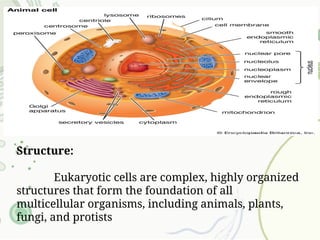
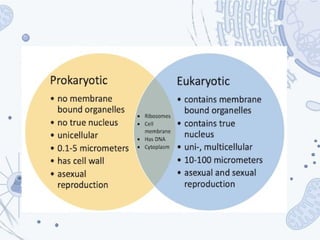
The document compares prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, detailing their structure and functions. Prokaryotic cells are simple, single-celled organisms lacking membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells are complex, multicellular organisms with specialized structures such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and organelles. Key features of both cell types, including cell membranes, ribosomes, and cytoplasm, are discussed, alongside their similarities and differences.