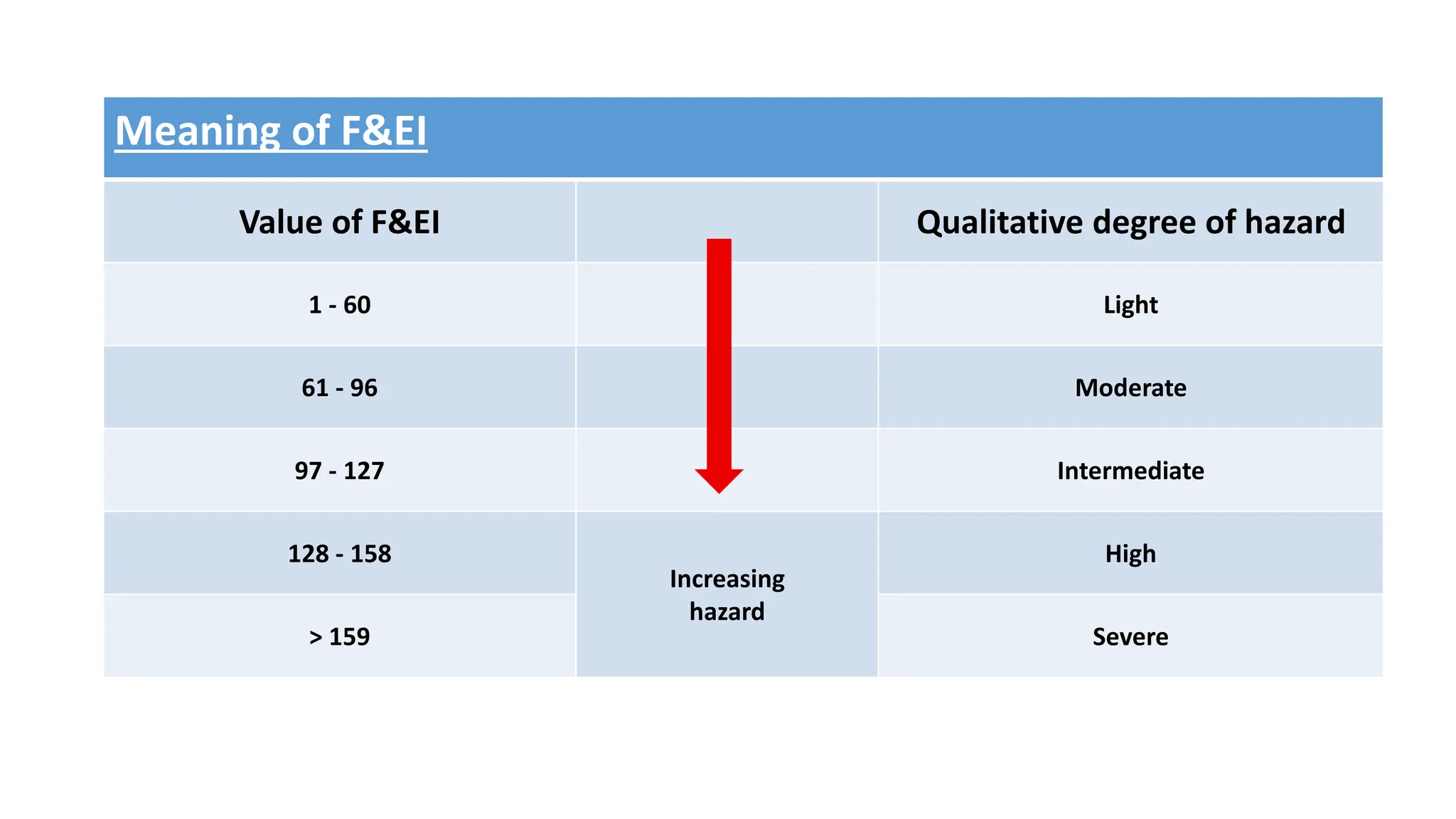
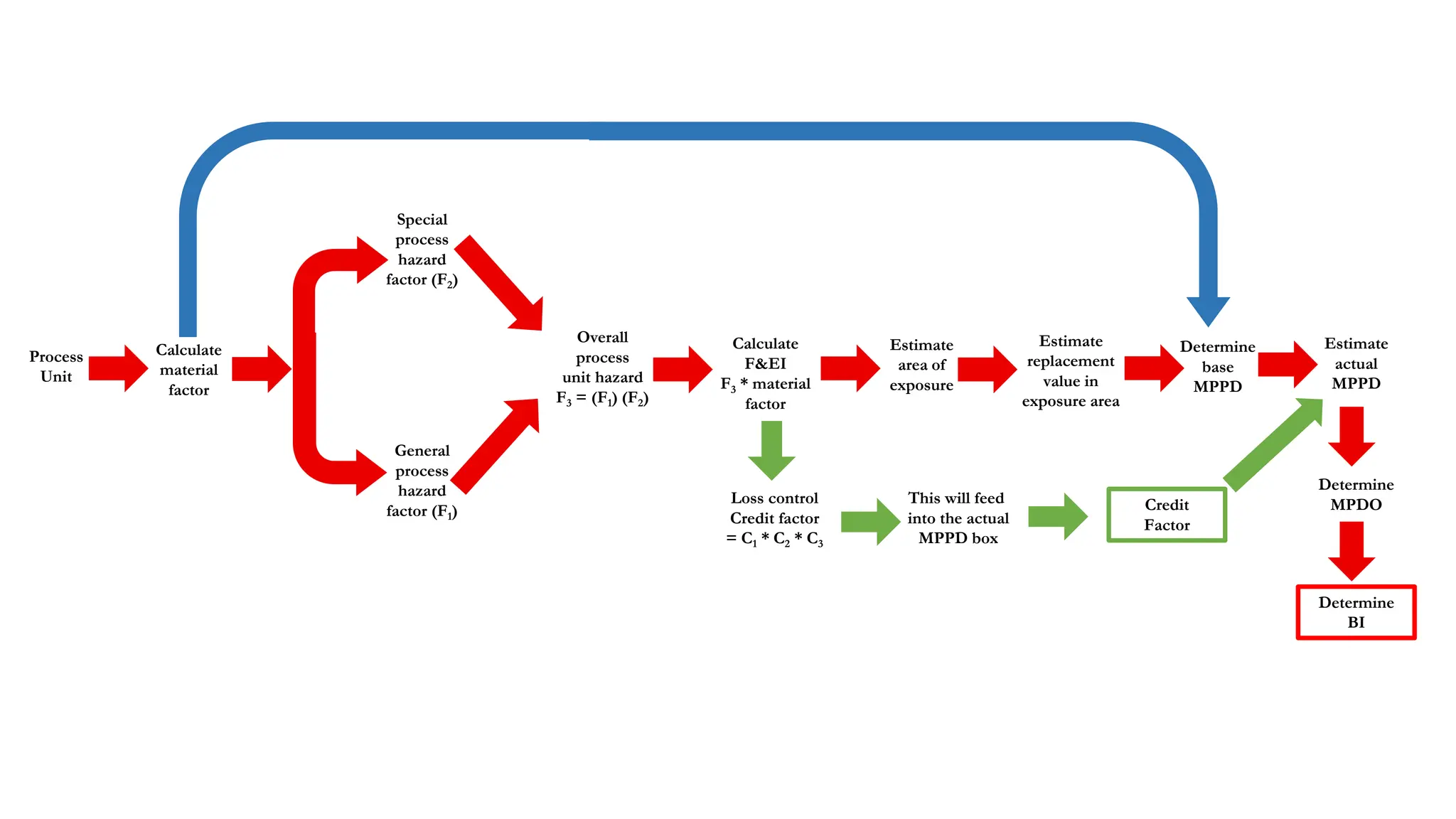
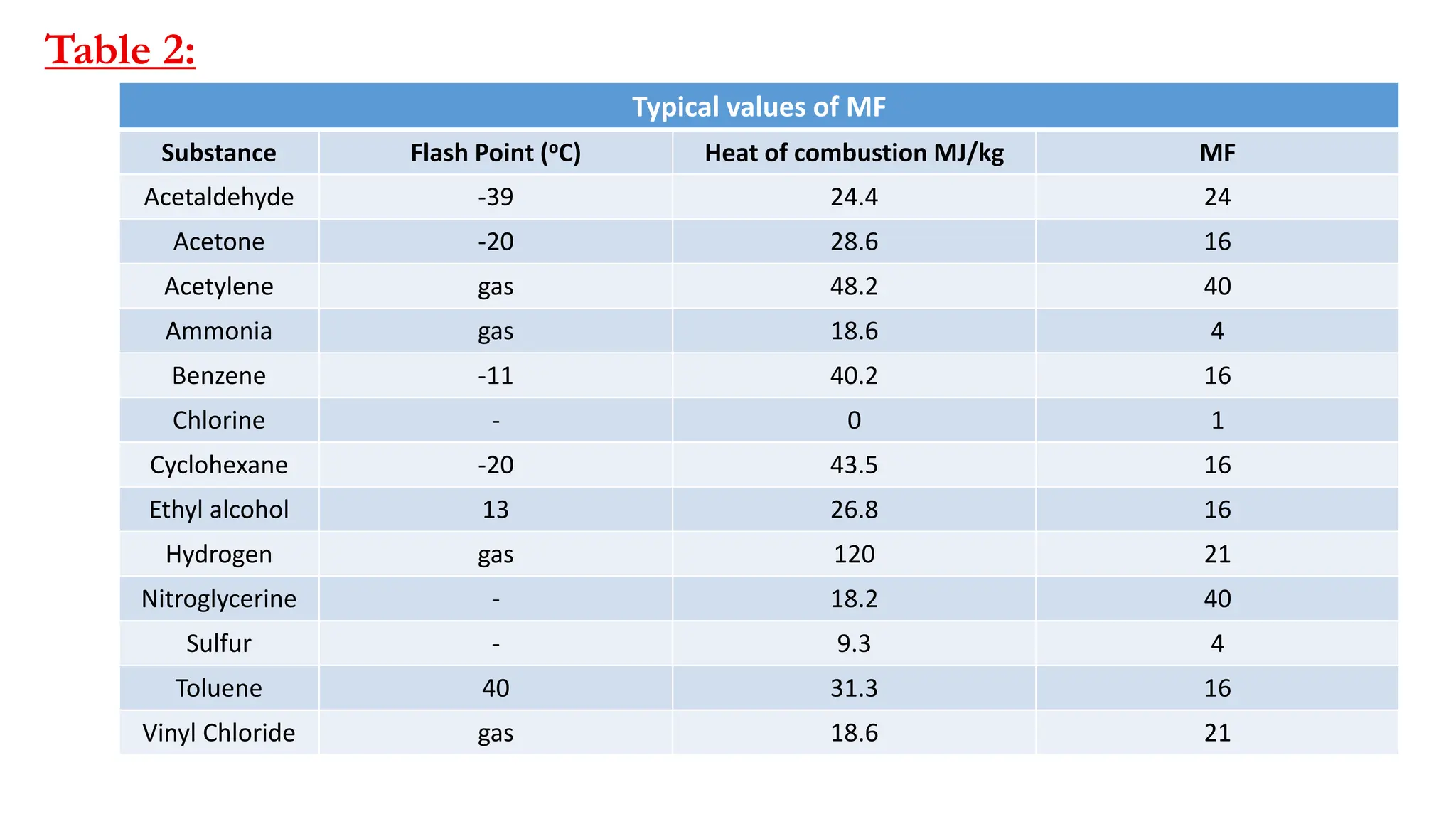
The document discusses Dow Chemical Co's Fire & Explosion Index (F&EI) which combines material properties and process hazards to assess risk. The F&EI is calculated by determining material and process factors then multiplying them. Material factors consider properties like flash point and reactivity. Process factors examine issues like exothermic reactions, enclosed spaces, toxic materials, dust explosions, corrosion and more. The F&EI is used along with estimates of potential loss to evaluate risk.