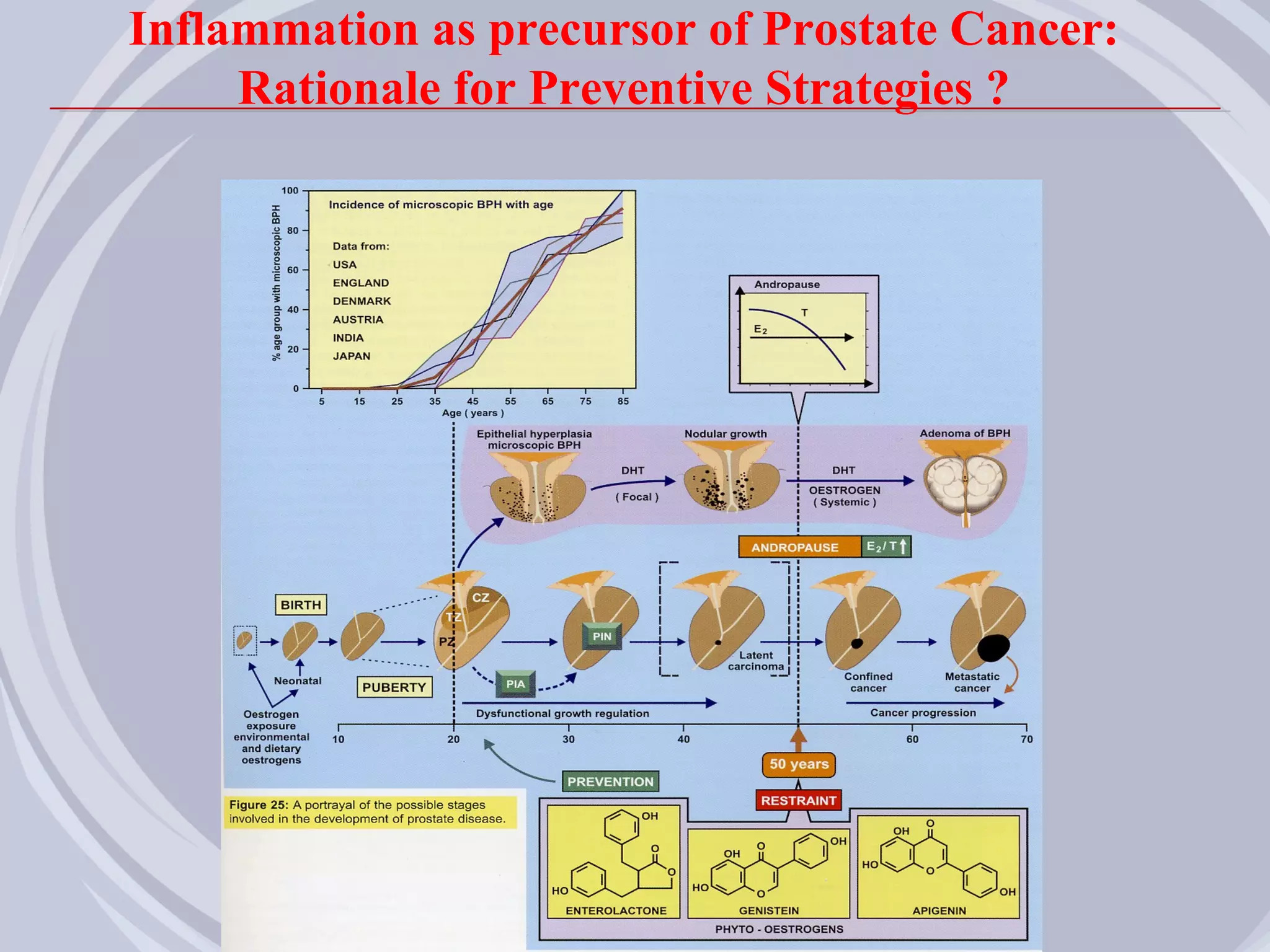
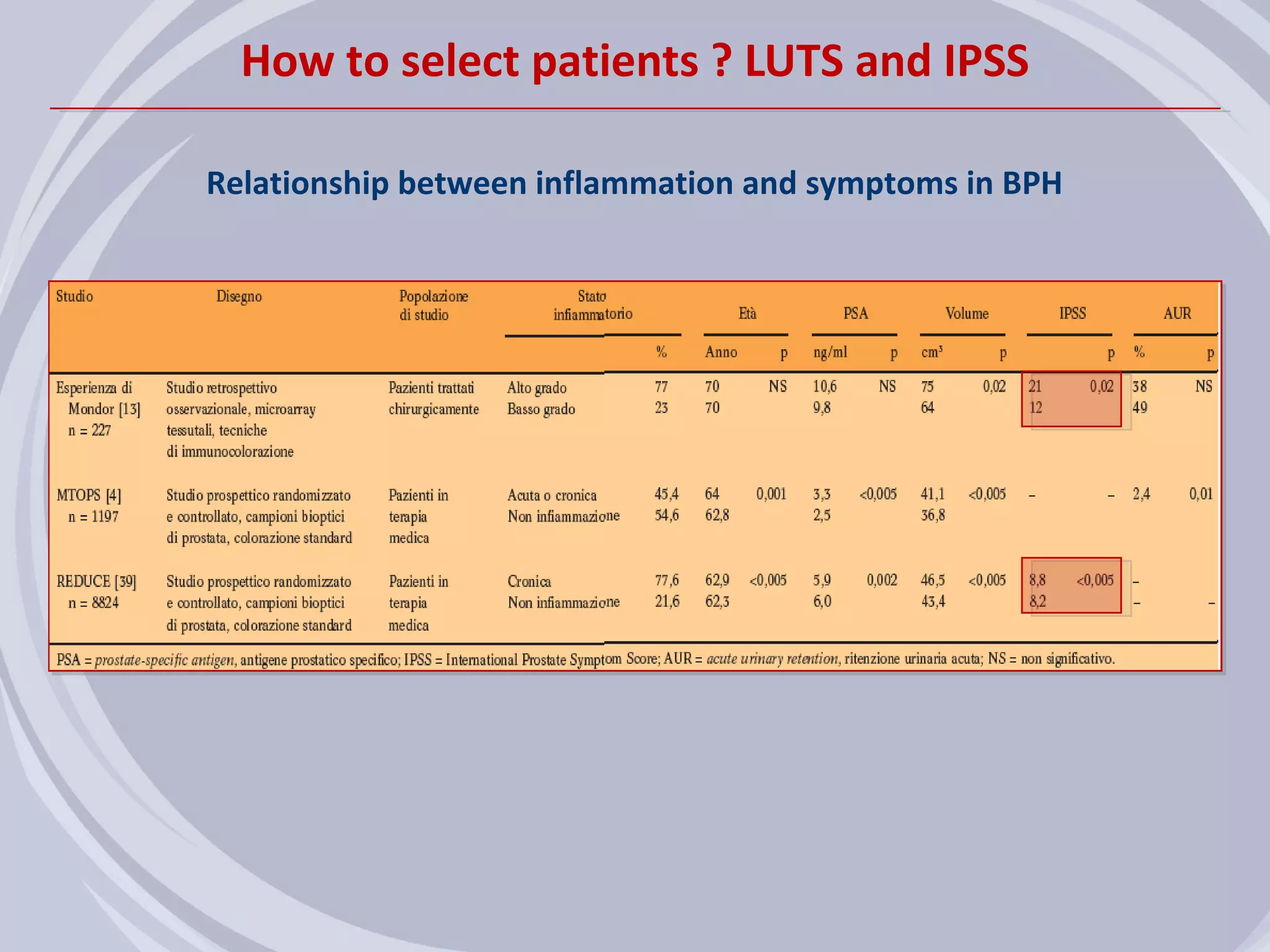
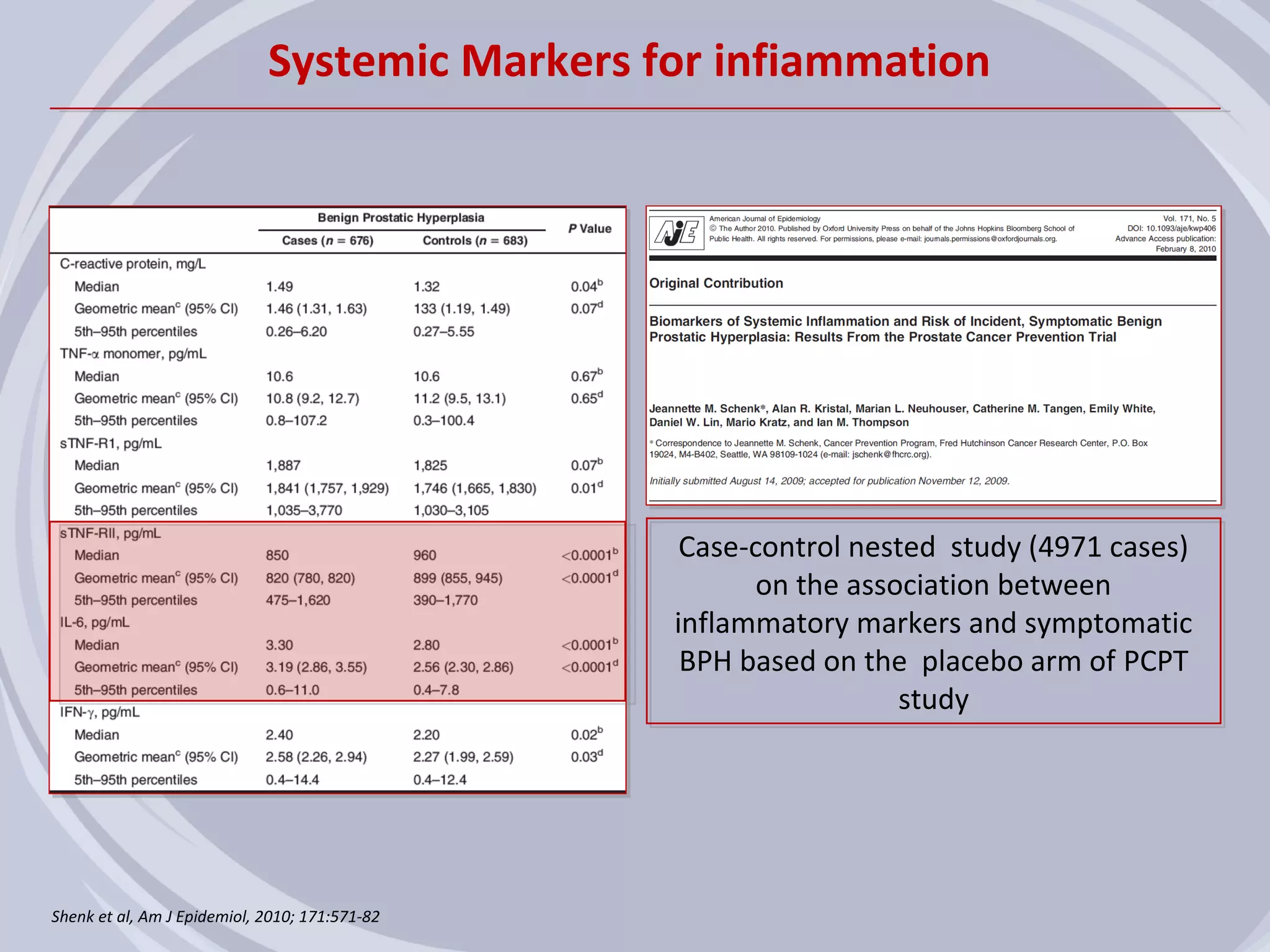
