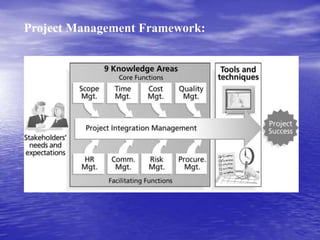
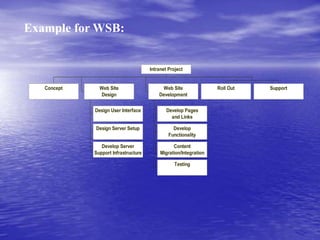
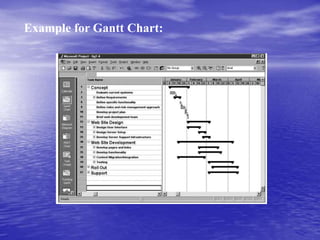
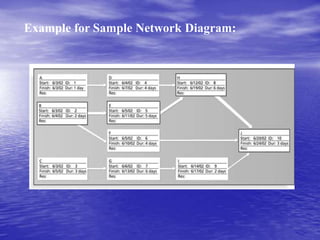
A project is defined as a temporary endeavor aimed at creating a unique product or service, constrained by scope, time, and cost goals. Project management involves applying knowledge and skills to meet project requirements, focusing on both leading the team and coordinating tasks. Successful project management leads to better resource control, improved customer relations, and greater project efficiency.