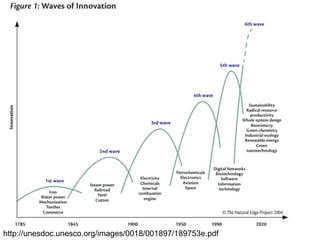
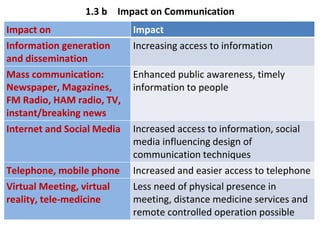
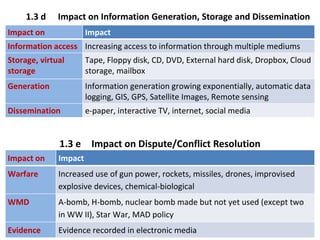
The document discusses the background and importance of professional ethics in engineering, tracing the historical evolution of engineering practices and their societal implications. It highlights the cultural, political, and societal factors influencing technological development, as well as the multifaceted impacts of technology on social values, communication, and livelihoods. Additionally, it emphasizes the necessity for continuous education and training for technologists to keep pace with rapid advancements and changing regulations.