2. Evidence from histological, clinical, and epidemiological studies suggests that chronic prostatic inflammation is associated with larger prostate volume and an increased risk of BPH progression.
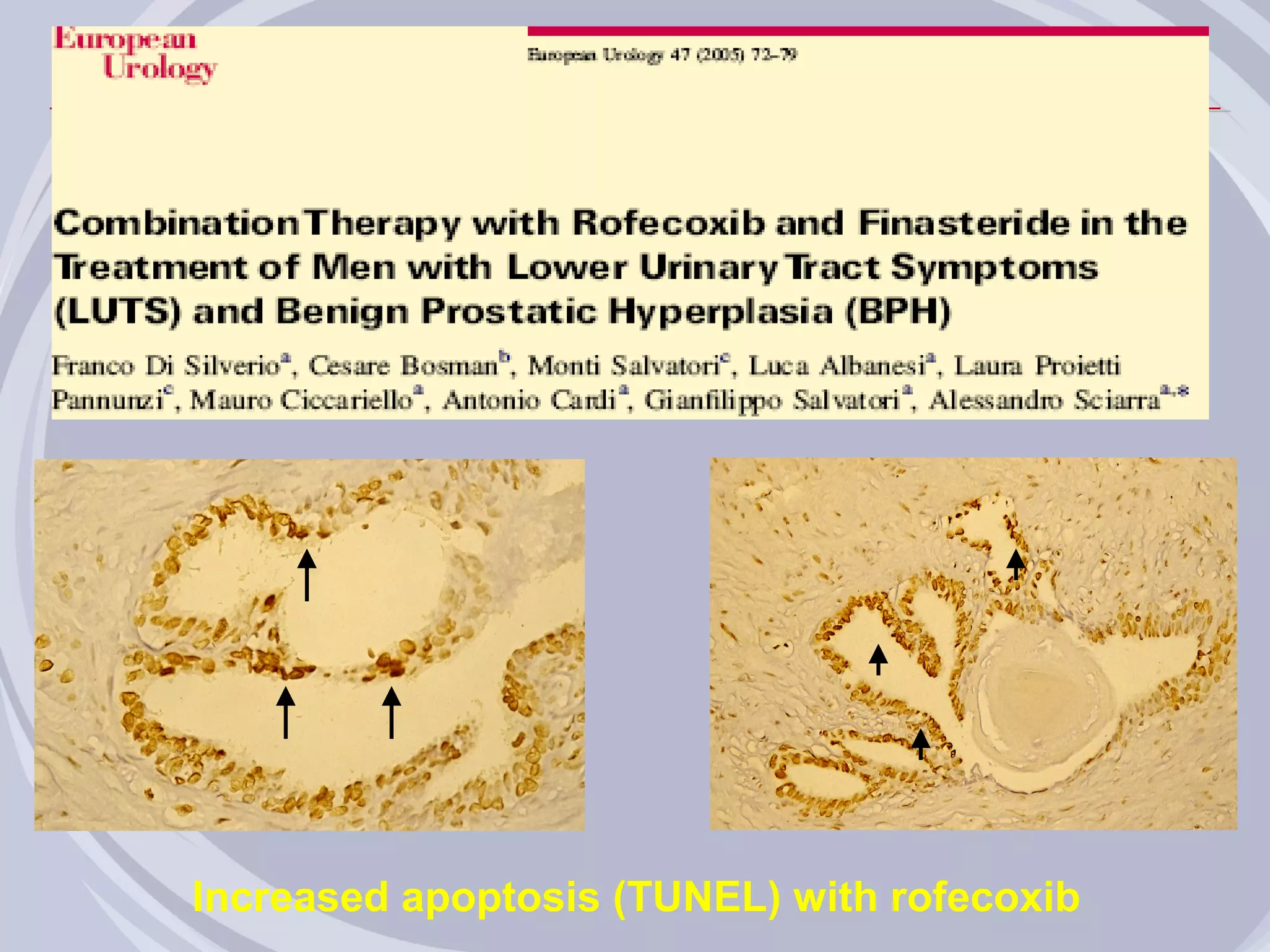
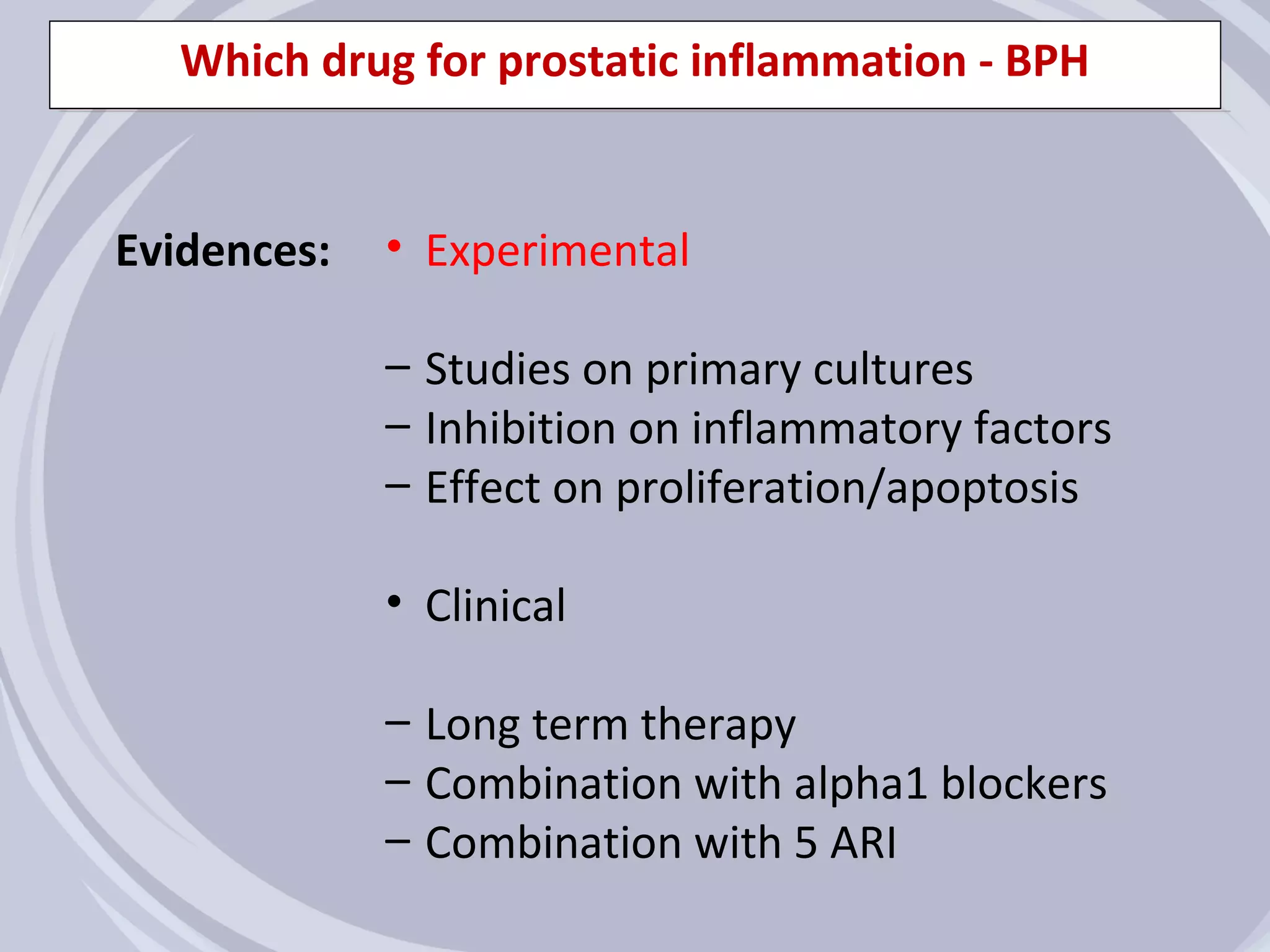
