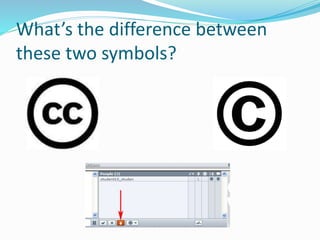
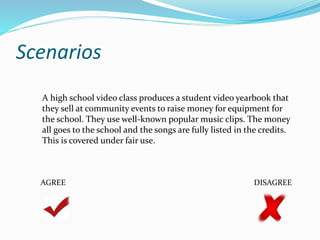
This document outlines Benjamin Harris's presentation on using multimedia and video in the classroom. It discusses having students actively create content like podcasts and videos rather than just passively consuming information. The presentation covers legal issues around copyright and fair use when using or creating media. It provides examples of how different subject areas like reading, science, social studies, and math can incorporate student-created videos. The document also addresses cyberbullying, piracy, and evaluating download sources for legal content.