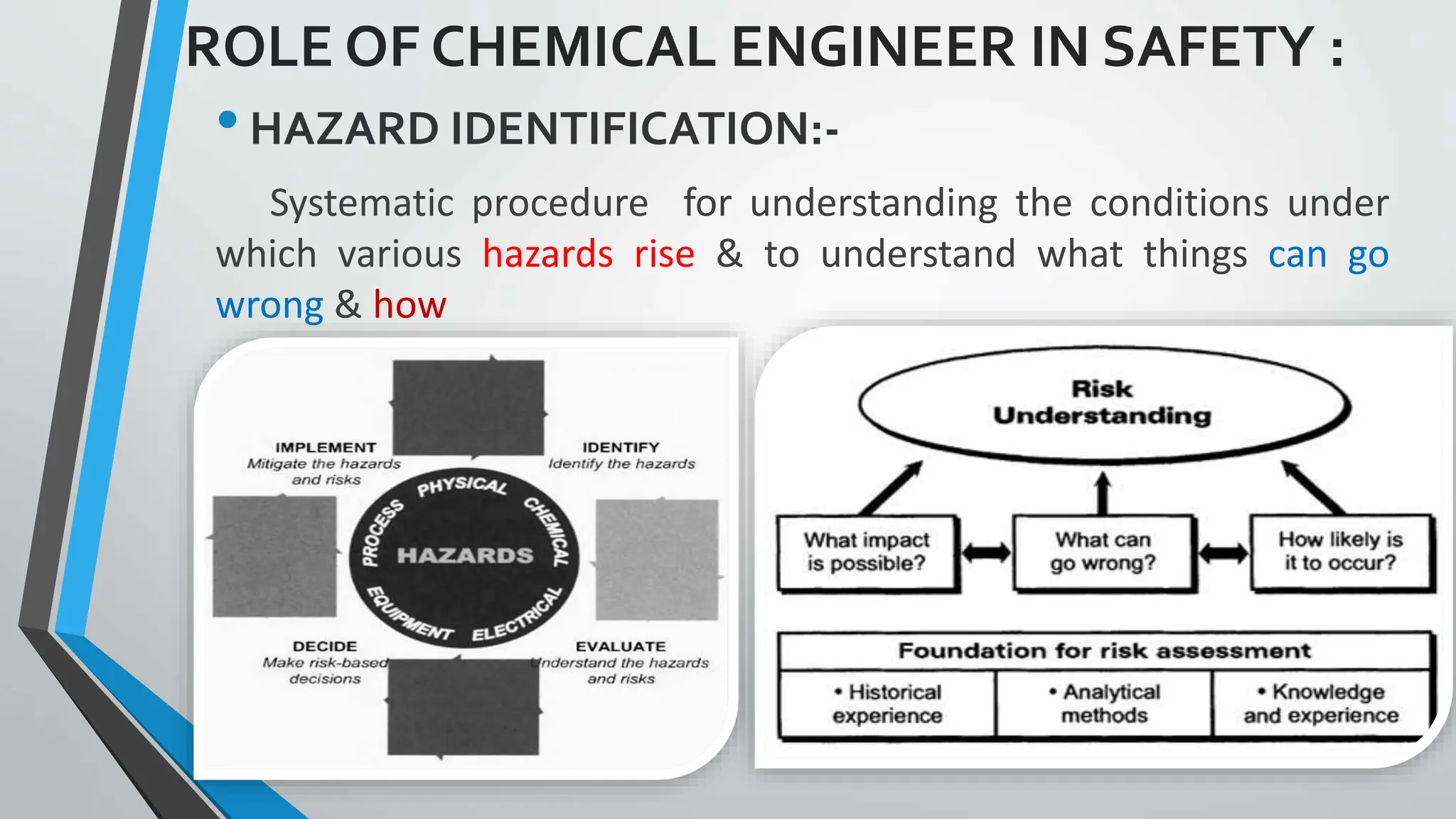
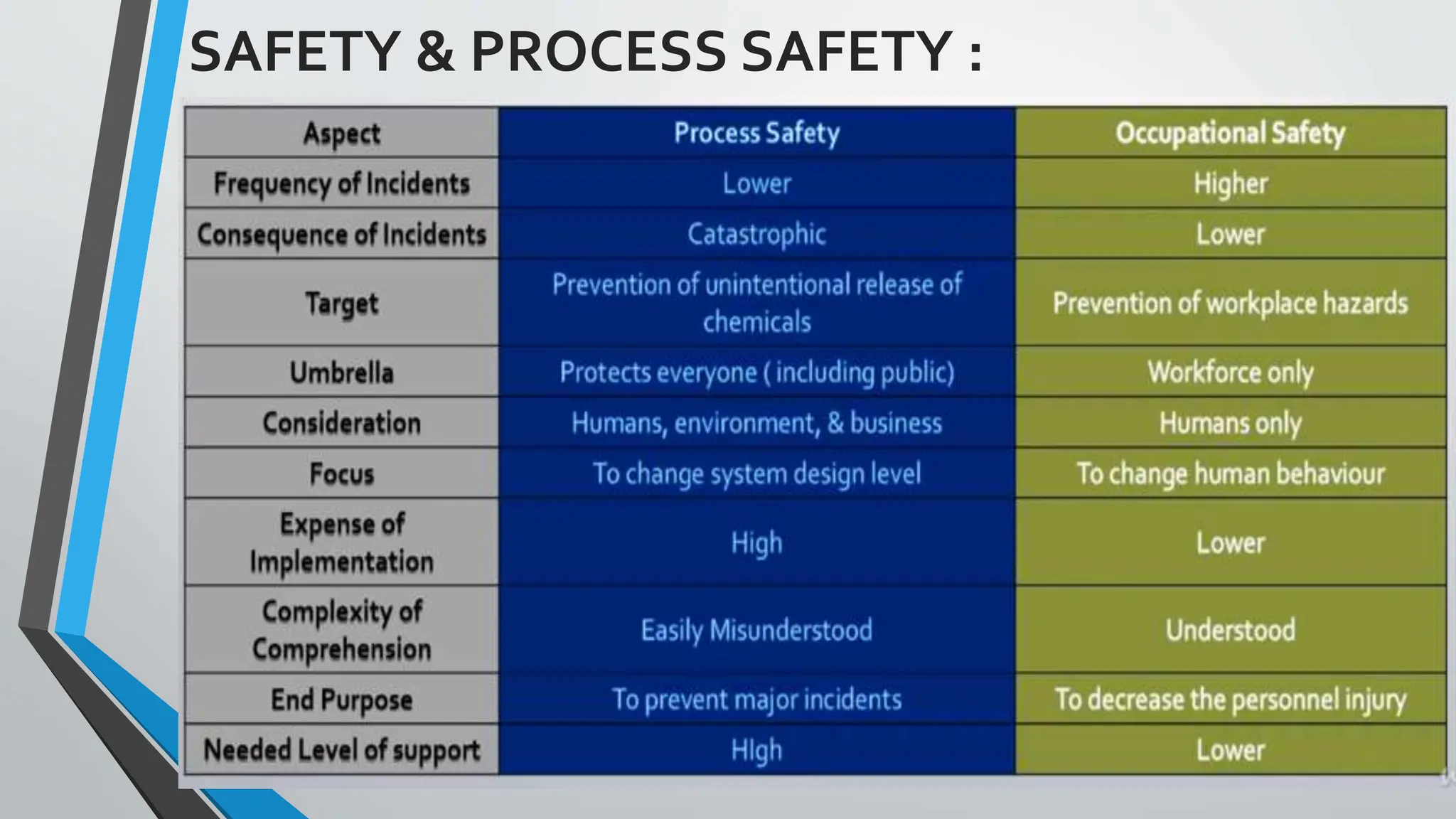
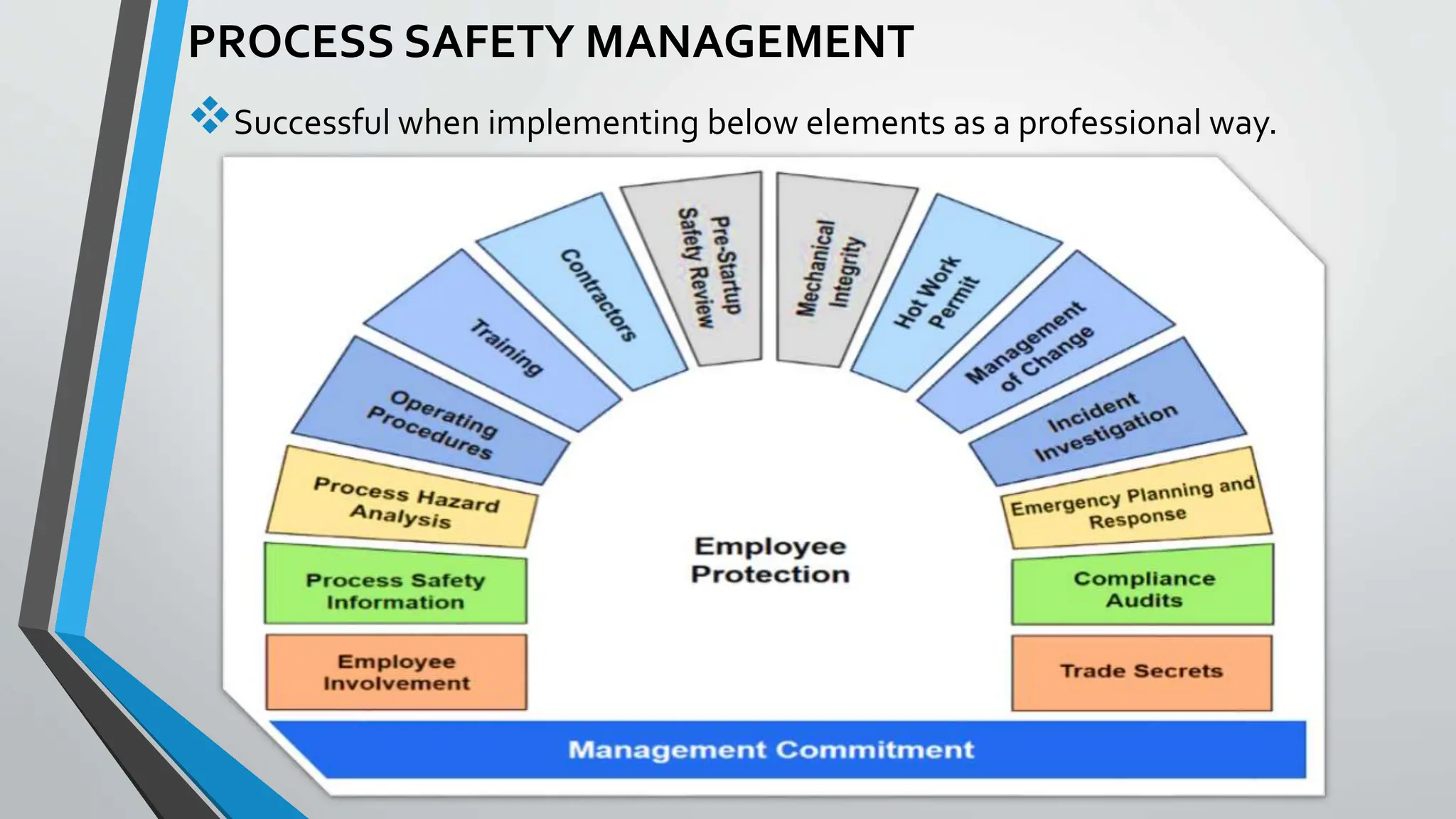
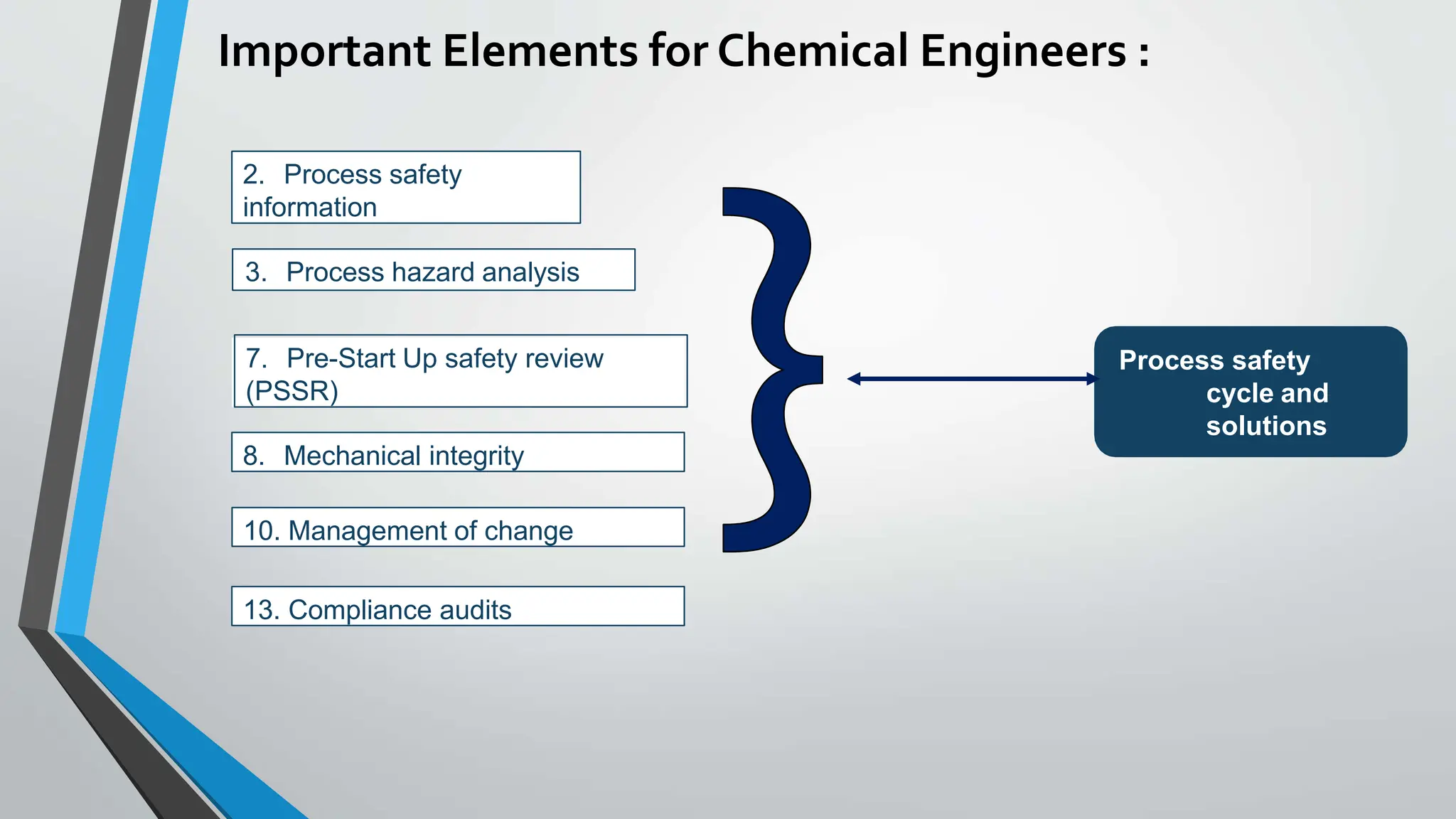