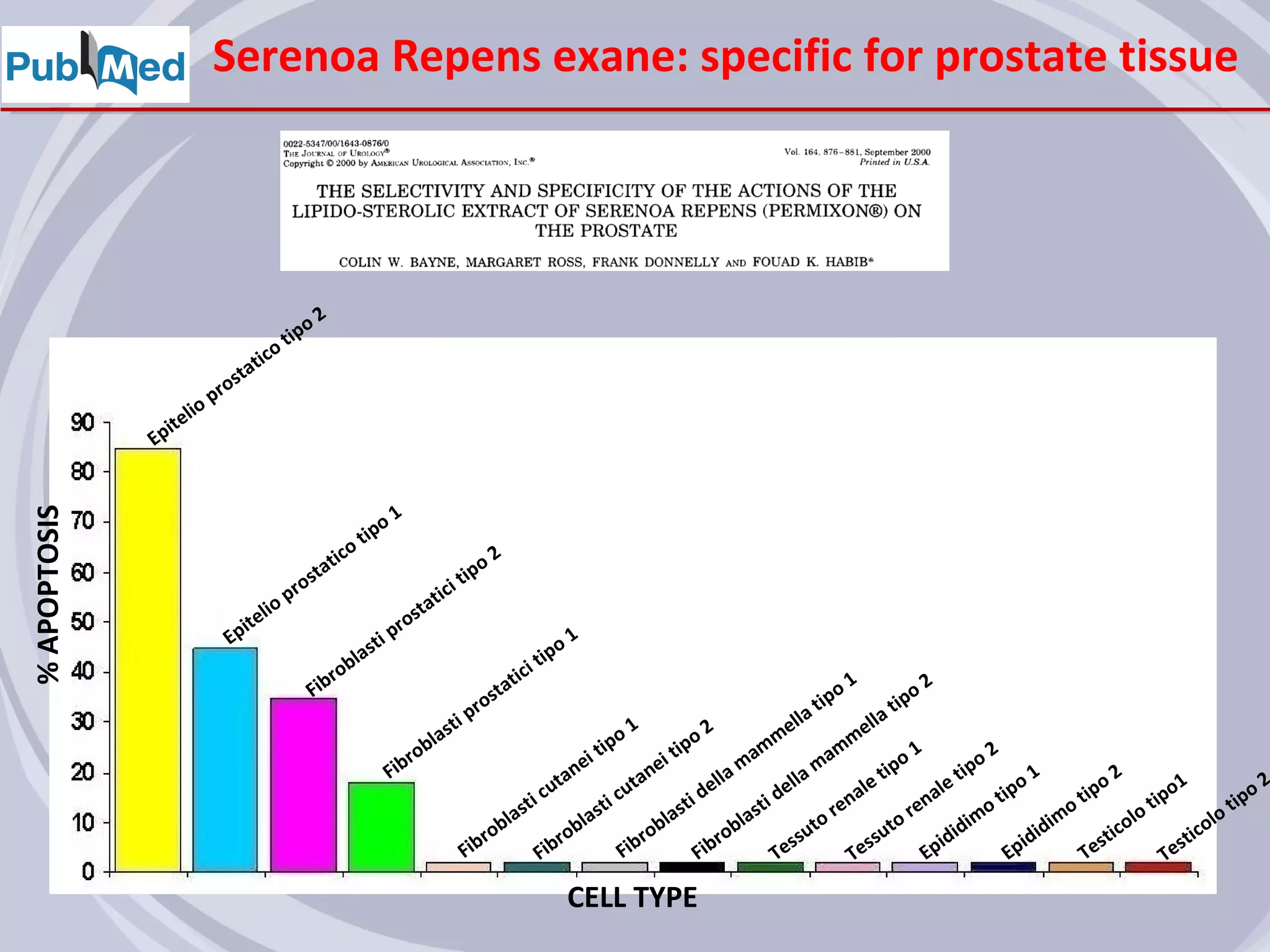
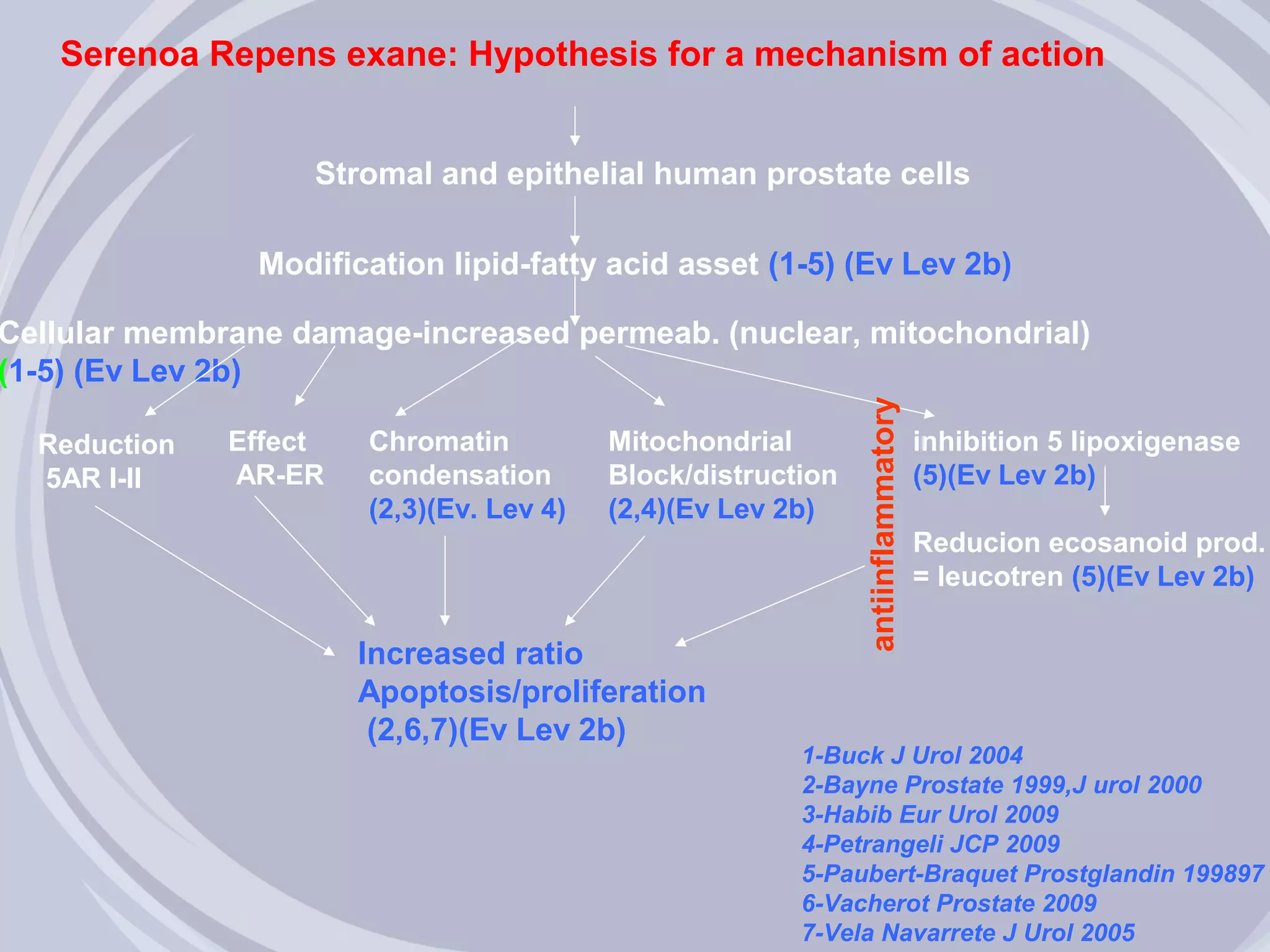
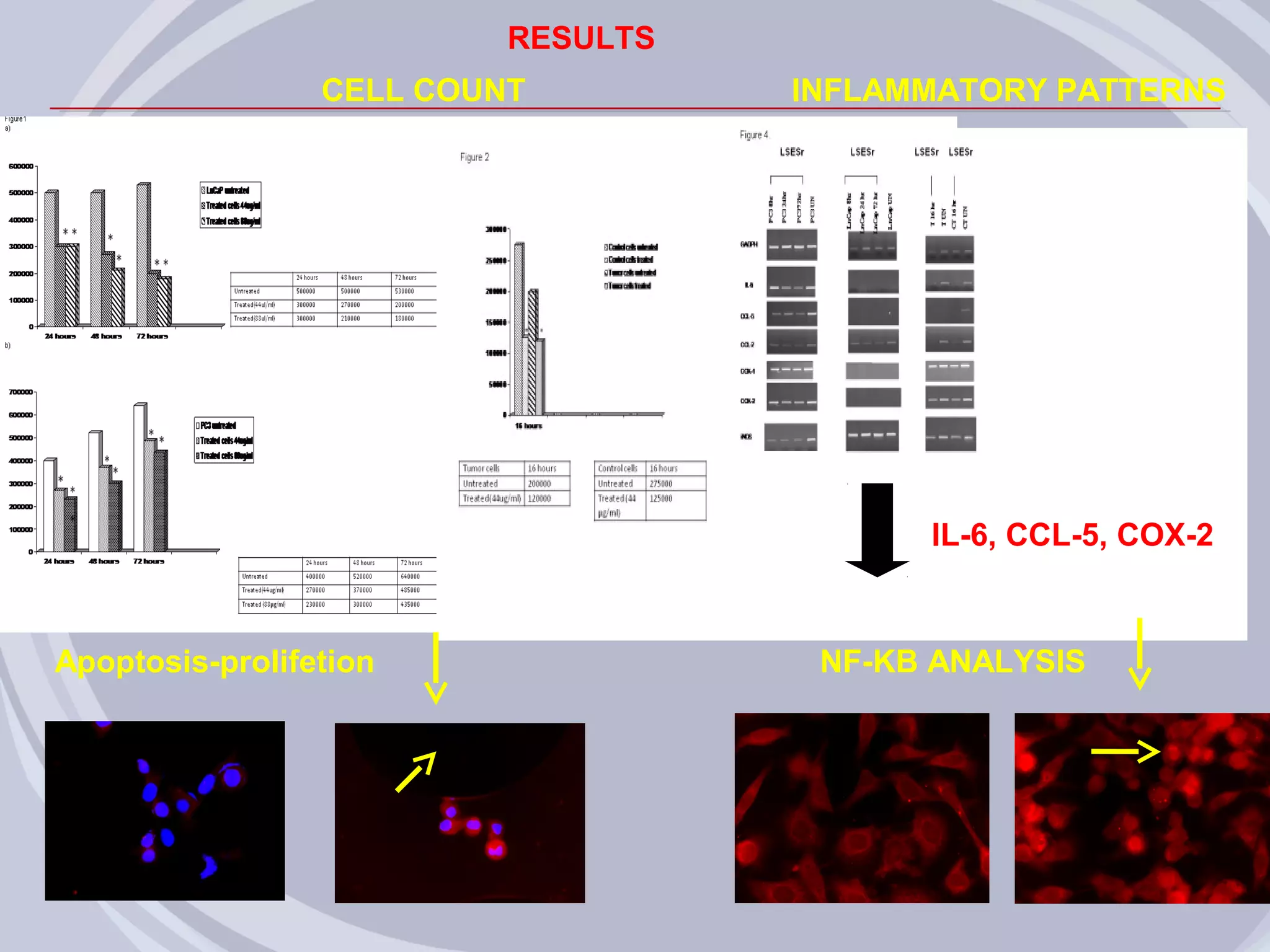
