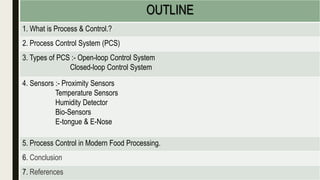
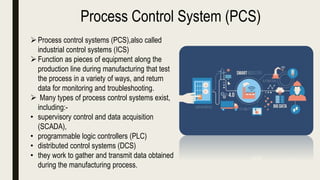
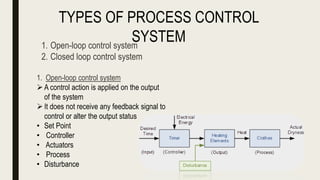
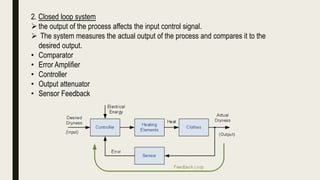
This document provides an overview of process control systems in the food industry. It defines process and control, and describes open and closed loop control systems. It outlines several sensor types used in food processing like proximity, temperature, humidity, biosensors, and electronic nose and tongue. Process control is important in modern food manufacturing to automate operations, maximize profits, and ensure quality and safety. Careful sensor selection is needed to effectively automate food processing.