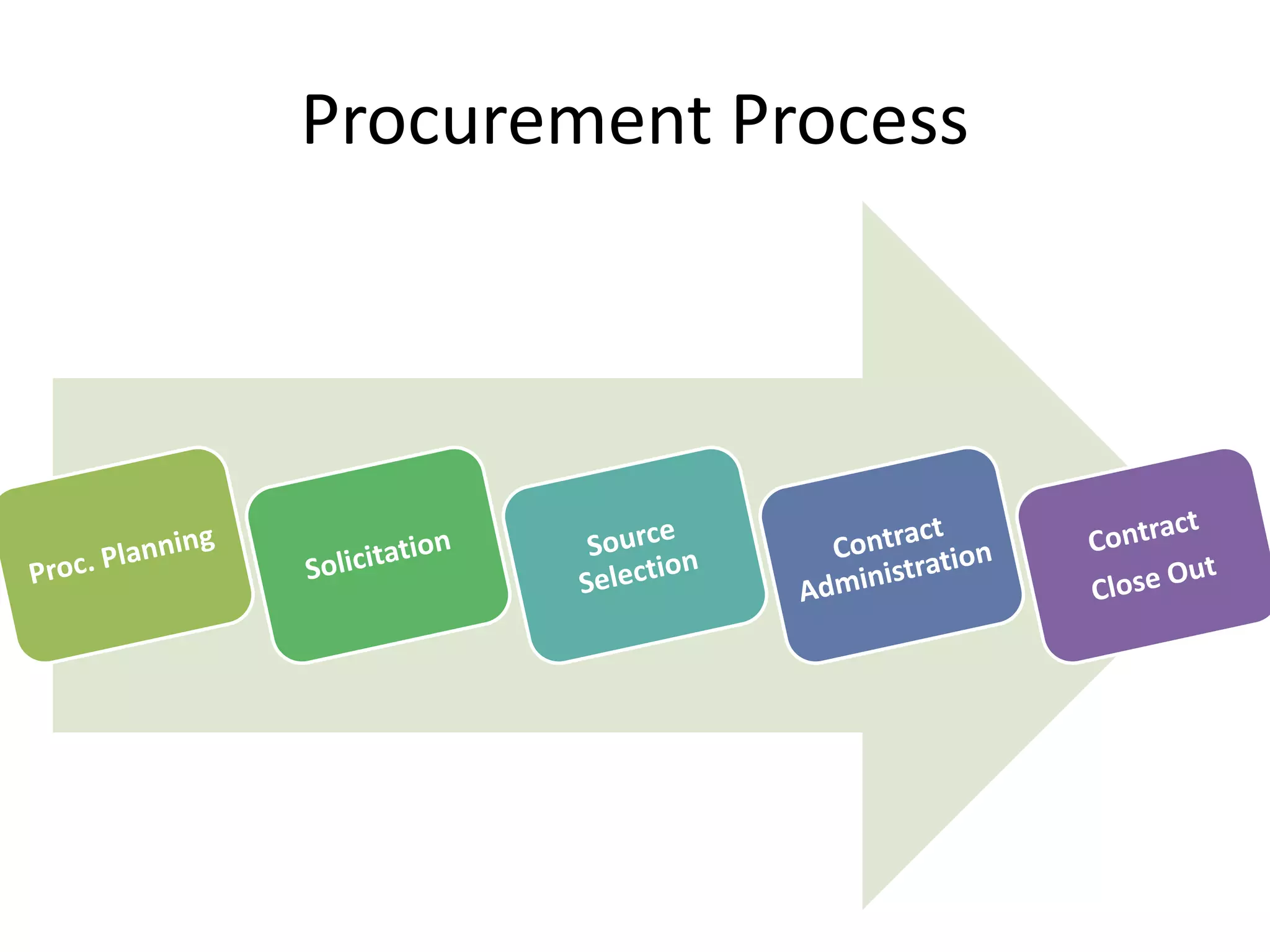
The document outlines procurement management in project environments, discussing the purchase of goods and services, vendor selection processes, and types of contracts. It covers make-or-buy analysis, solicitation strategies, contract administration, and various contract types such as fixed price and cost reimbursable contracts. The document includes examples and calculations to illustrate procurement decisions and contract costs.