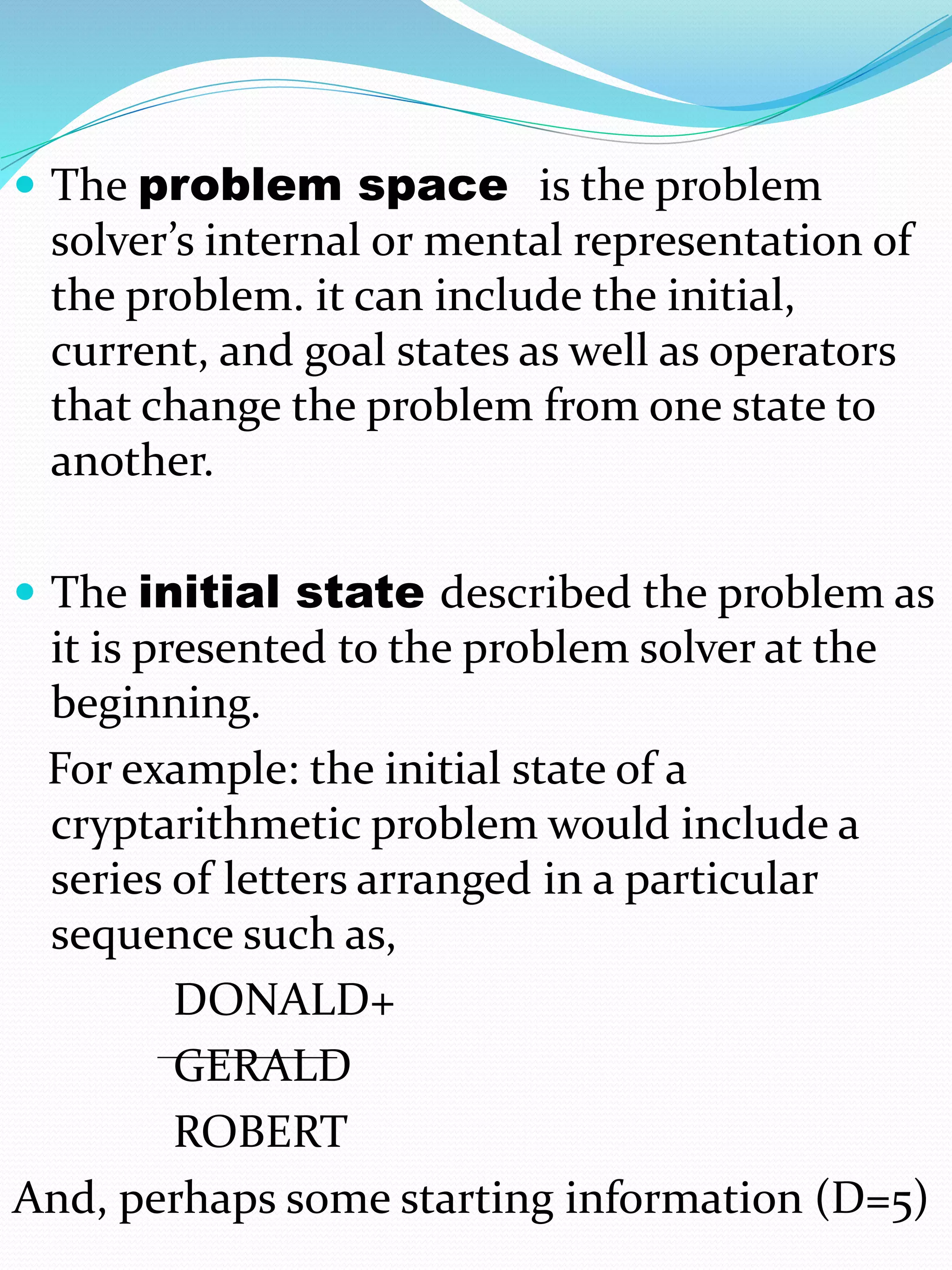
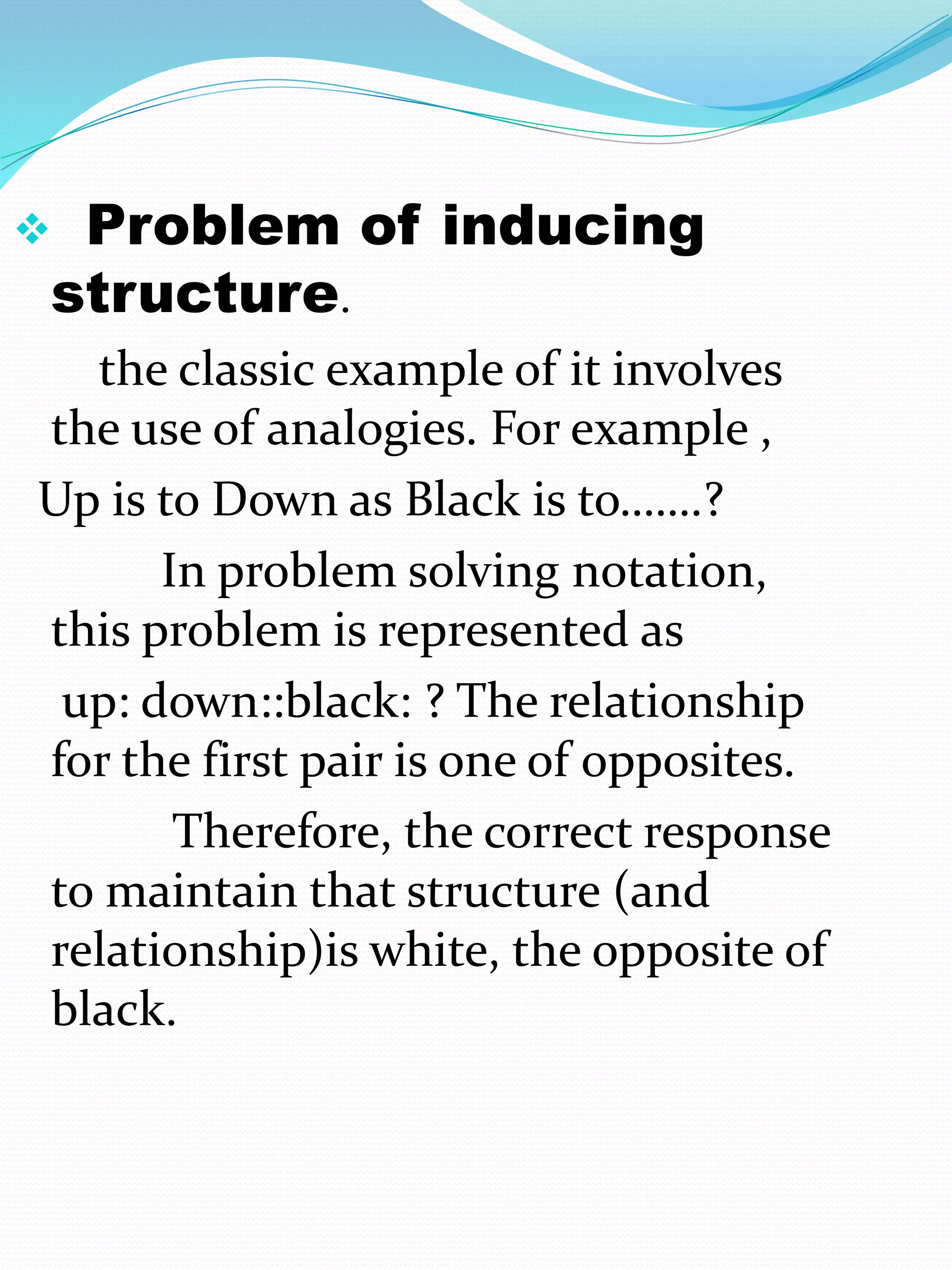
The document explores problem-solving behavior, emphasizing the framework established by Newell and Simon, which categorizes problems into well-defined and ill-defined types, as well as routine and non-routine problems. It also differentiates between adversary and non-adversary problem contexts, highlighting the complexities introduced by competition in problem-solving scenarios. Additionally, the distinction is made between knowledge-rich and knowledge-lean problems, noting that most traditional research focuses on the latter.