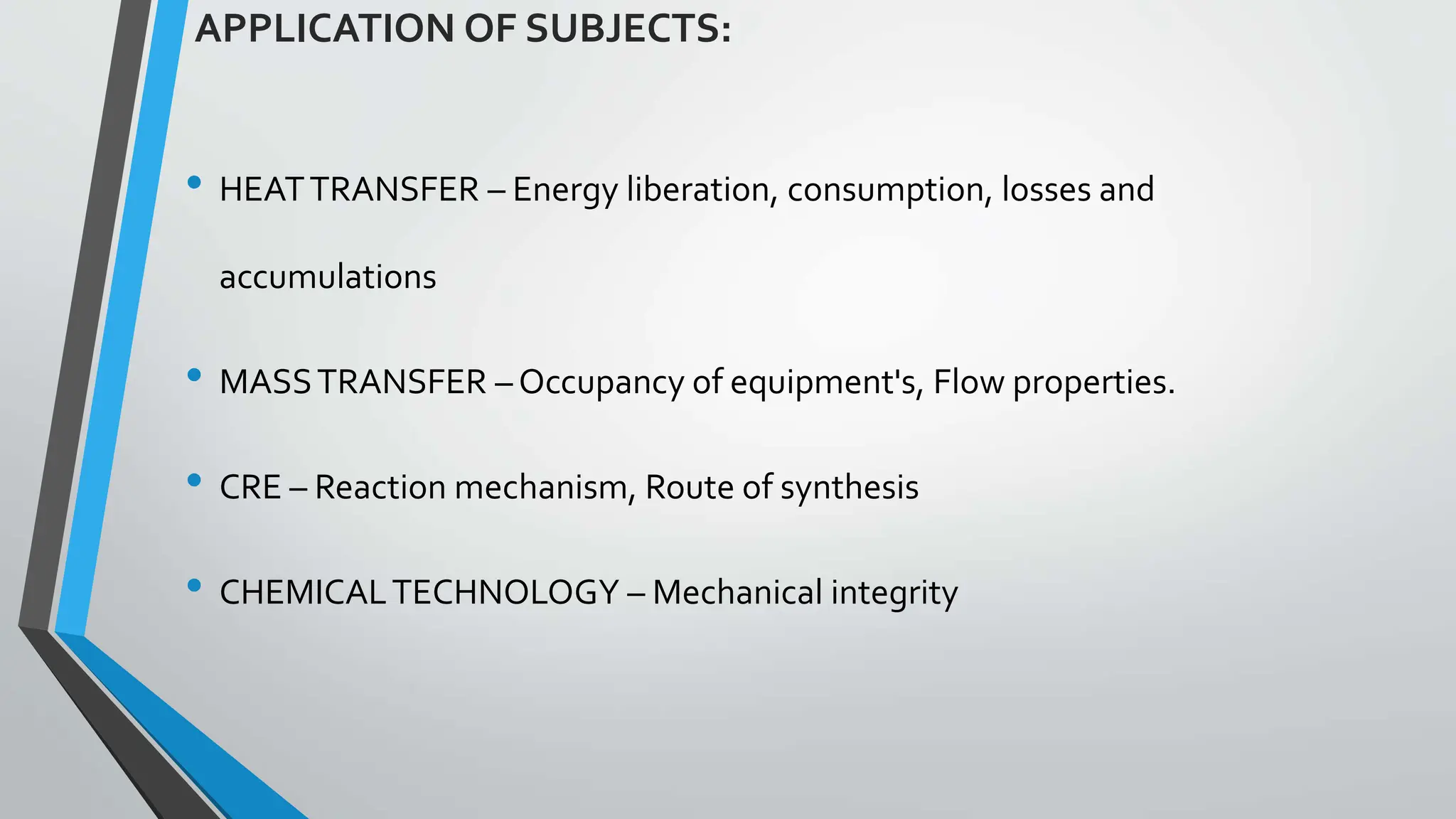
The document presents a comprehensive overview of safety in process industries, detailing definitions of safety, hazards, and risks, as well as the critical role of chemical engineers in safety management and hazard identification. It outlines process safety engineering as a systematic approach to prevent hazardous events such as explosions and toxic releases, highlighting various methods and tools employed in safety evaluations. Additionally, it references significant industrial disasters to underscore the importance of effective process safety management.