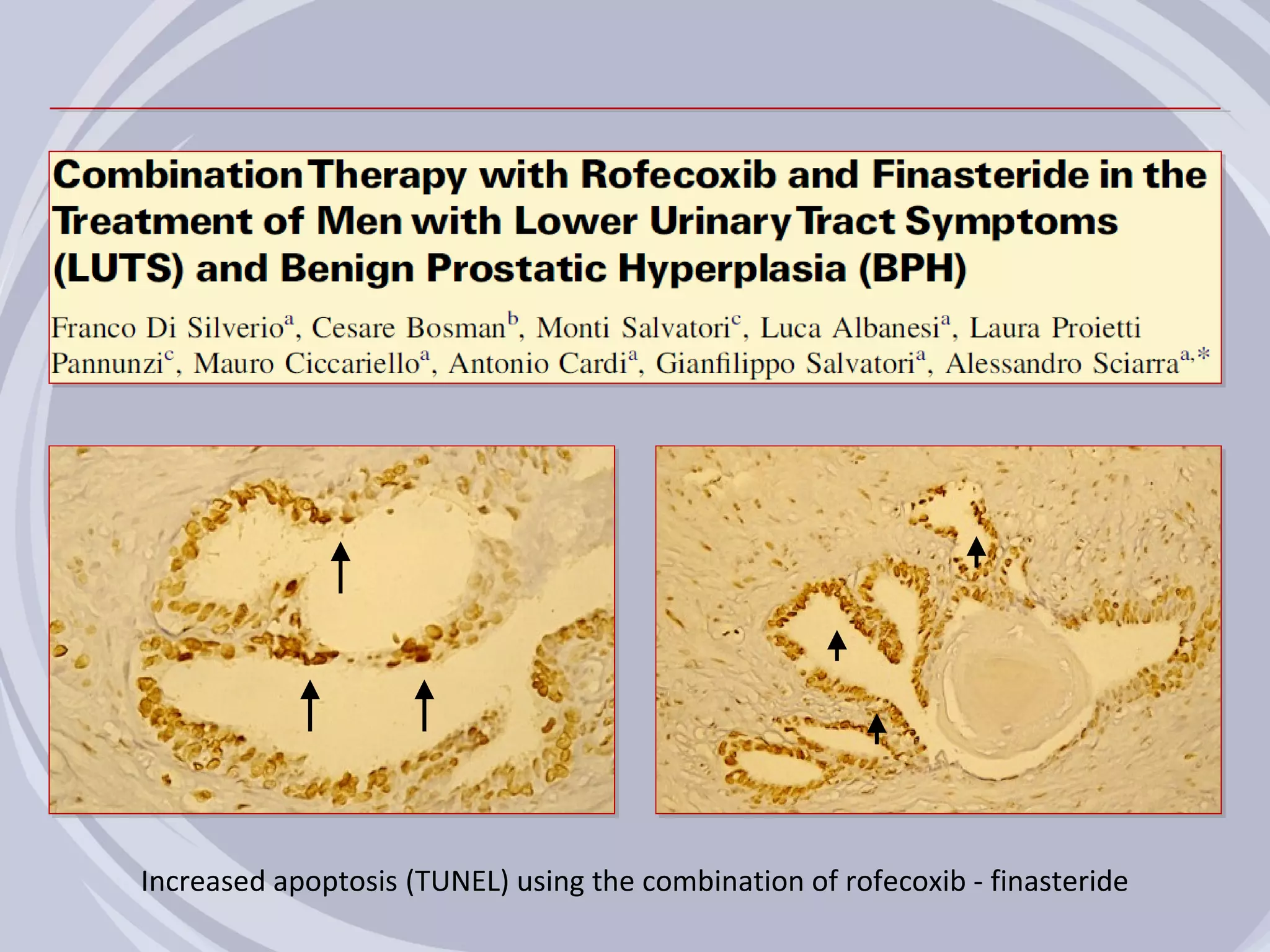
3. Drugs that inhibit prostatic inflammation, such as Serenoa repens extract, may help prevent BPH progression when used alone or in combination with other BPH drugs. Treatment should be tailored based on a patient's symptoms, prostate size, and inflammation markers.