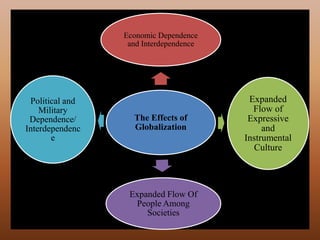
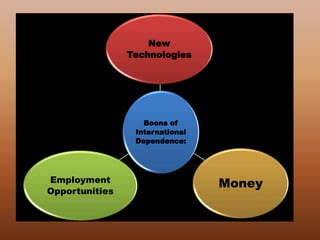
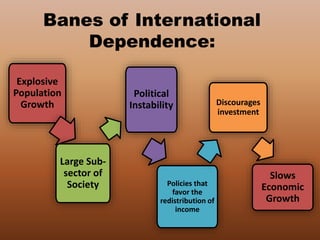
The document discusses globalization as the interaction and integration of nations driven by trade, investment, and technology, highlighting its economic, political, and cultural effects. It emphasizes economic interdependence, which can lead to wealth concentration and inequalities, while also noting both benefits and drawbacks of international dependence. Additionally, it explores the expansion of expressive and instrumental cultures and the flow of people across societies, particularly emphasizing the impact of overseas Filipino workers.