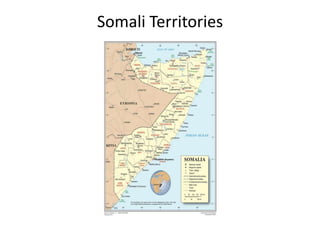
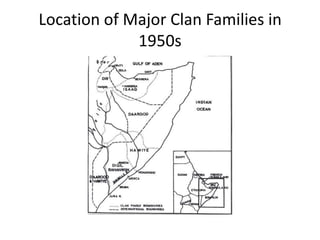
This document discusses the statelessness of Somalia and Somali territories since 1991 when the central government collapsed. It examines the questions of what caused the lack of an effective state, the consequences, and how order can be maintained without a state. It outlines the various Somali polities that have emerged and their systems of local governance based on clan structures. While state-building efforts from international groups have failed, some areas like Somaliland have successfully established governance from the local level. The challenges of piracy in Puntland and terrorism spreading from al-Shabaab in southern Somalia into Kenya are also discussed.